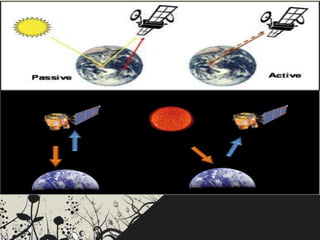
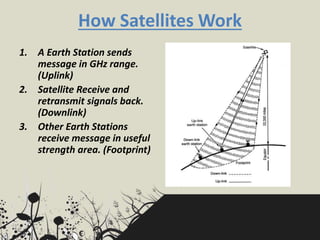
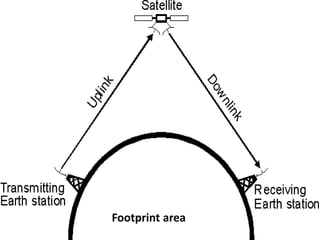
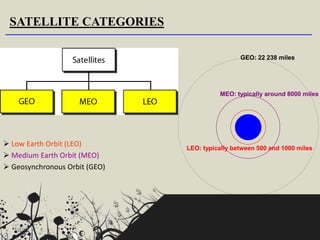
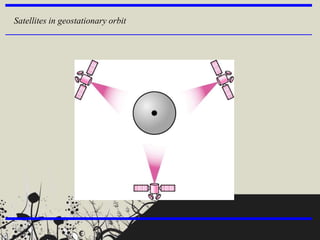
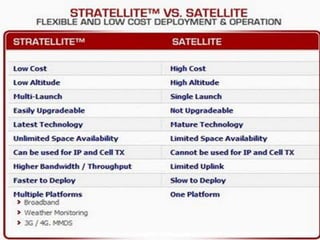
The document categorizes satellites into passive and active types, explaining their roles in communication systems. It provides a brief history of satellite launches, including significant milestones like the launch of Sputnik and India's first communication satellite, Aryabhata. Additionally, it details various orbit categories and introduces concepts like the Global Positioning System (GPS) and stratellites.