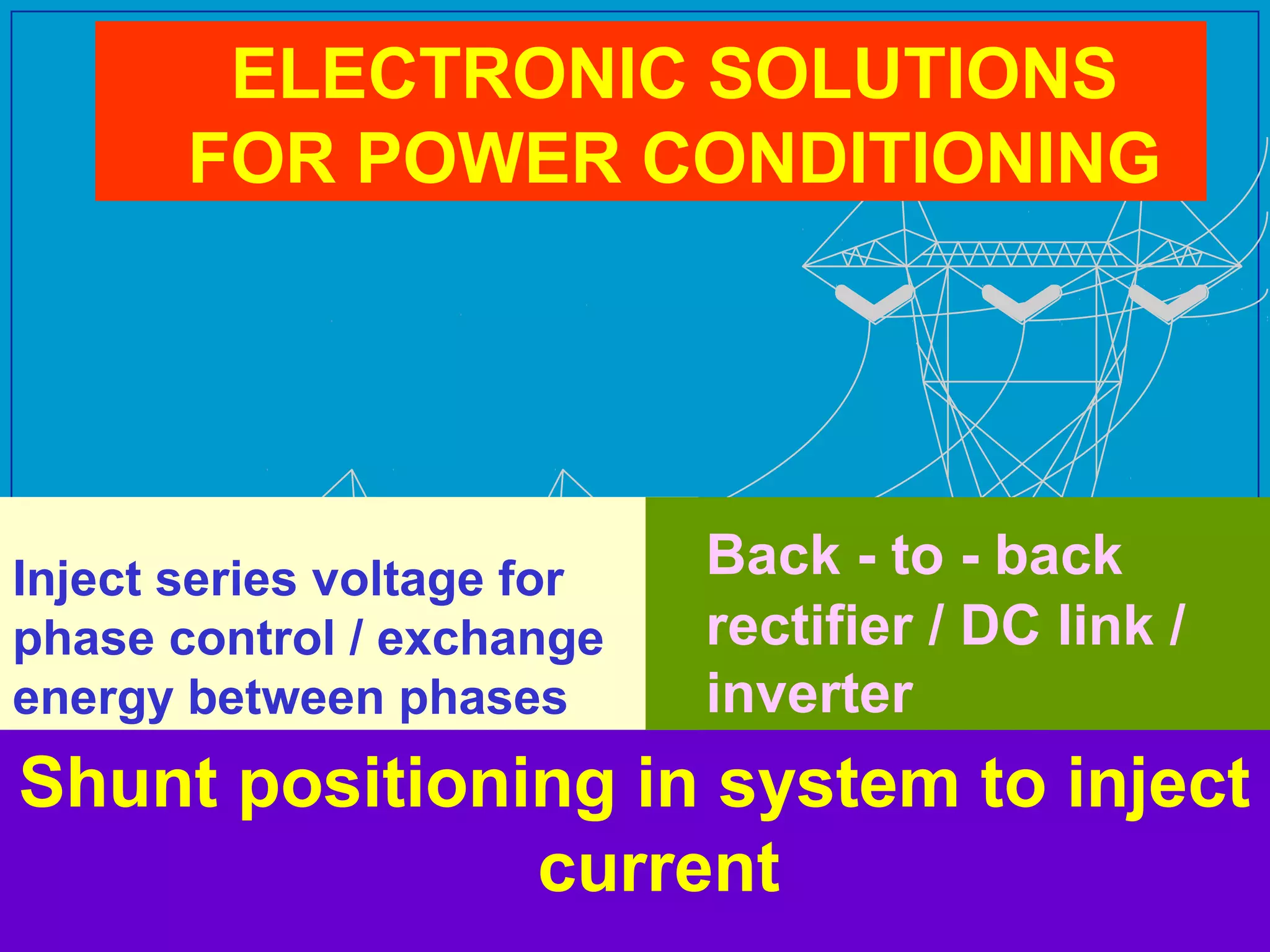
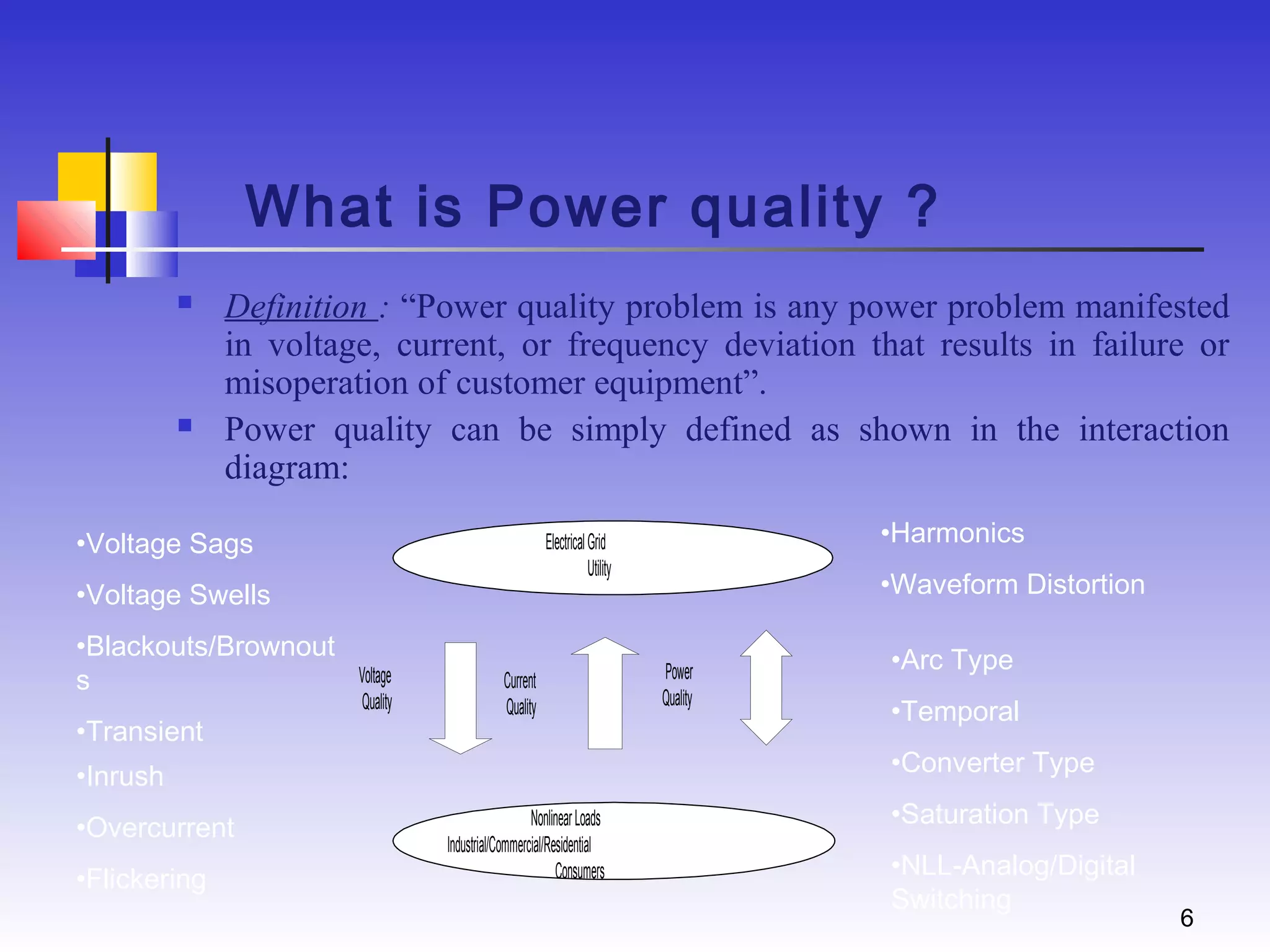
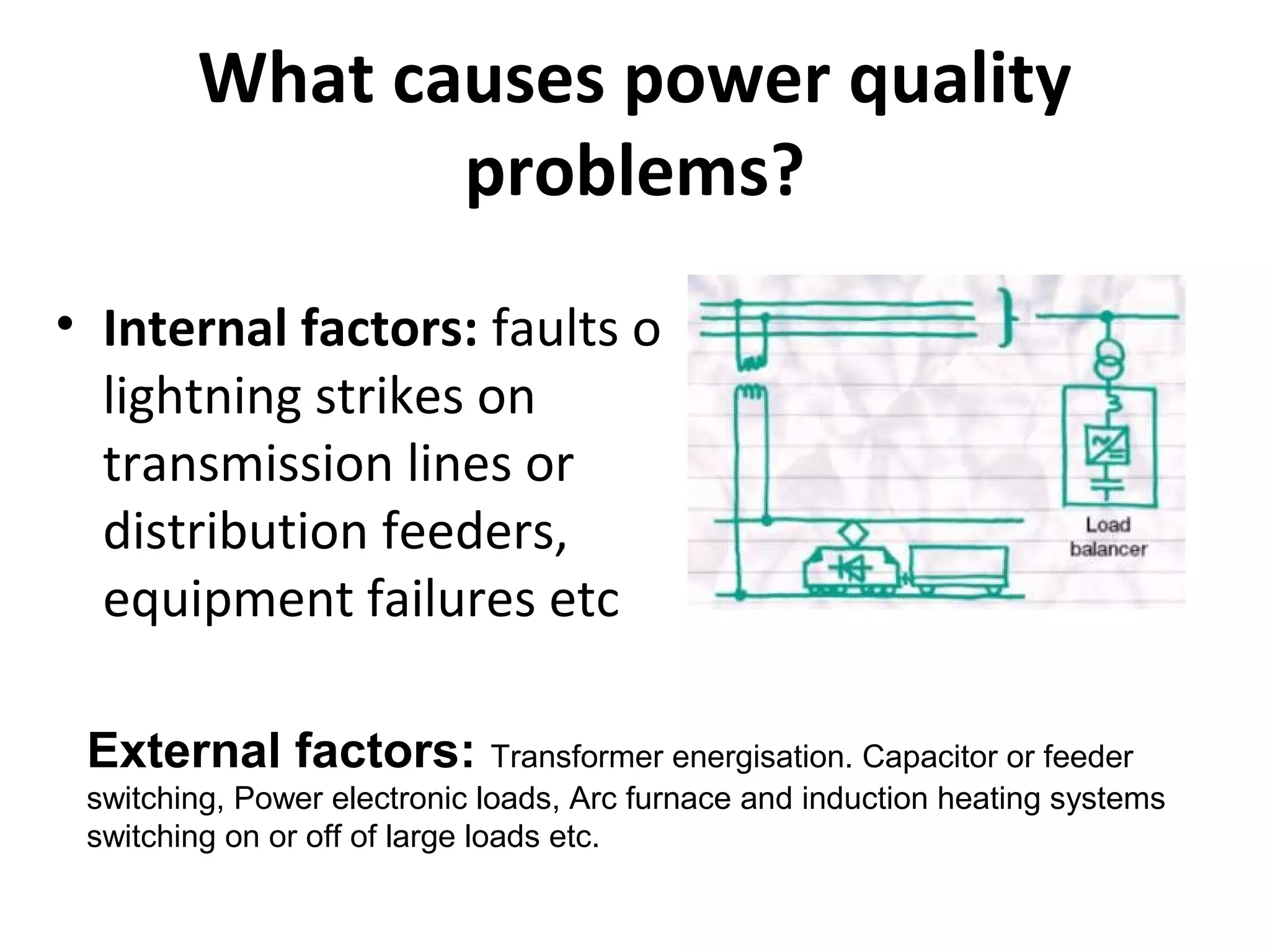
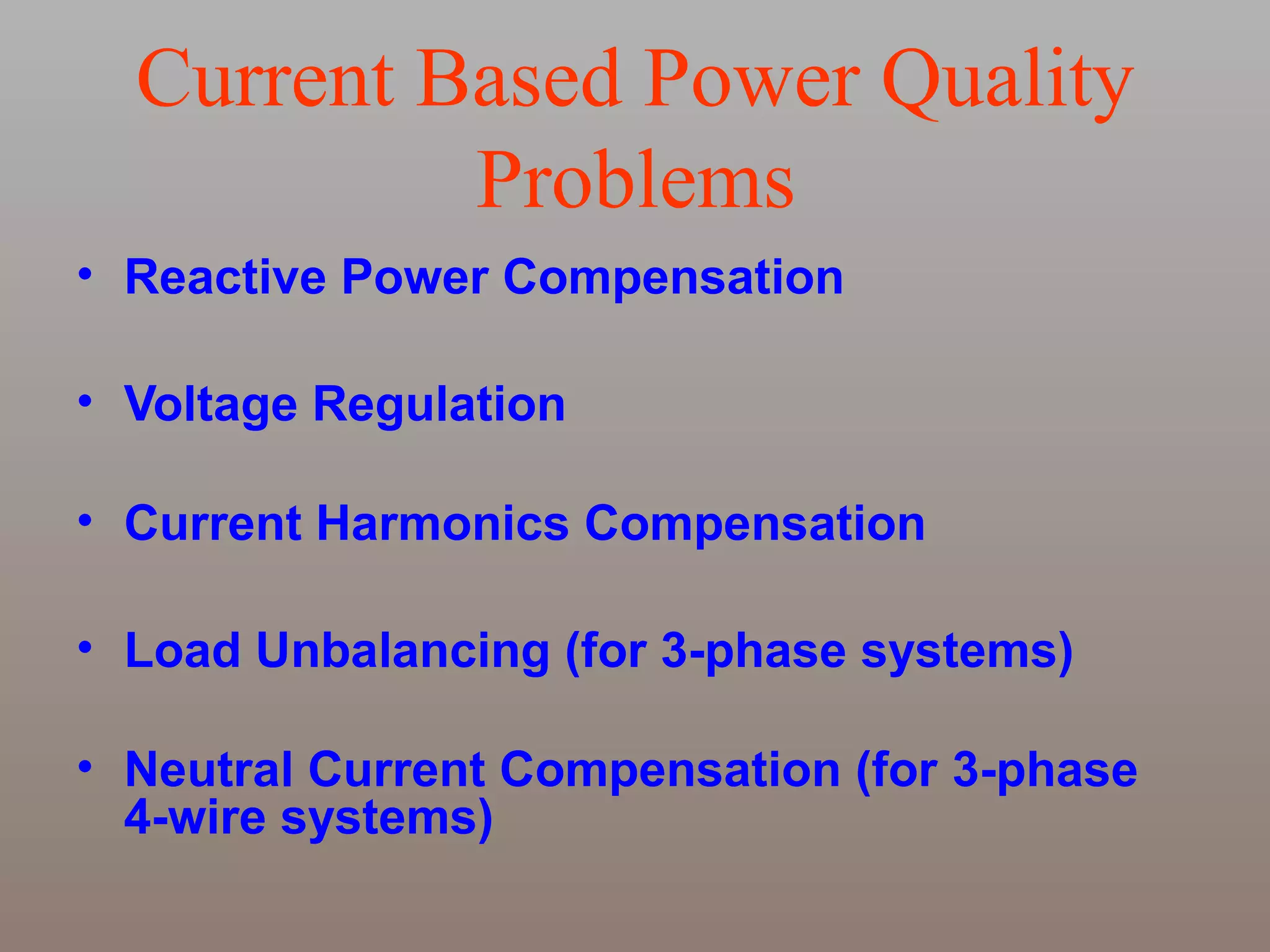
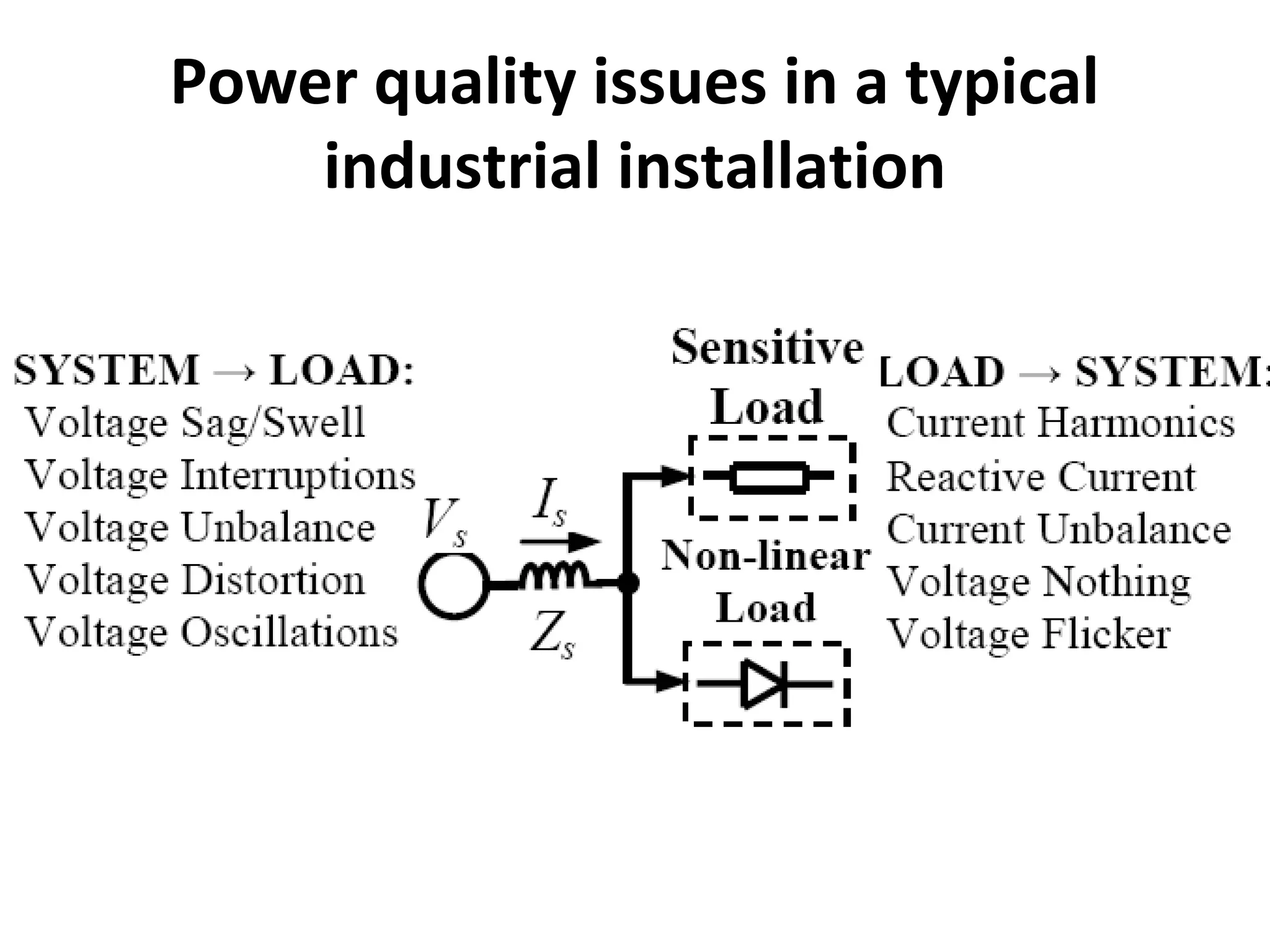
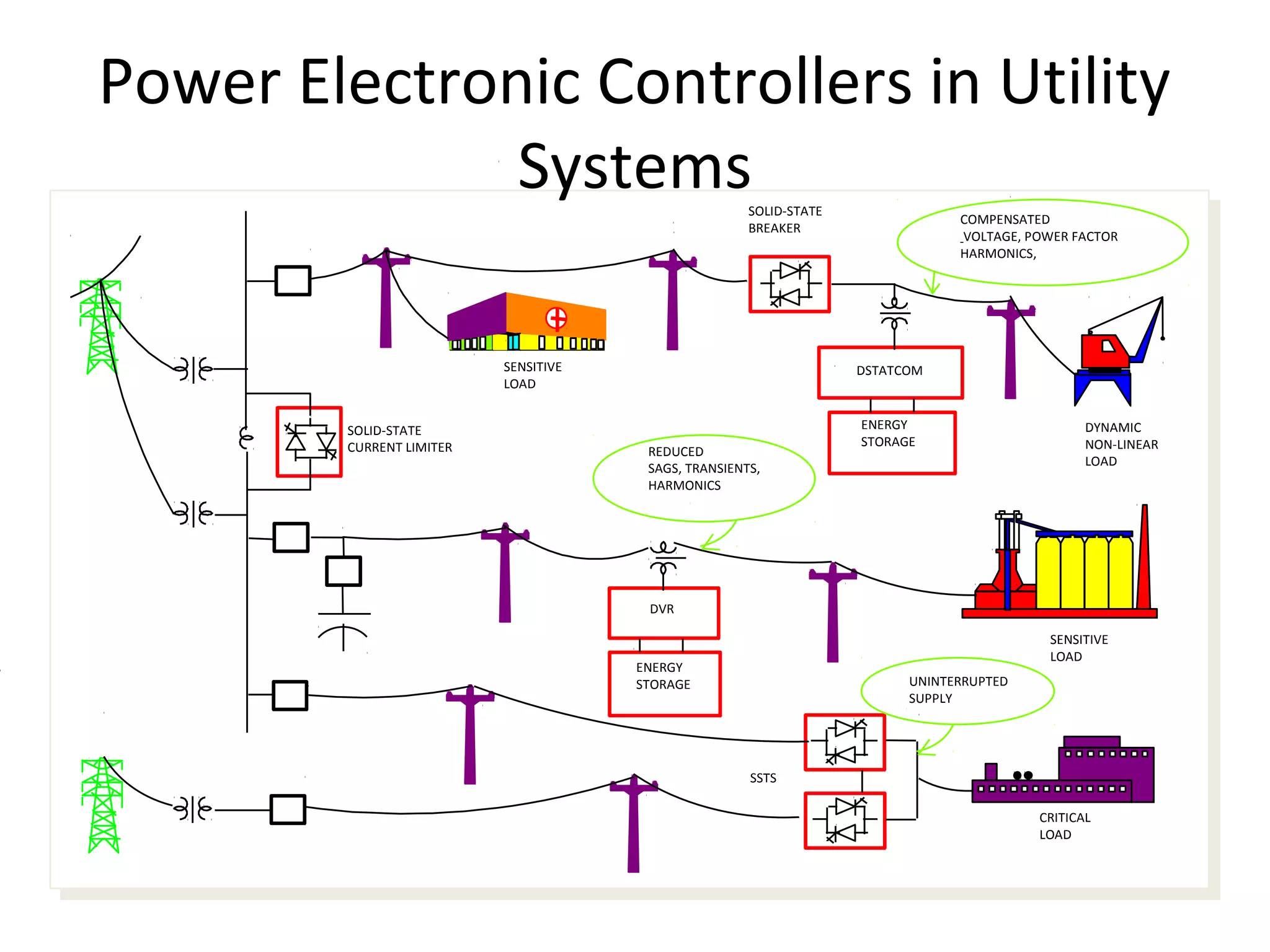
