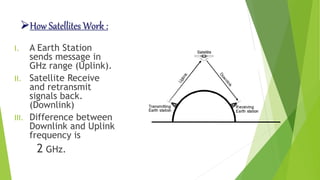
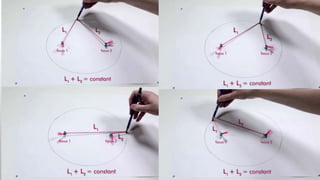
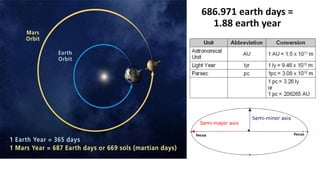
This document summarizes different types of satellites and orbits. It defines a satellite as a solid object that revolves around another due to gravitational forces. Satellites are either passive, simply reflecting signals, or active with onboard processing equipment. The first artificial satellite was Sputnik 1, launched in 1957. Satellites in low-Earth orbit have shorter lifespans but provide better signals, while geostationary satellites remain fixed over one position from the ground. The document also briefly discusses Kepler's laws of planetary motion and their application to Earth.