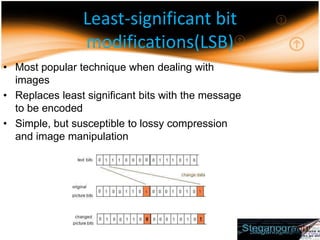
Steganography is the practice of hiding secret messages within other non-secret files or messages. The document discusses different techniques for digital steganography, including least significant bit modifications to hide messages in image pixel values, as well as masking/filtering and transformations in frequency domains. Lossless image compression works best for cover images to embed secret messages stealthily. While steganography has legitimate uses, it can also enable covert or illegal communications if abused.