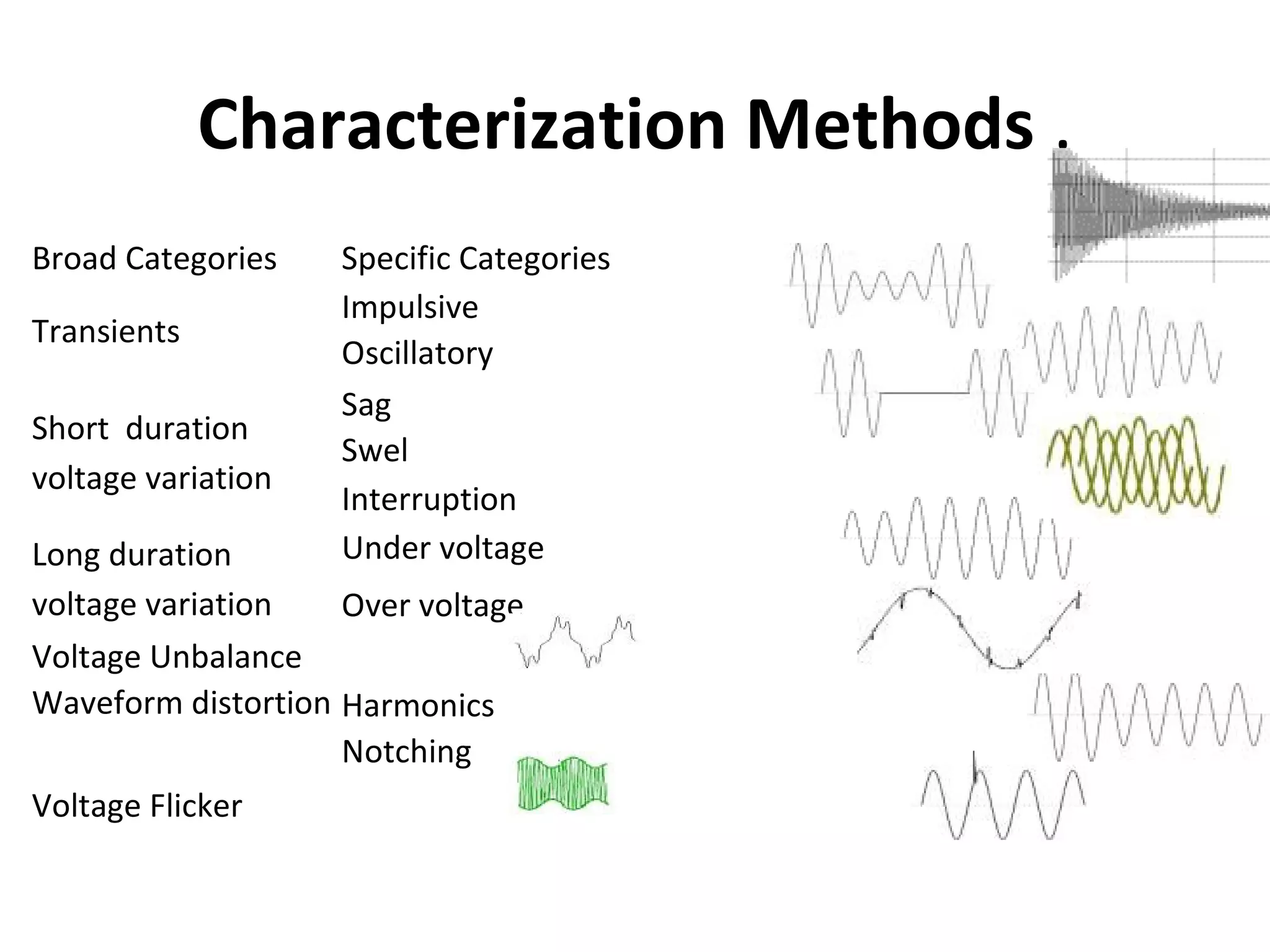
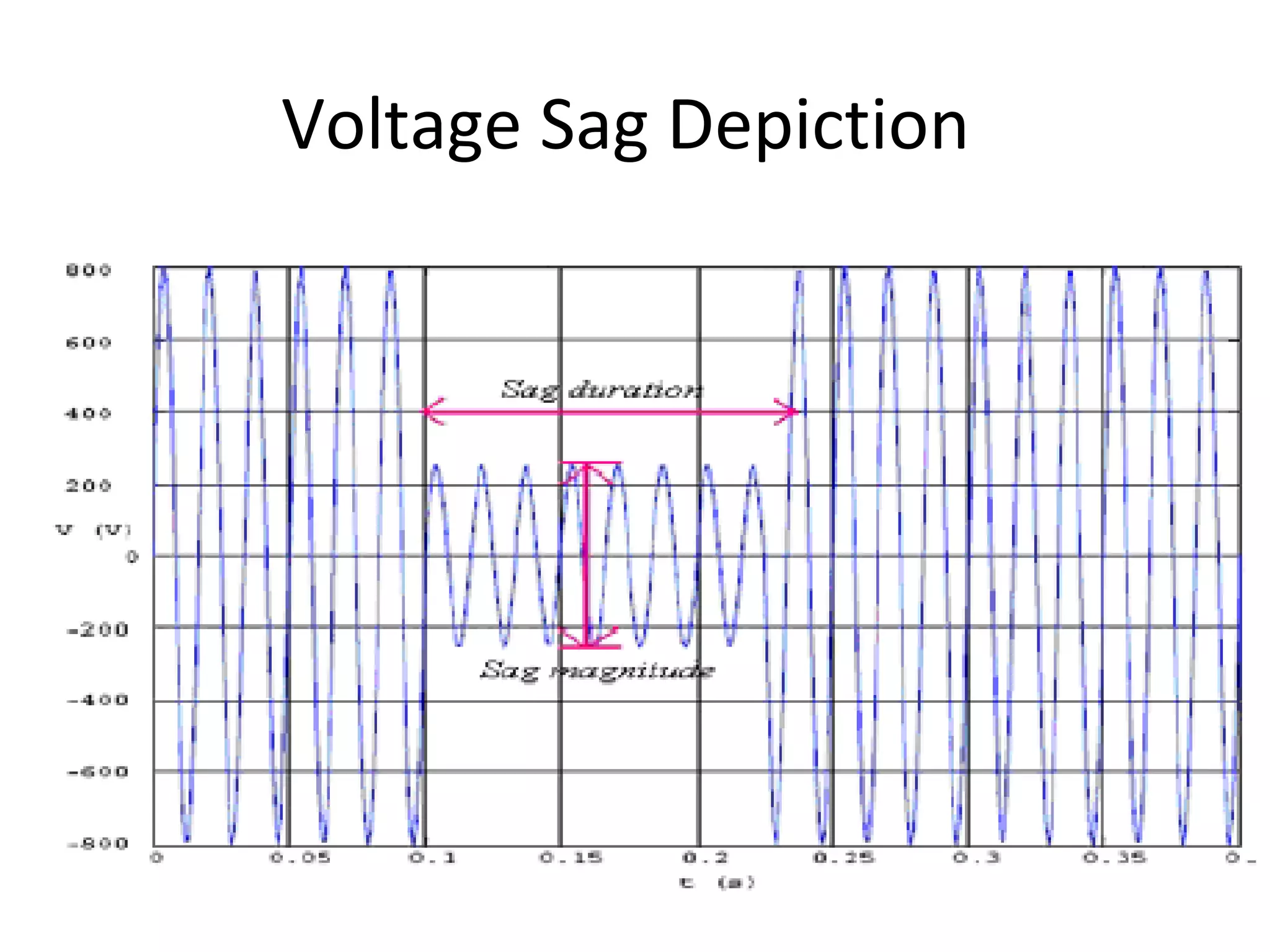
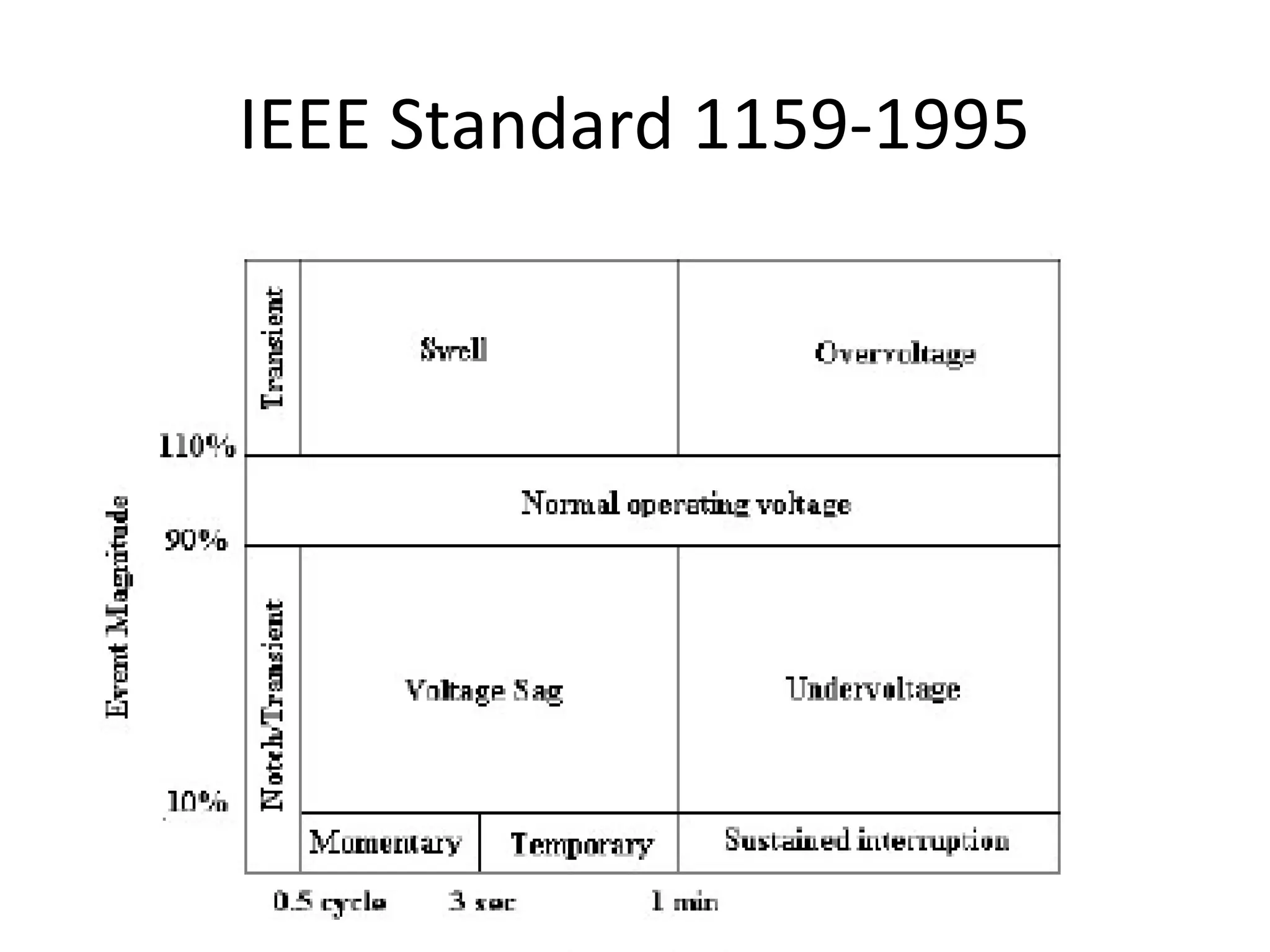
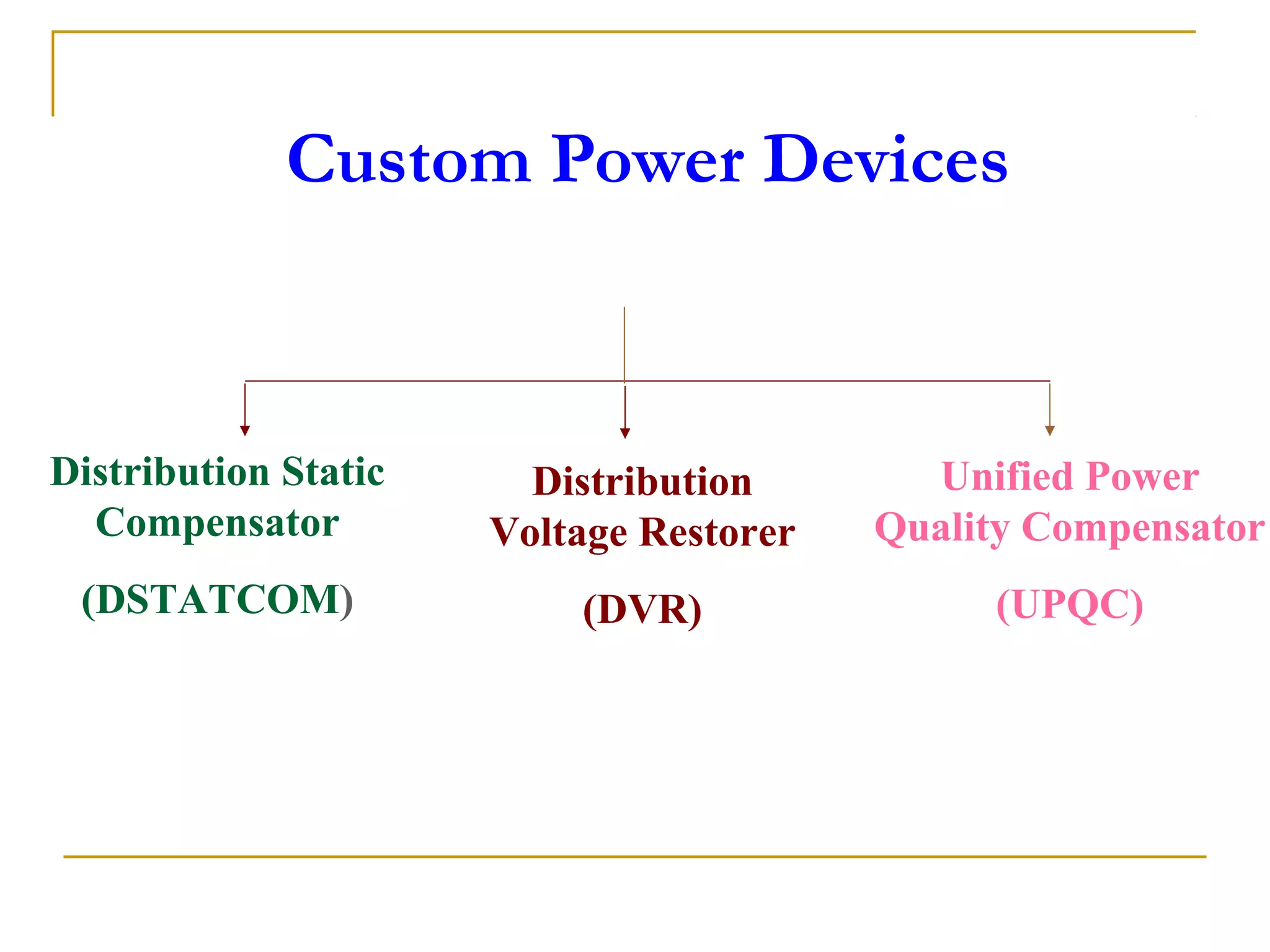
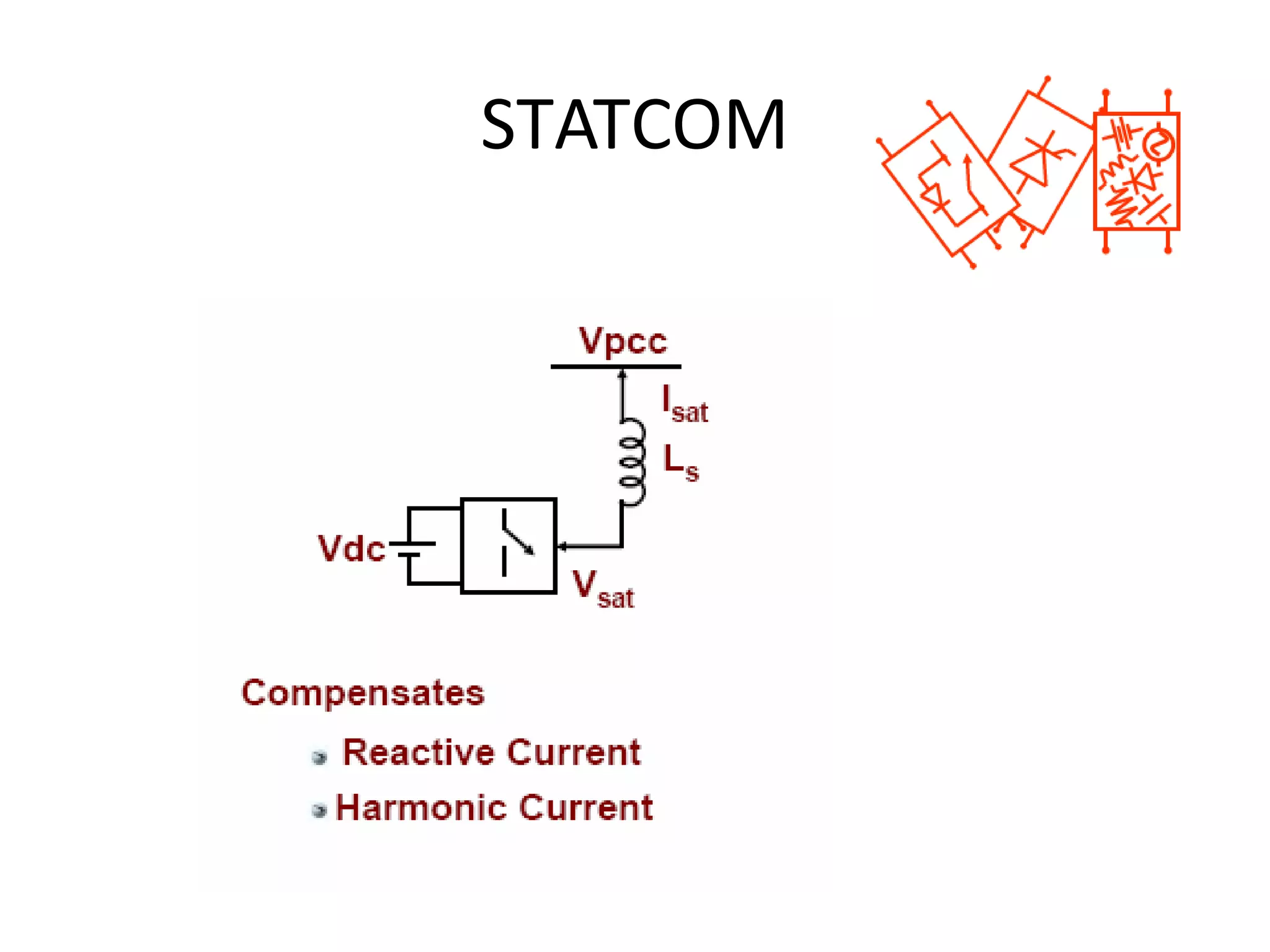
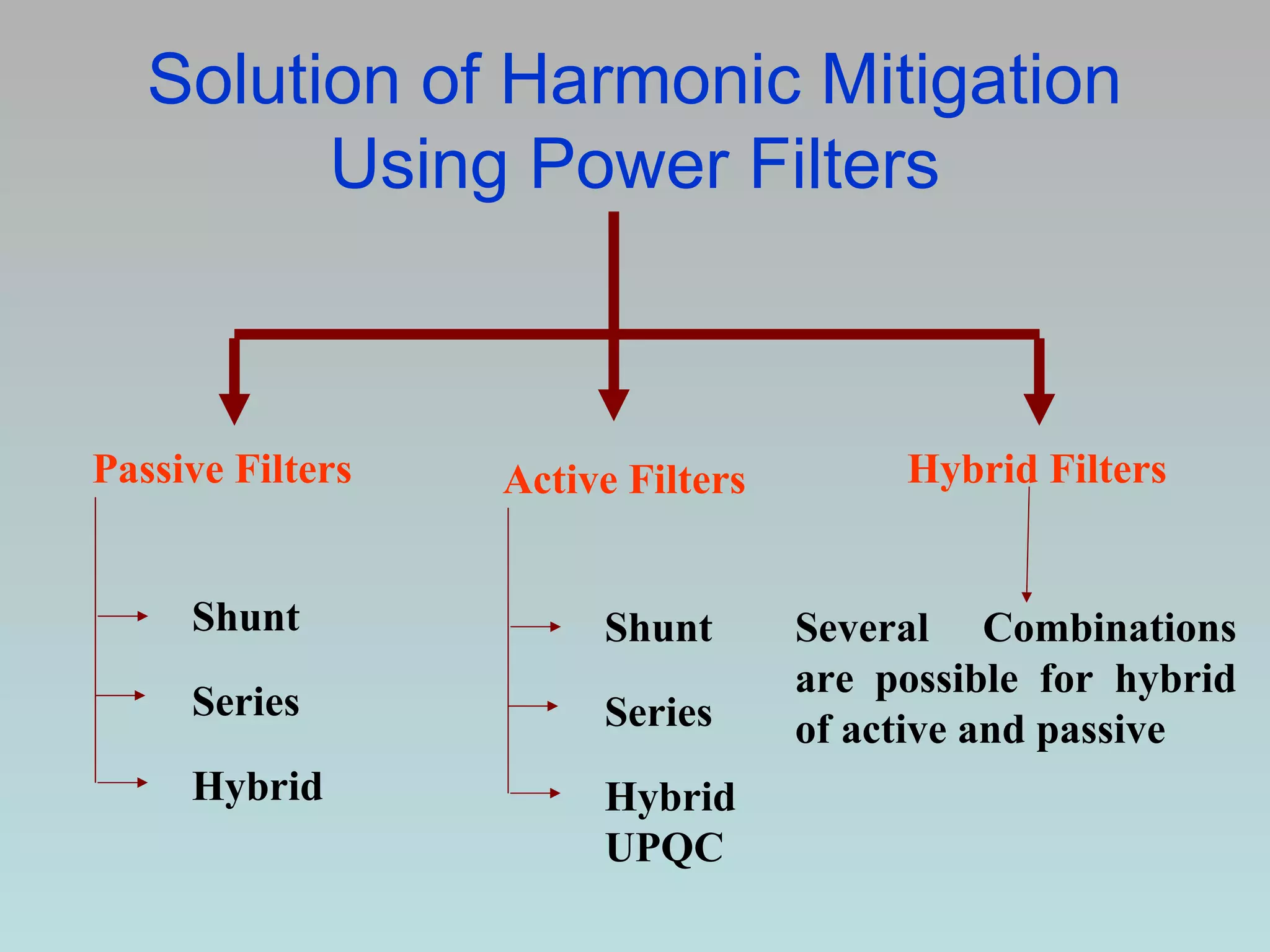
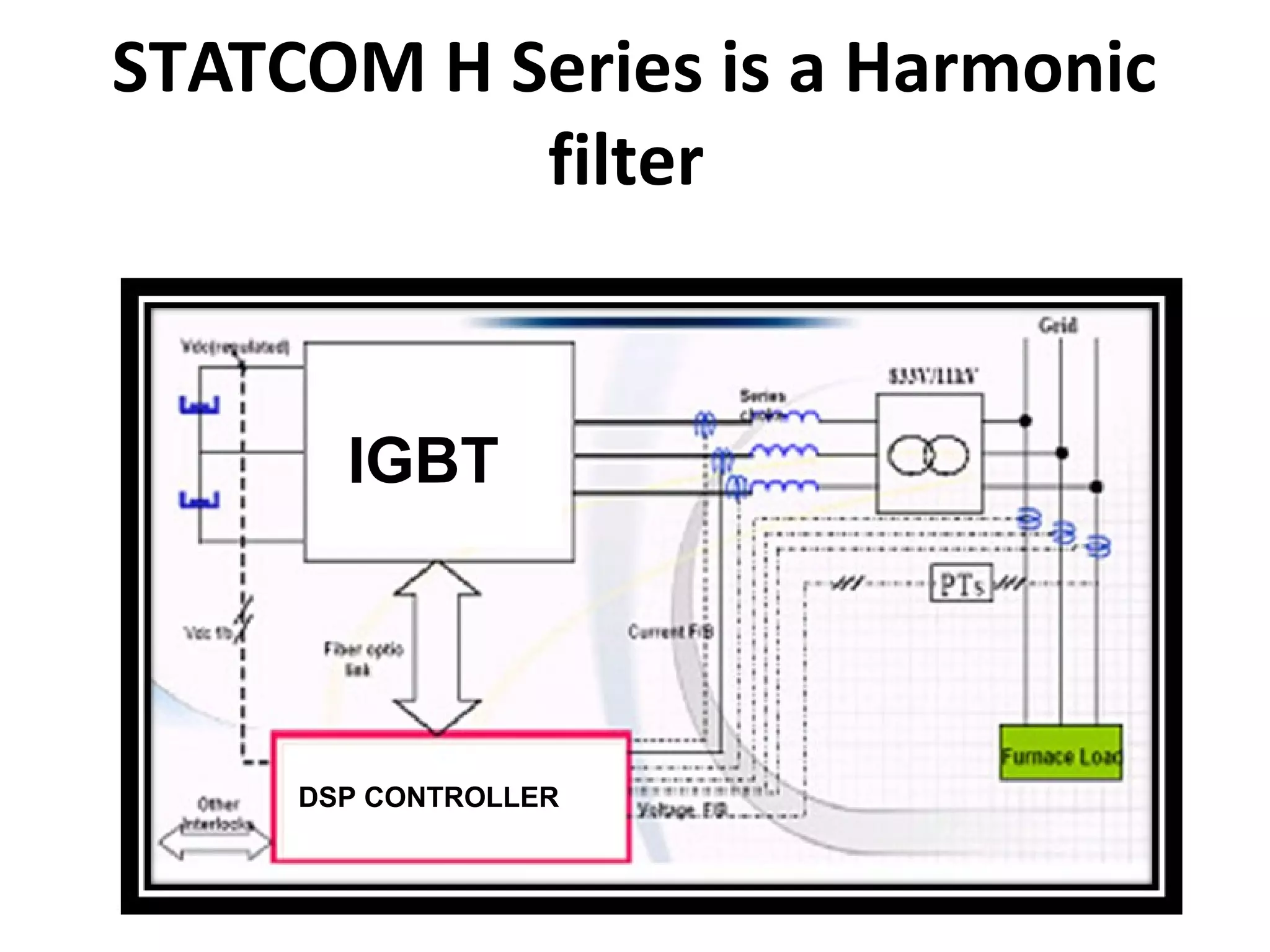
