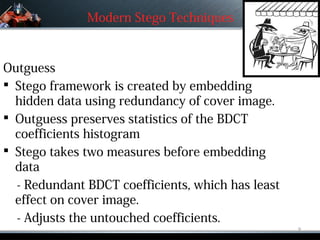
The document discusses and compares different steganographic algorithms and steganalysis techniques. It defines steganography and steganalysis, describing various steganographic schemes like LSB embedding, Outguess, F5, and Model-based steganography. It also covers past and modern work in steganalysis, including statistical methods for detecting hidden messages. The document concludes by discussing the future of steganography and its potential limitations under laws.