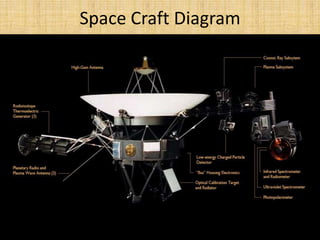
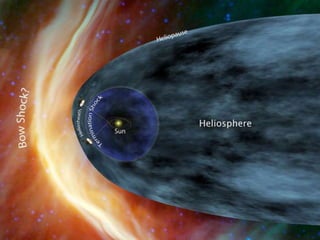
Voyager 1 was launched in 1977 to take advantage of a rare alignment of the outer planets. It conducted flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, and was designed to last 5 years but is still operating over 35 years later. Voyager 1 carries instruments to study the solar system and a Golden Record with photos and sounds of Earth. It has traveled over 18 billion km from Earth and will be the first human-made object to leave the solar system.