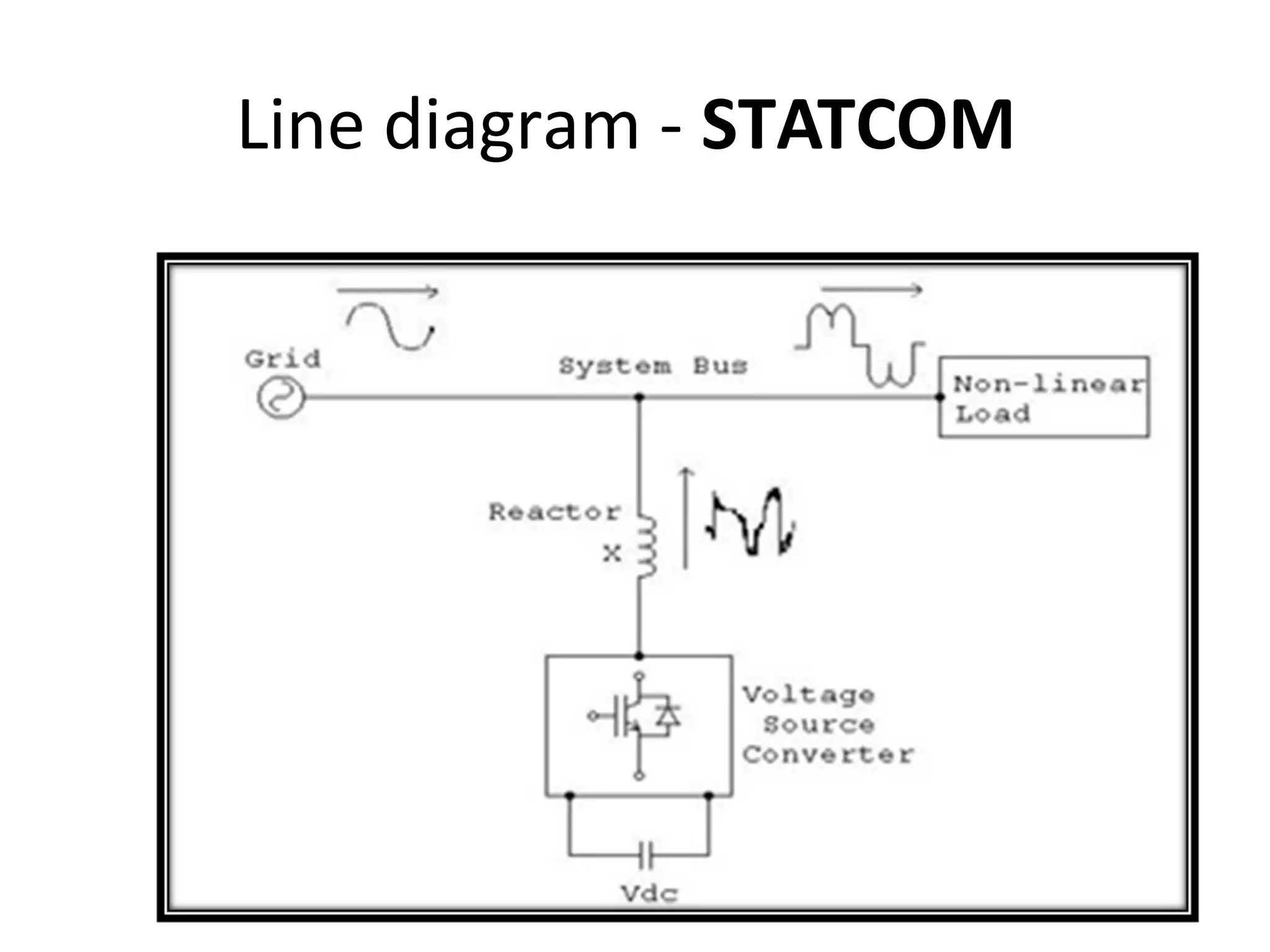
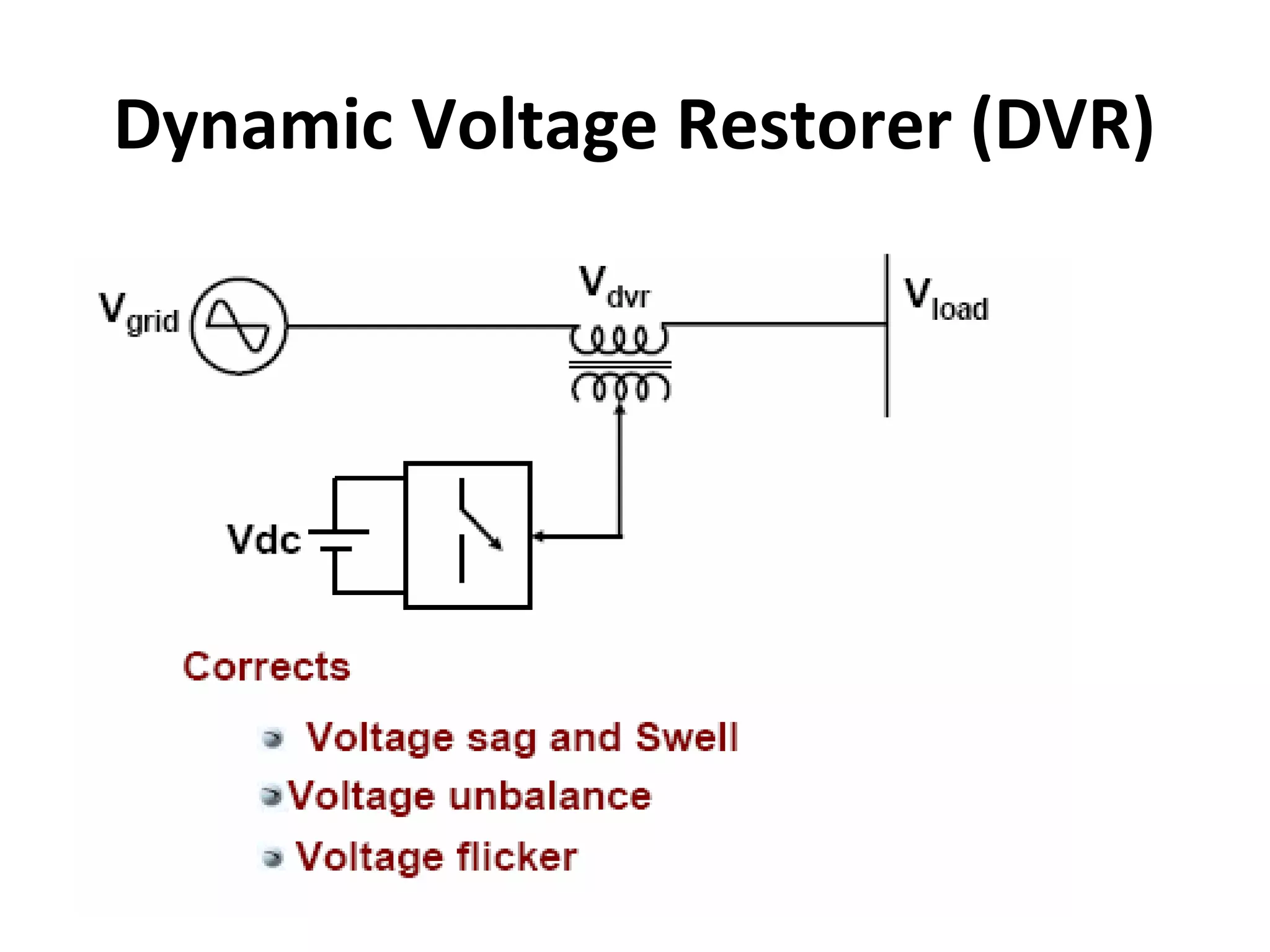
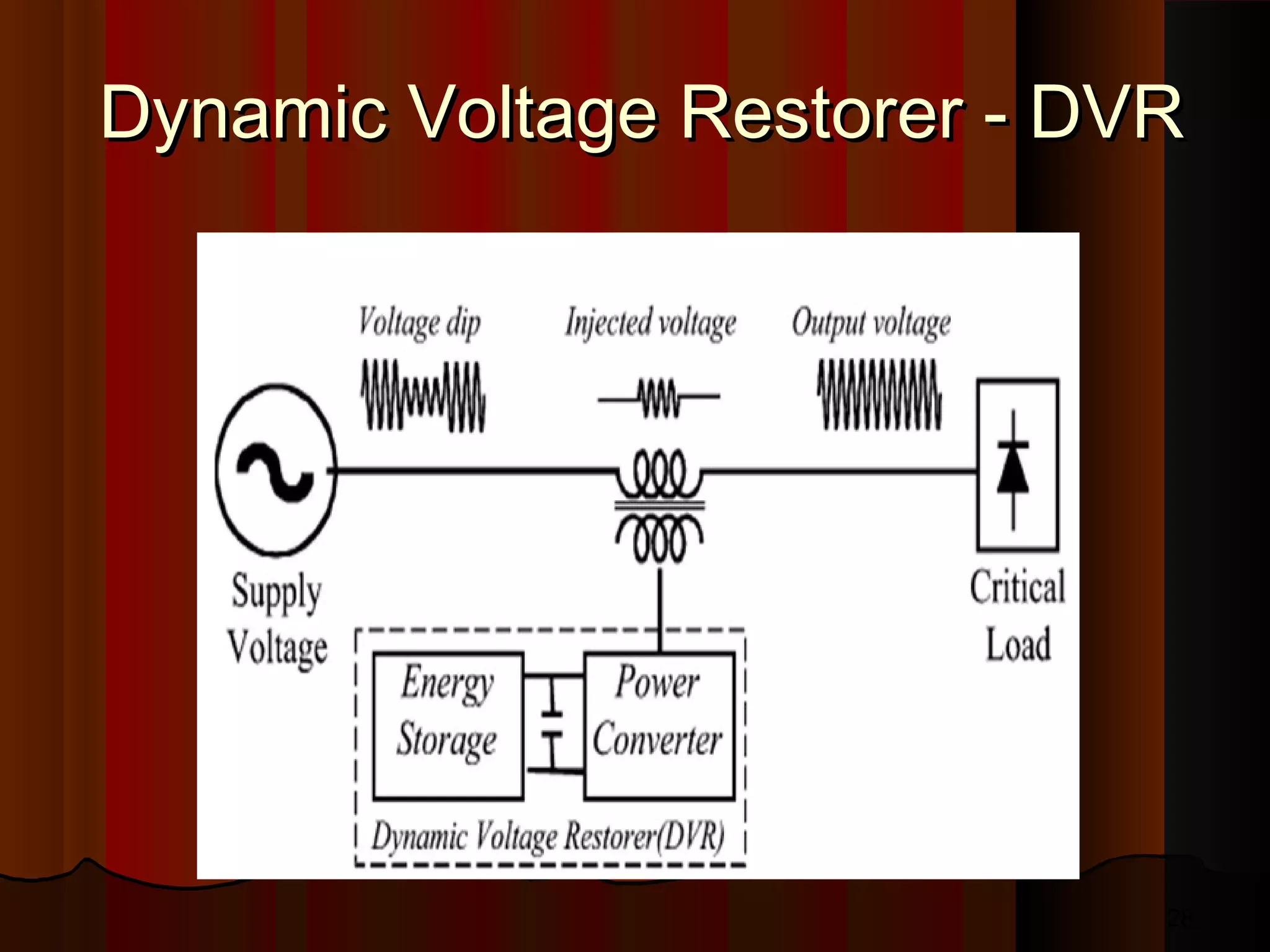
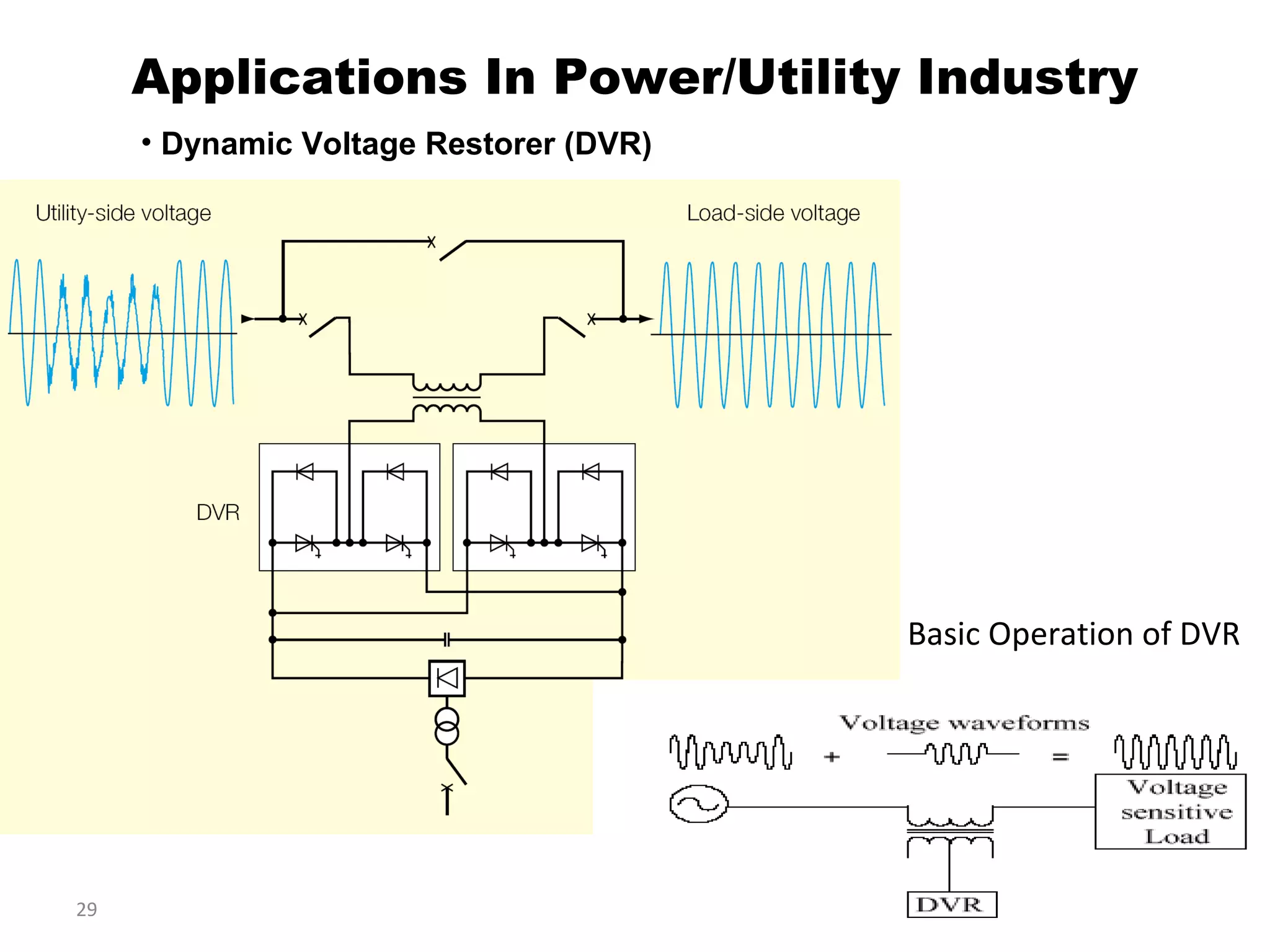
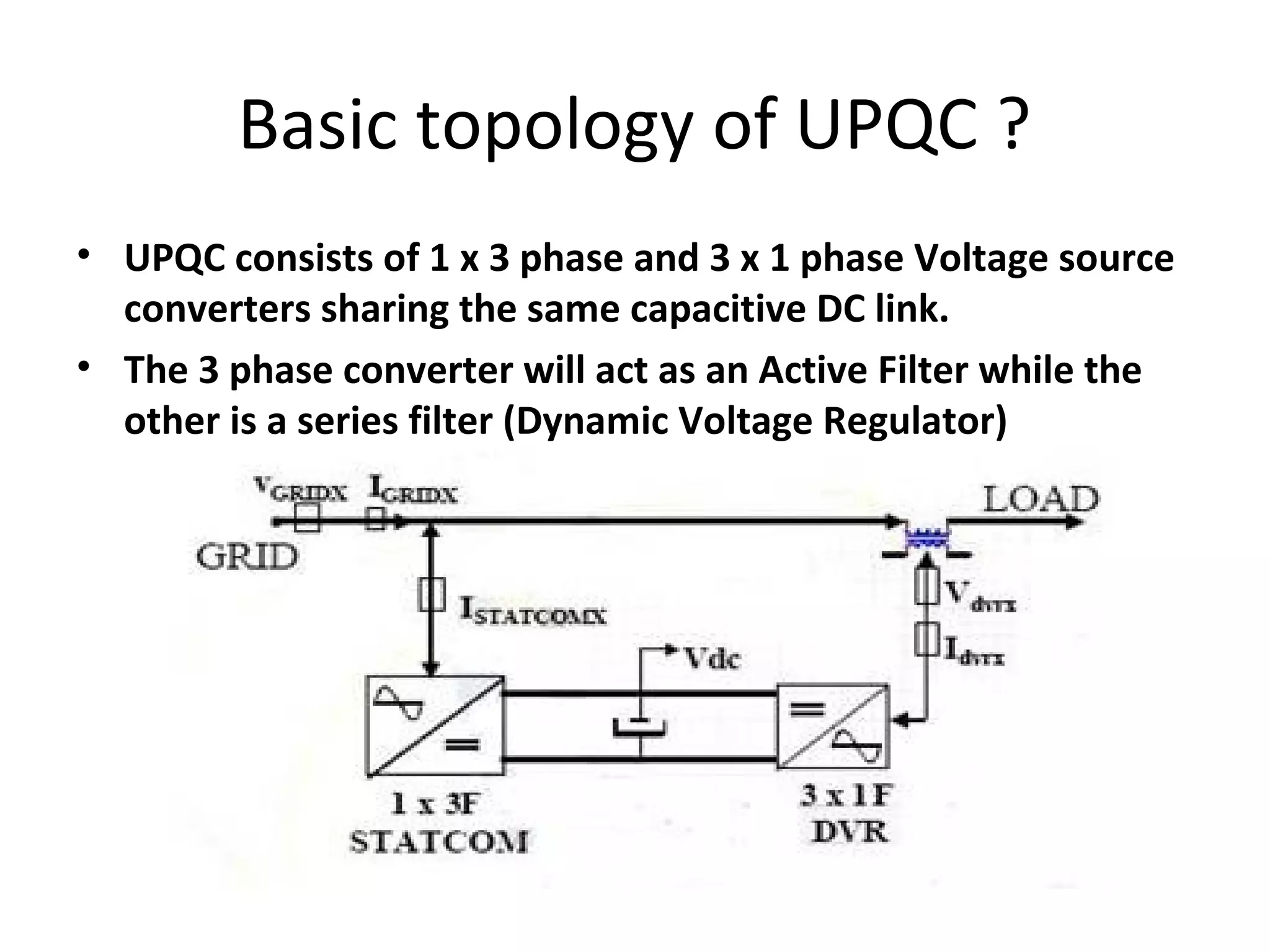
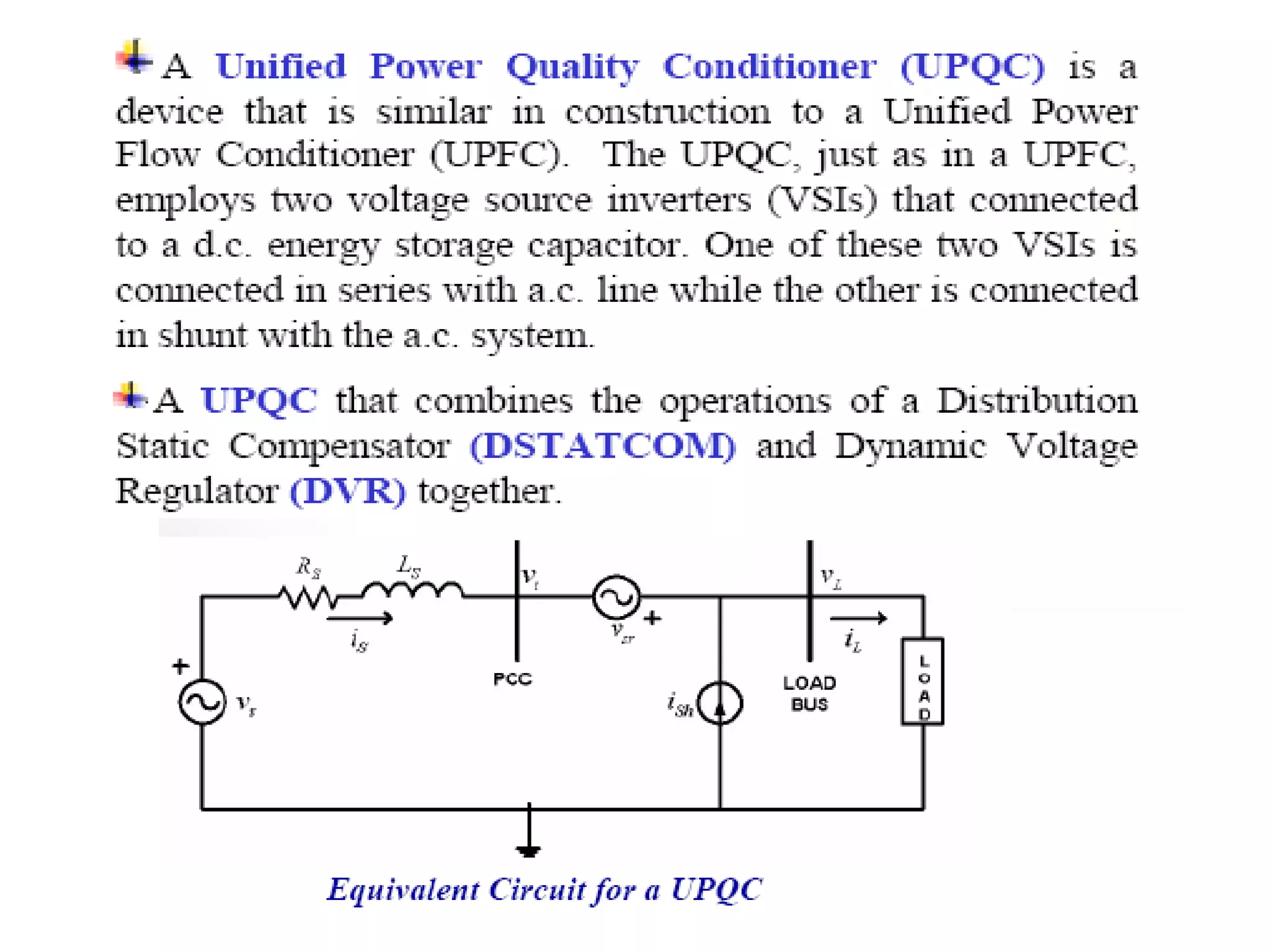
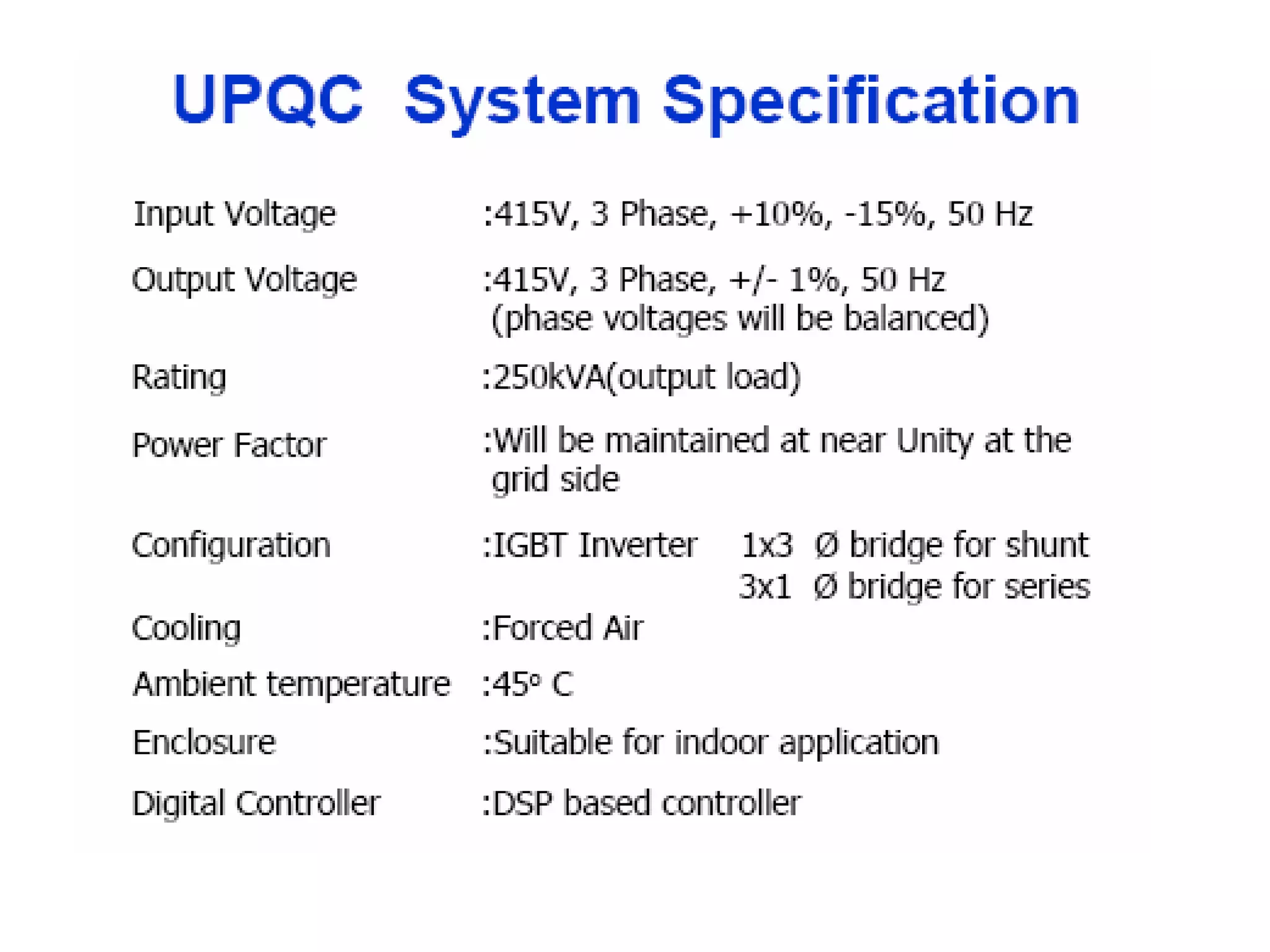
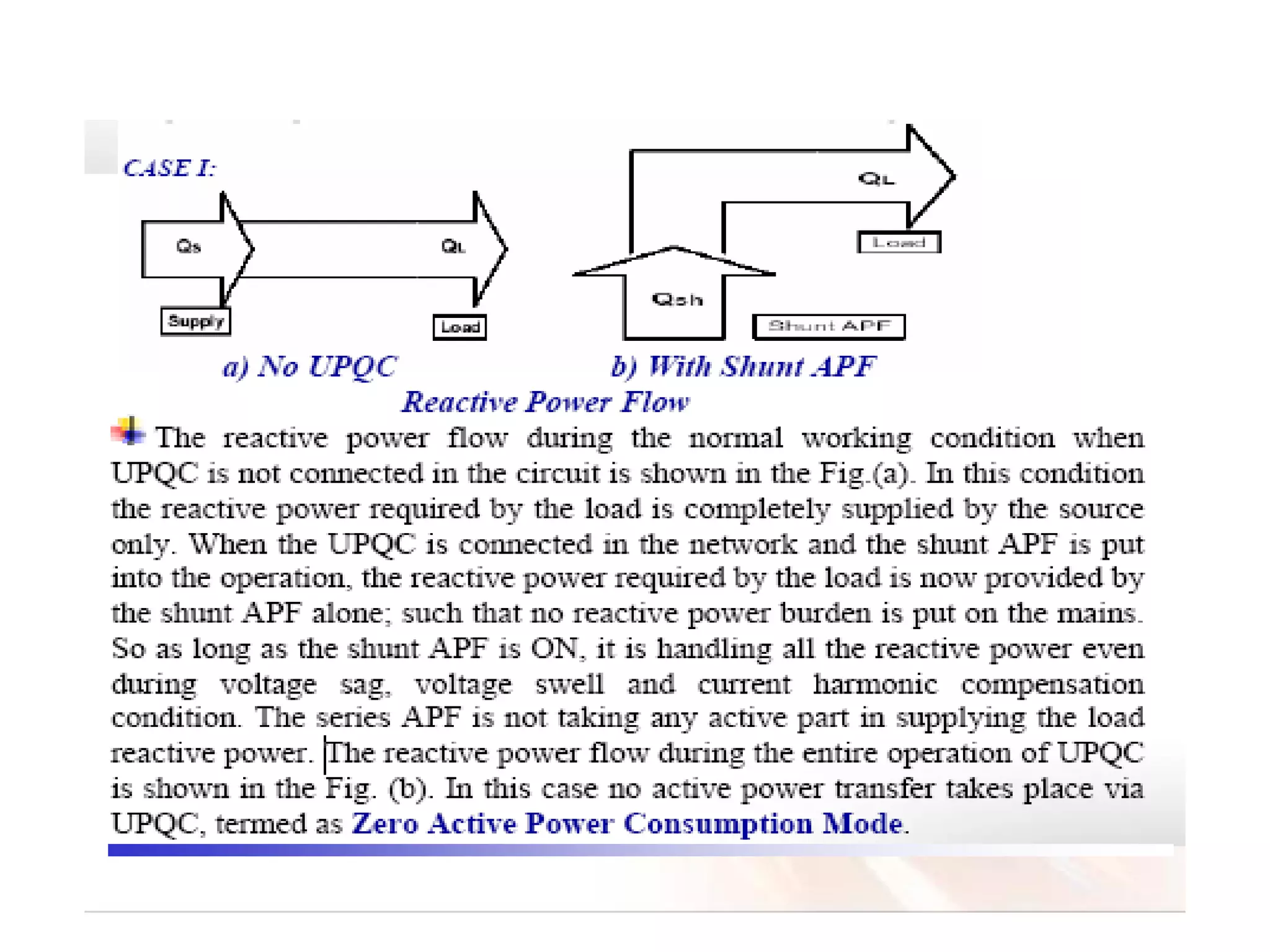
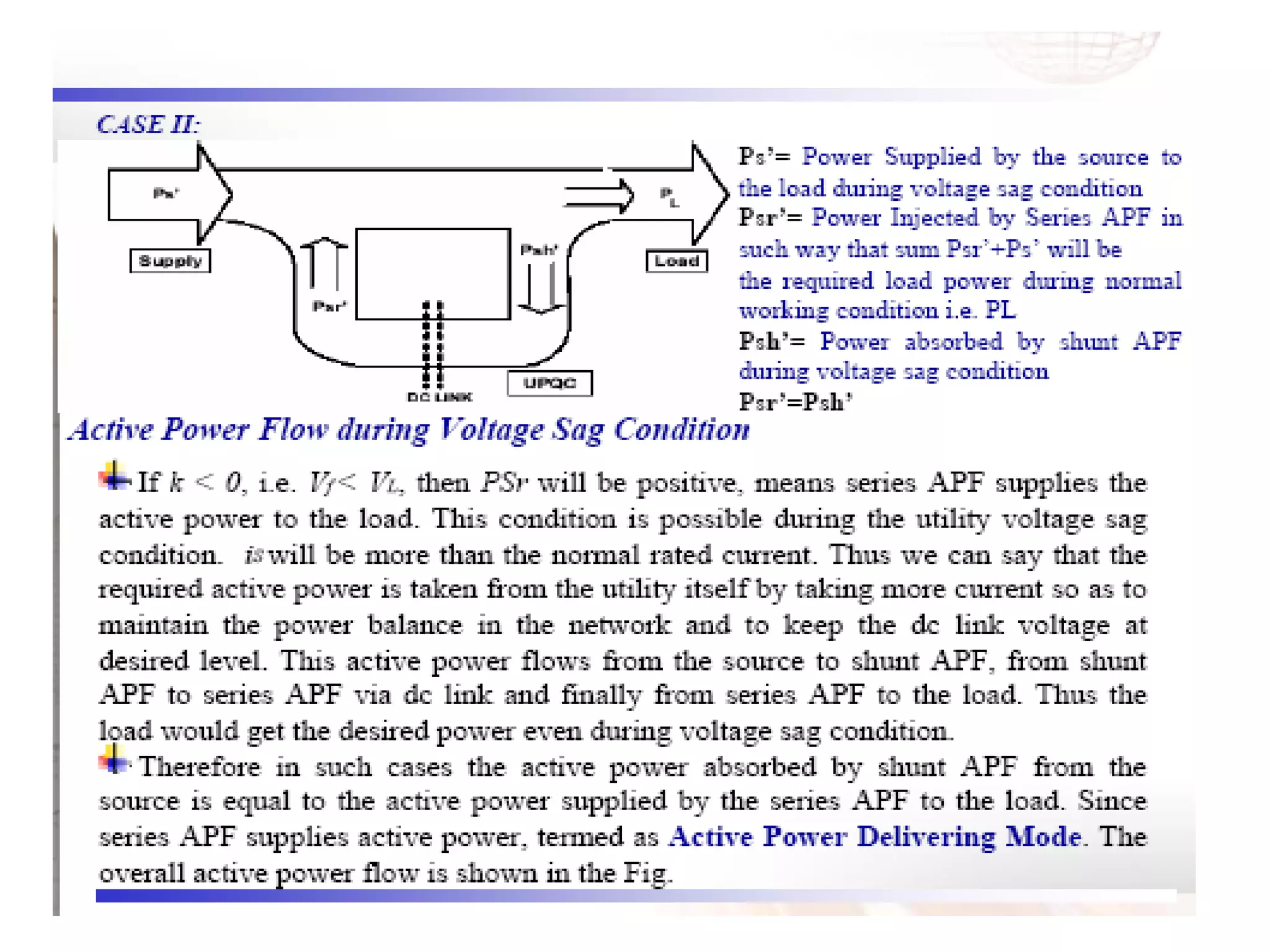
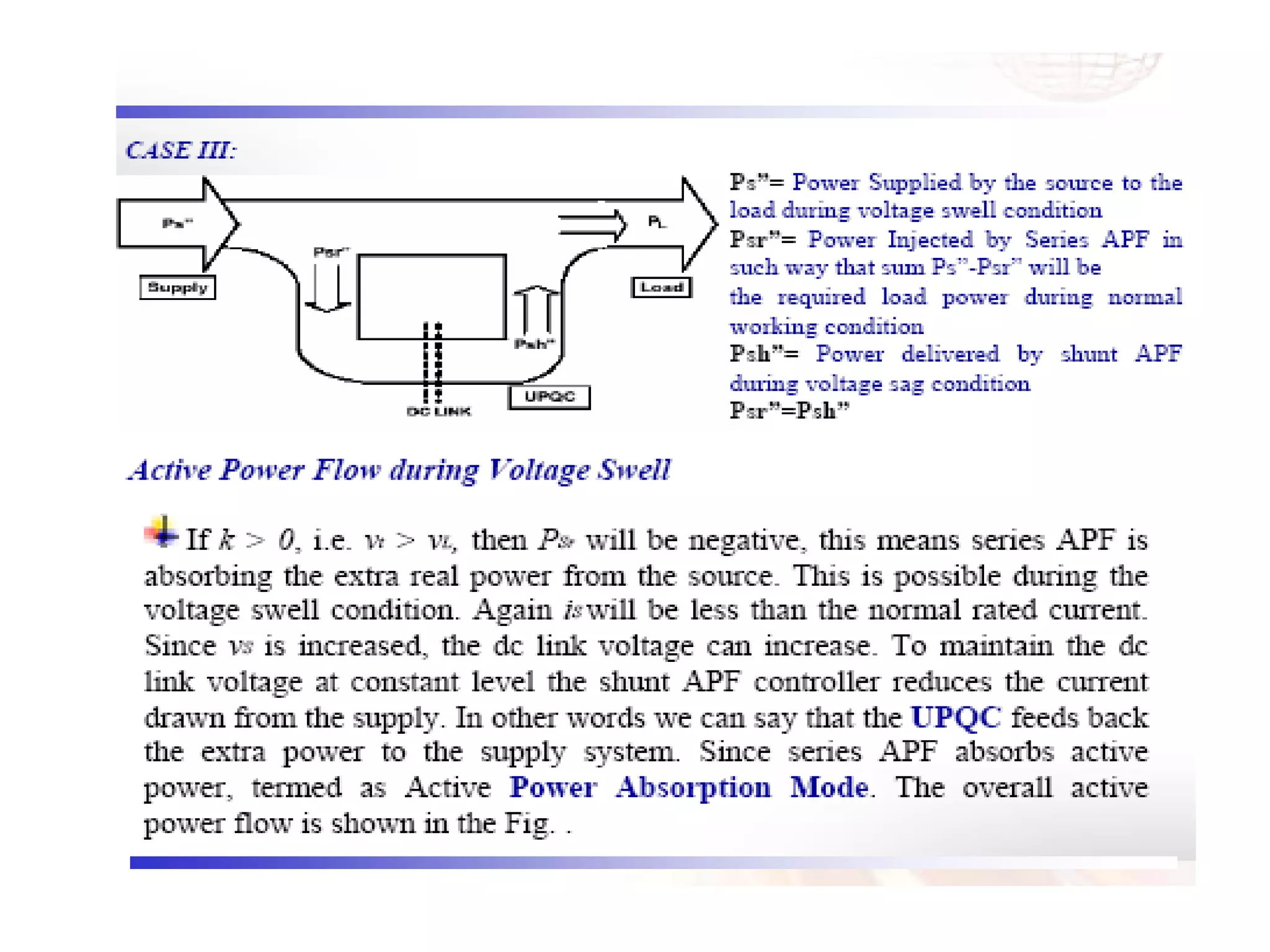
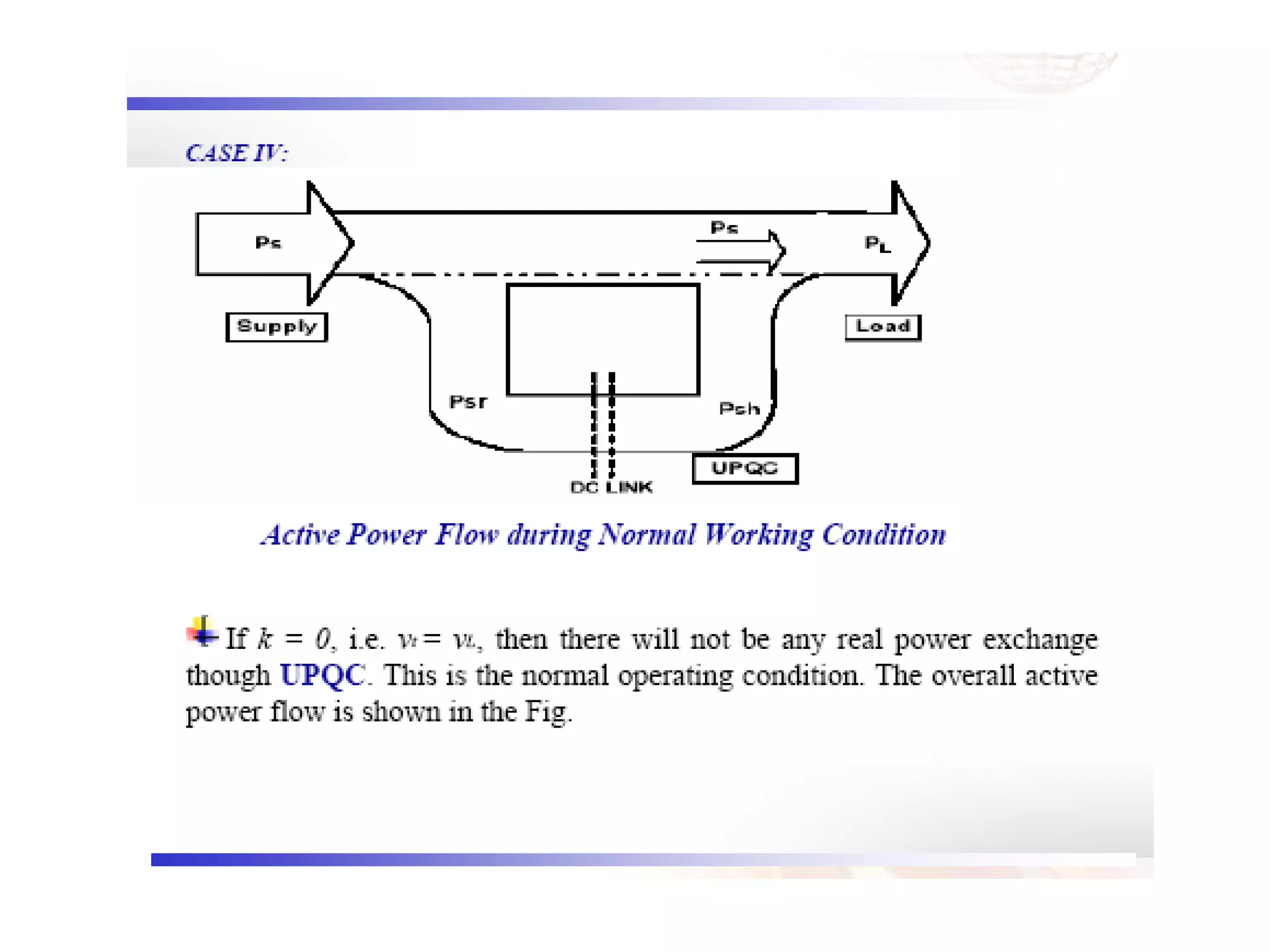
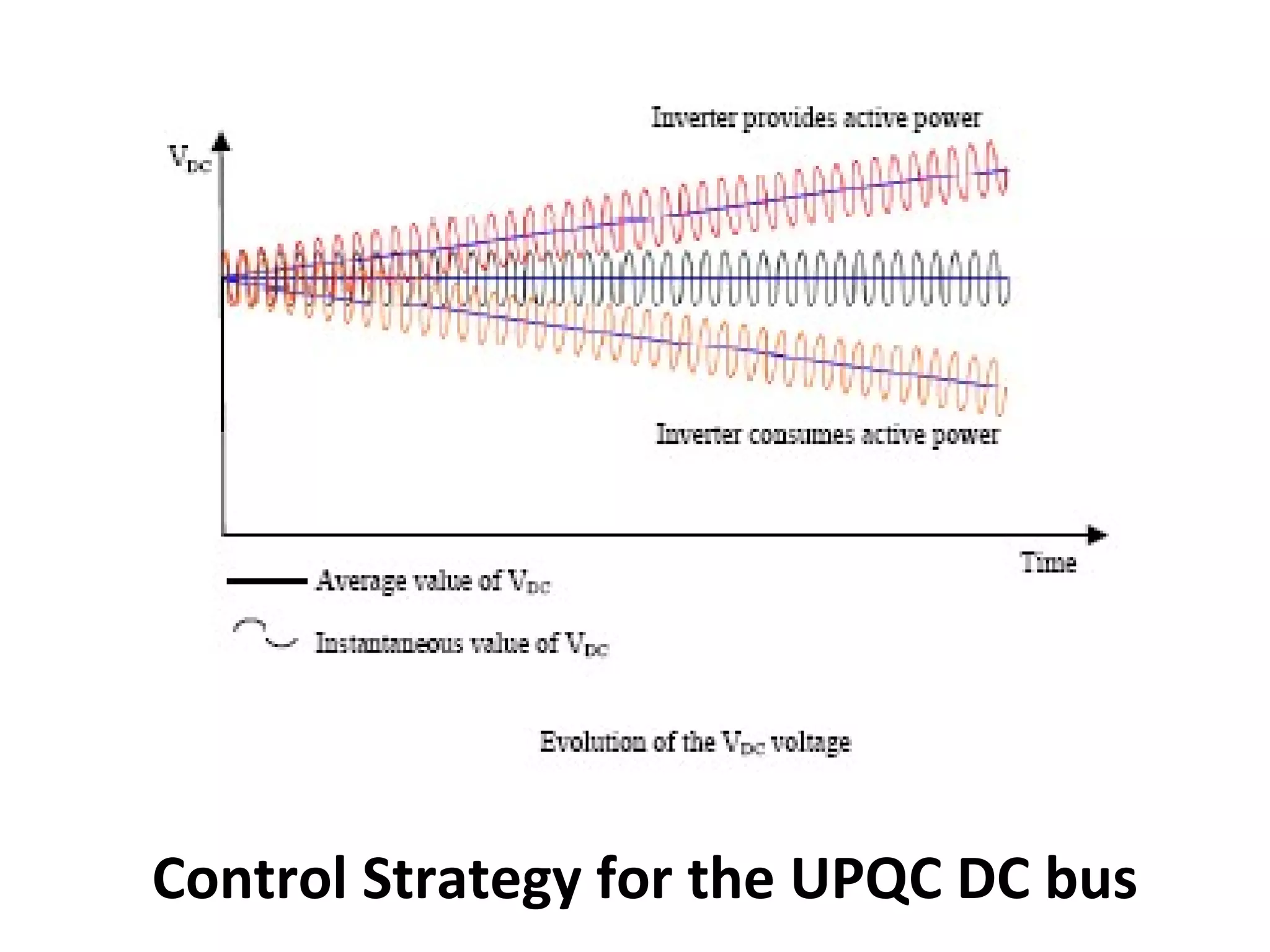
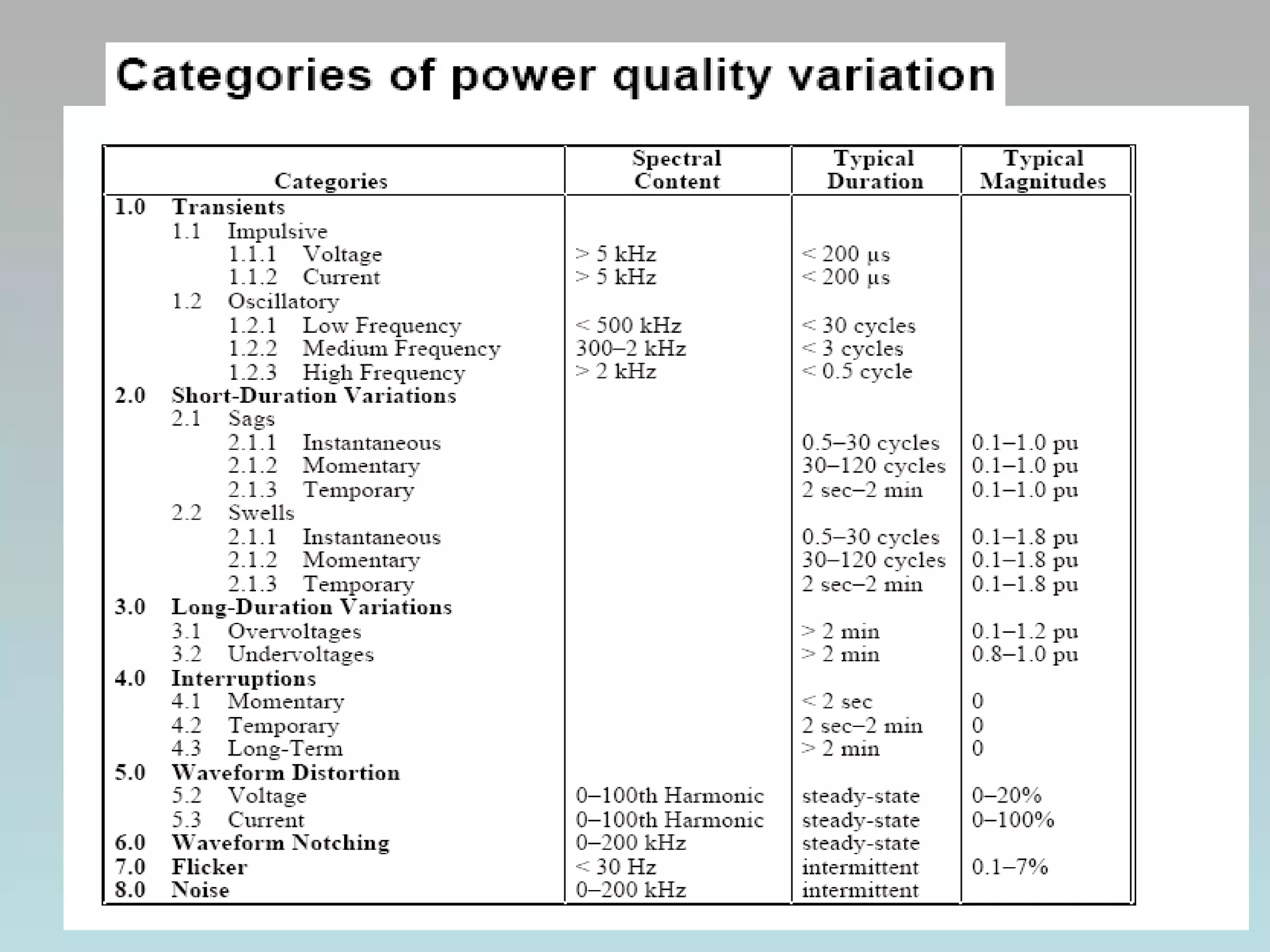
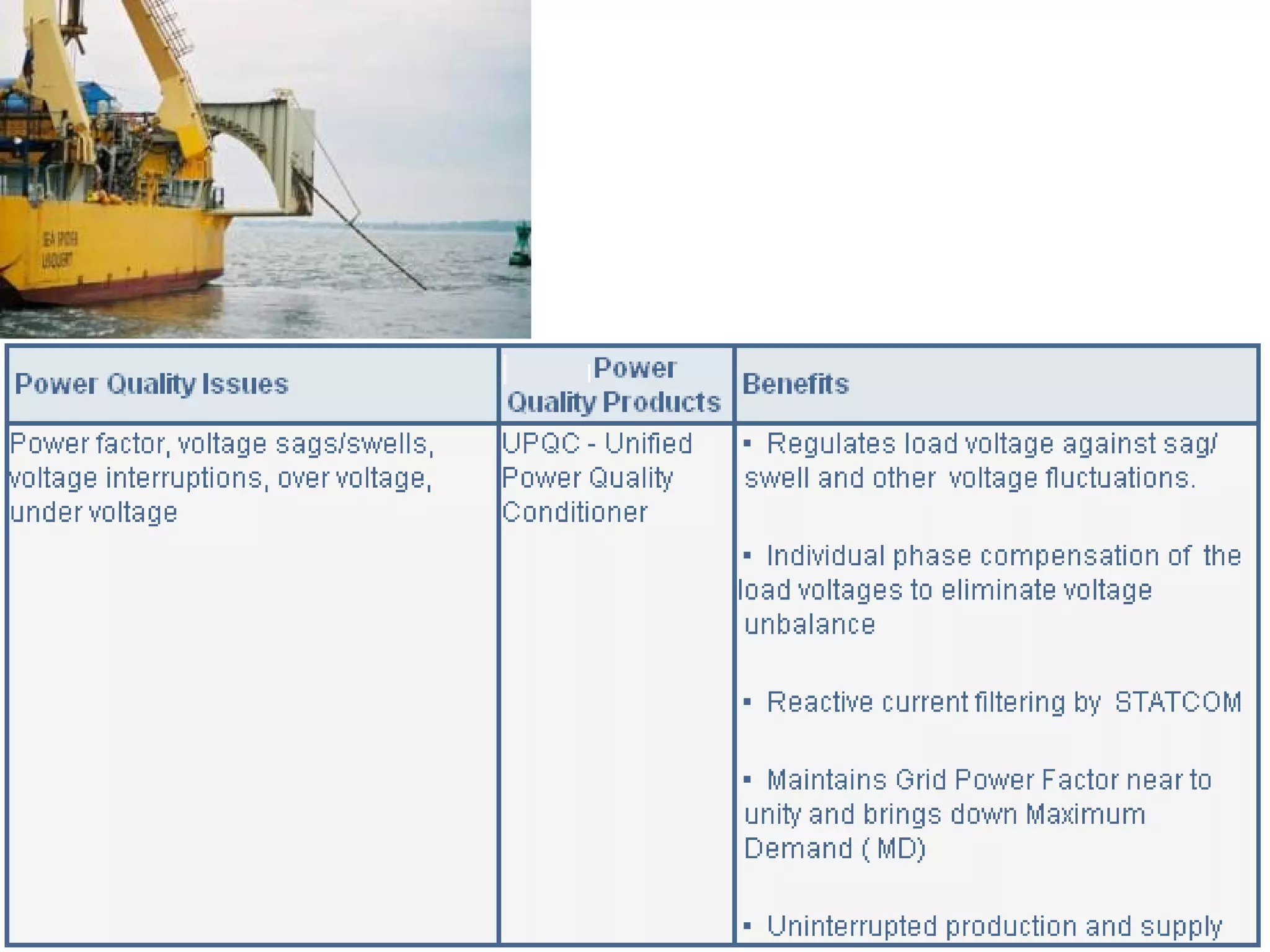
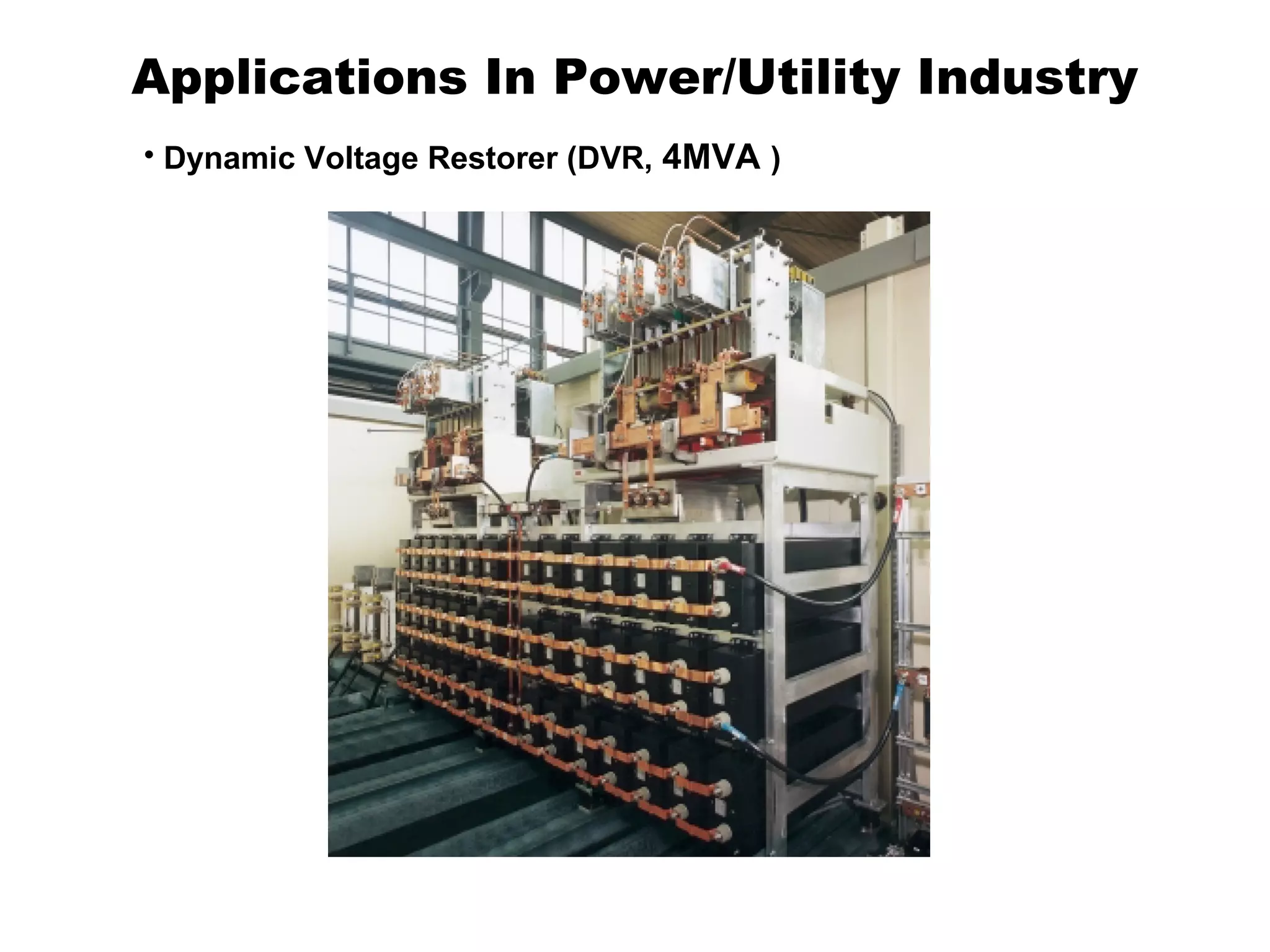
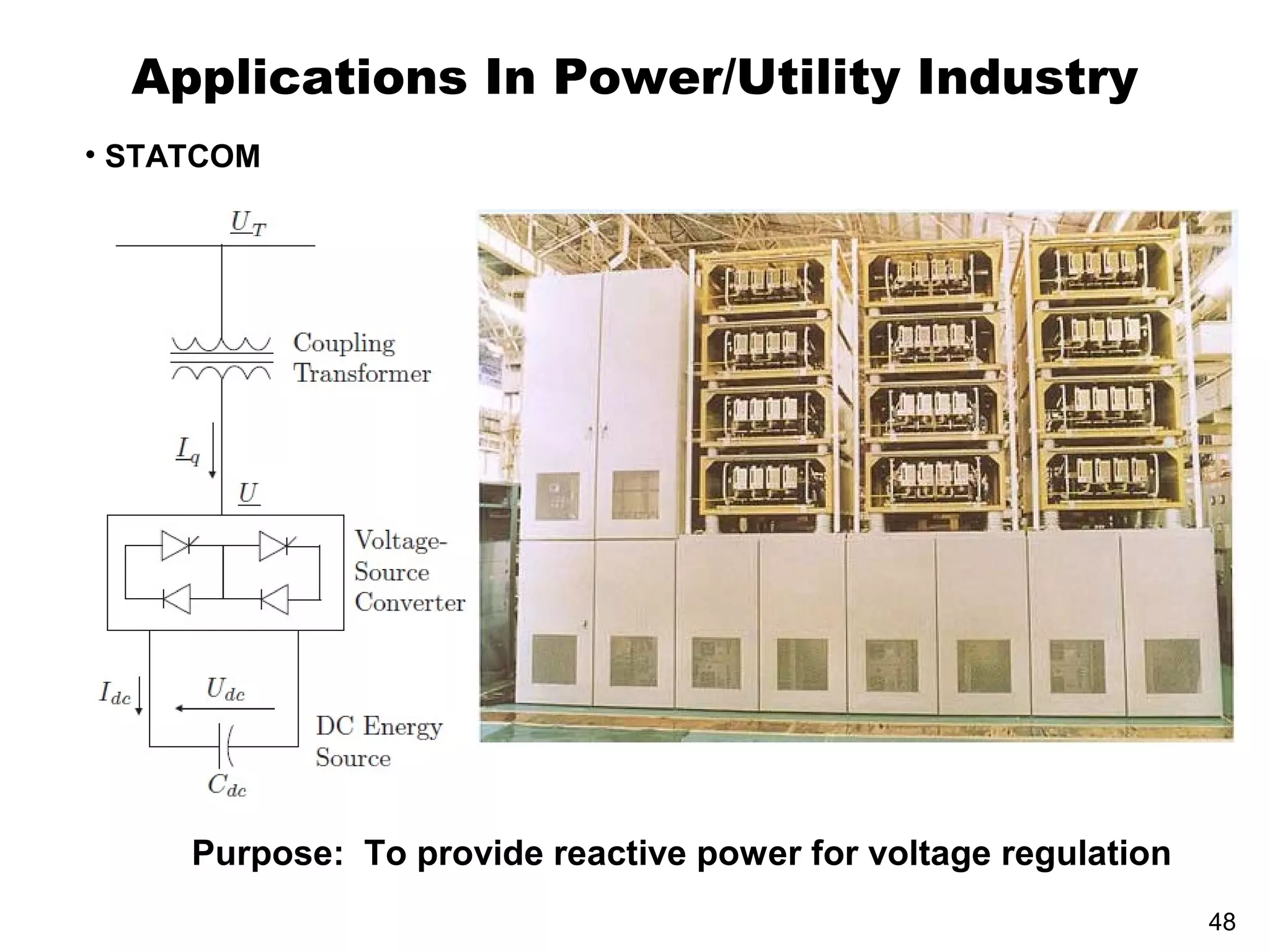
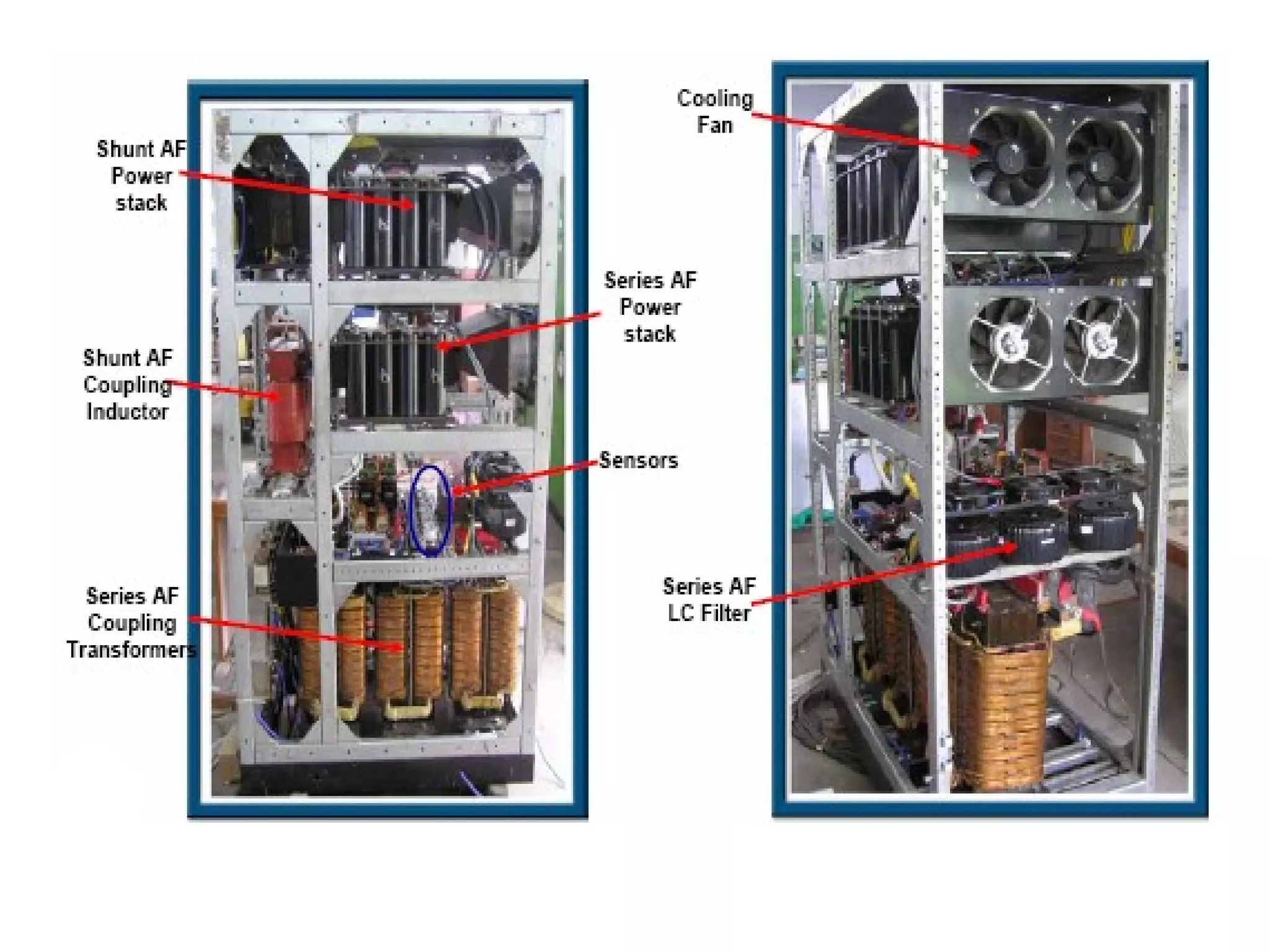
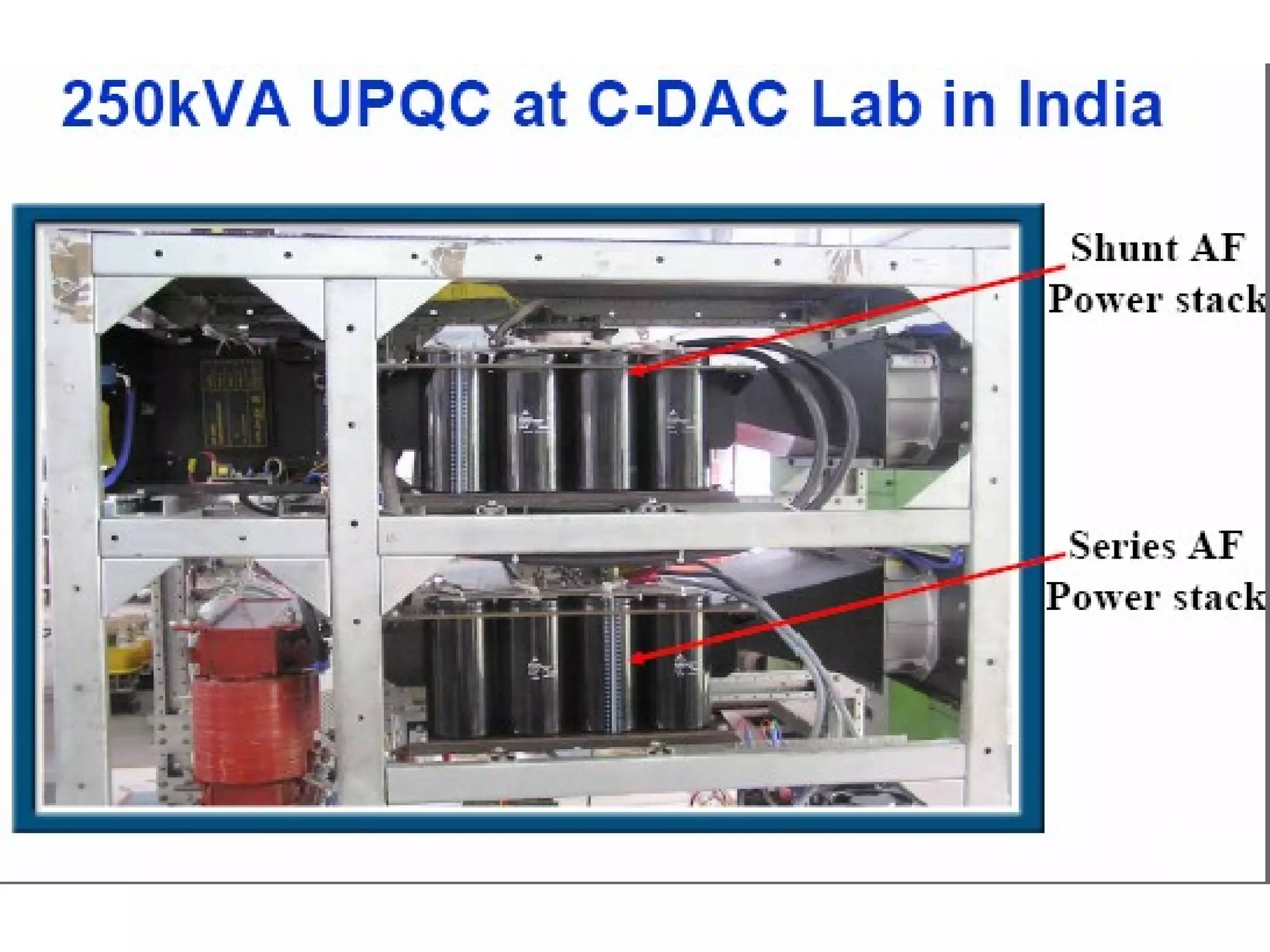
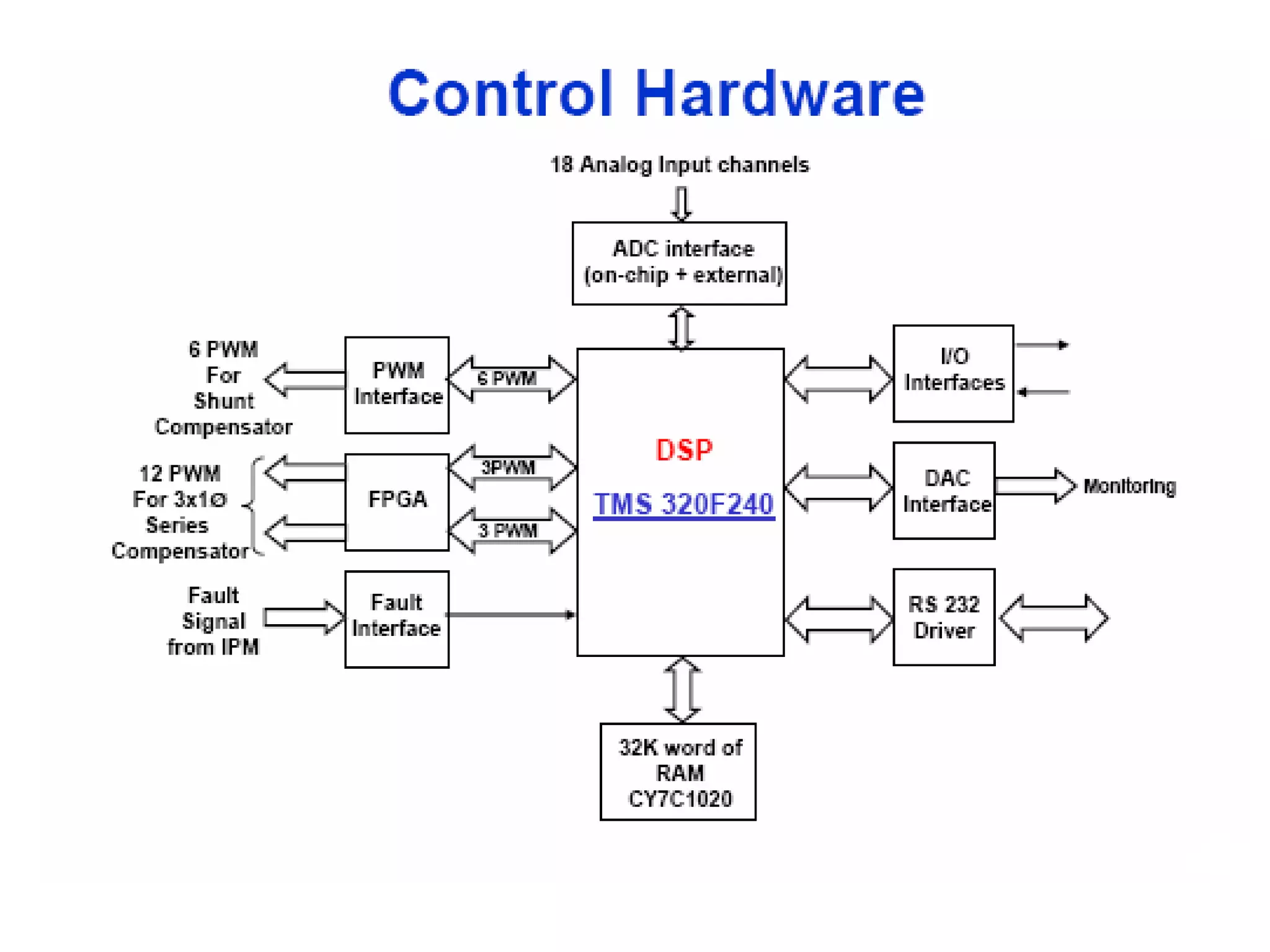
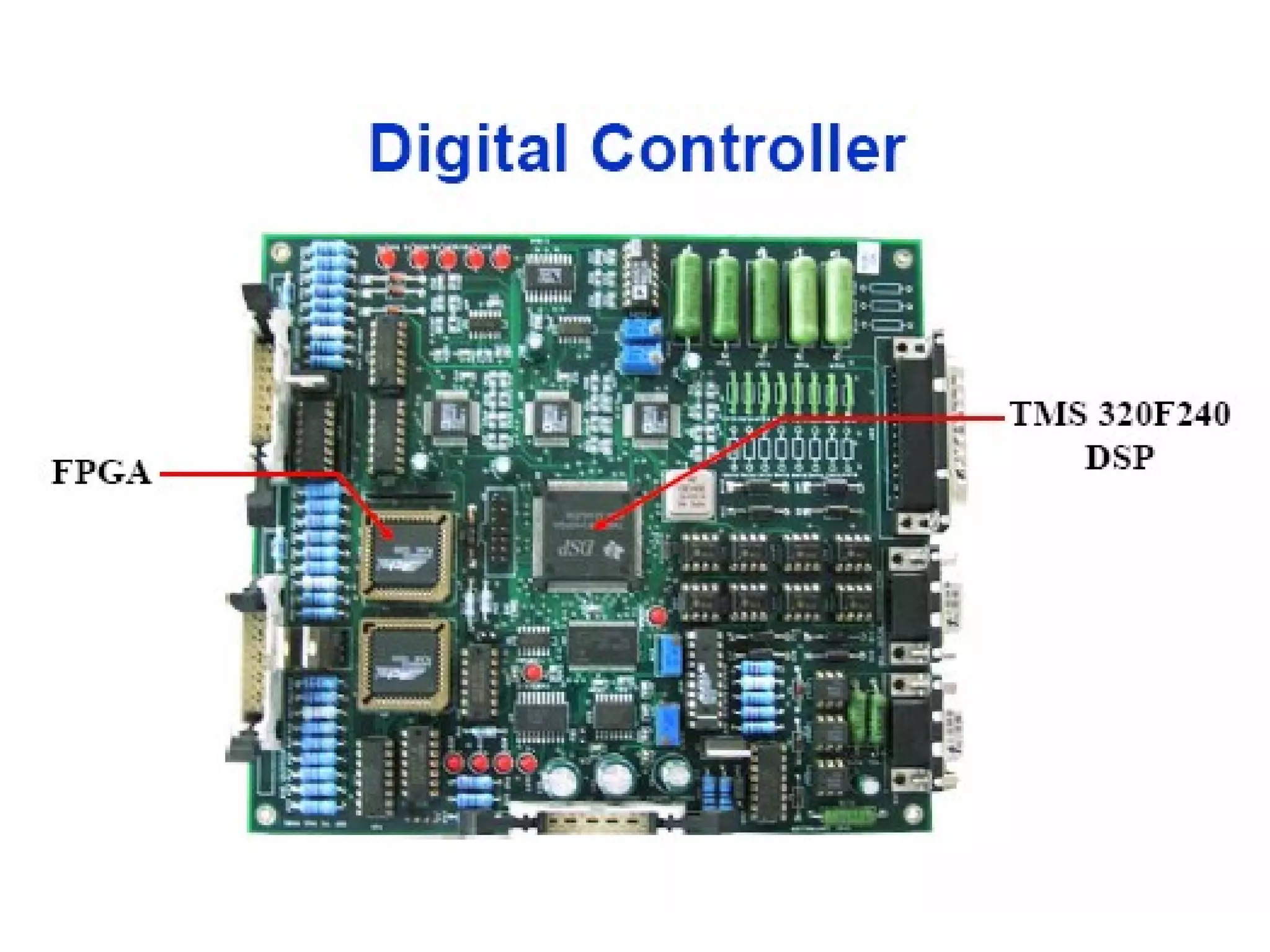
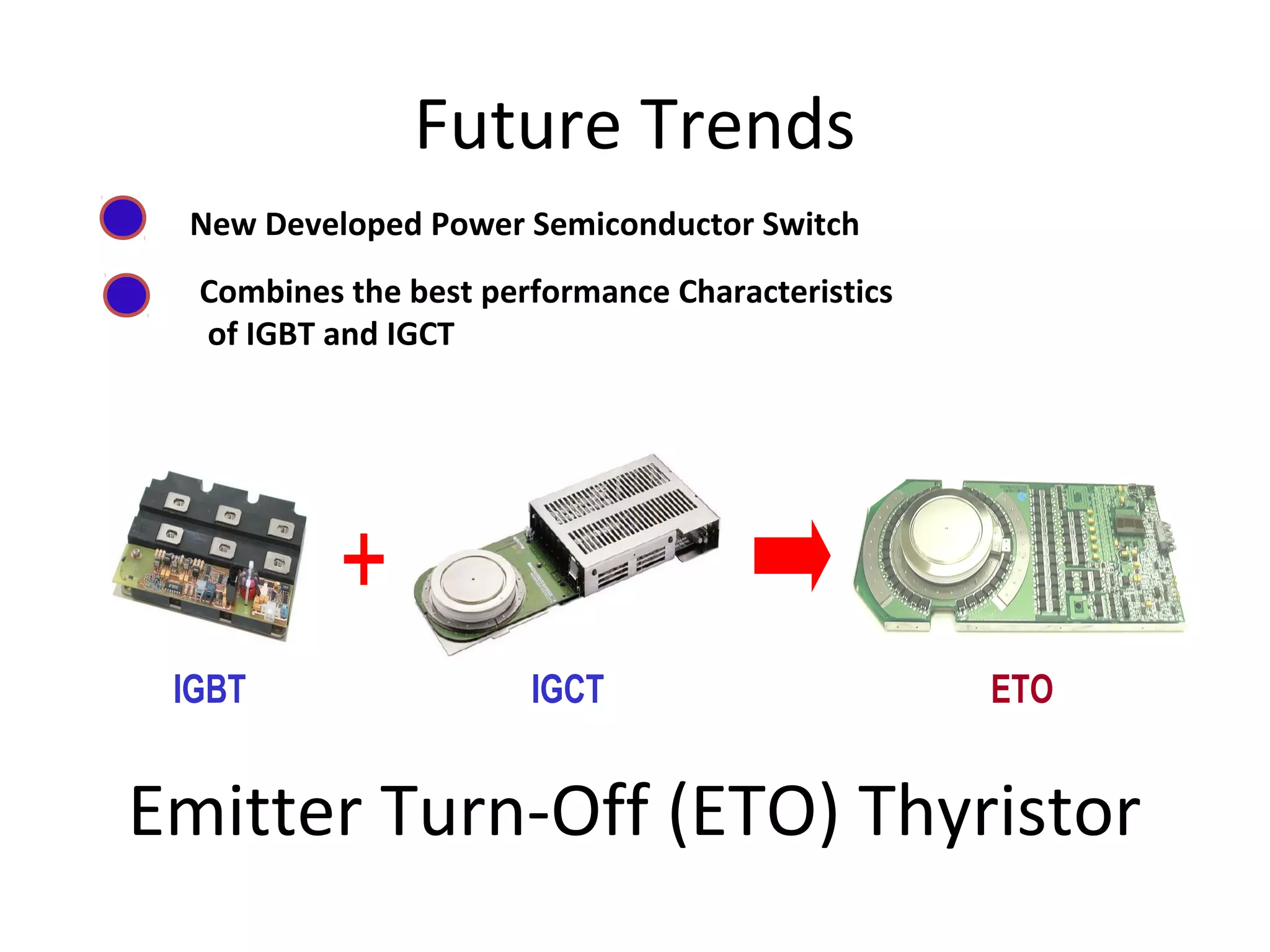
UPQC a novel method to efficiently utilize Sustainable / Alternate Energy Sources is a presentation about power quality issues and solutions. It discusses different power quality problems such as voltage sags, swells, harmonics, and reactive power issues. It then introduces several custom power devices that can address these problems including the STATCOM, DVR, and UPQC. The UPQC is described as an active series-shunt power line conditioner that can compensate for various power quality issues such as voltage sags/swells, imbalance, flicker, and harmonics. The presentation concludes by discussing future trends in power semiconductor switches and the balanced application of these new technologies.