This document summarizes a study that used group contribution methods to predict the solubility of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in biodiesel. The study used three versions of the Universal Functional Activity Coefficient (UNIFAC) model to predict infinite dilution activity coefficients for VOCs in fatty acid methyl ester solvents that make up biodiesel. The results showed that activity coefficients decreased with increasing molecular weight for alkanes, amines, alkenes, organic acids, and alcohols. Shorter esters with lower carbon counts had higher activity coefficients than longer esters with higher carbon counts. Solubility of VOCs in biodiesel also decreased with increasing ester hydrocarbon unsaturation.
![
Abstract— This work investigated the suitability of biodiesel
(predominantly Methyl Linolenate, Methyl Palmitate, Methyl
Oleate and Methyl Stearate) as an absorbent for the recovery
of VOCs from waste gas process streams through absorption.
The objective was to predict the vapour liquid equilibria
(VLE) data, in the form of infinite dilution activity
coefficients for five VOC families, in fatty acid methyl ester
solvents. The Original Universal Functional Group Activity
Coefficient (UNIFAC) model (Fredenslund et al., 1975),
Modified UNIFAC (Larsen et al., 1981) and Modified
UNIFAC (Bastos et al., 1988) was used to predict the infinite
dilution activity coefficients. The solubility of alkanes,
amines, alkenes, organic acids and alcohols showed a decrease
in activity coefficients with an increase in molecular weight.
Shorter chained esters with a lower carbon count had higher
activity coefficients when compared to the longer chained
esters with a higher carbon count. The solubility of VOCs in
biodiesel decreases with increase in ester hydrocarbon
unsaturation.
Keywords— Activity coefficients, biodiesel, phase equilibrium,
Universal Functional Activity Coefficient.
I. INTRODUCTION
The legislation on environmental conservation in South
Africa, as outlined in the National Environmental
Management: Air Quality Act 39 of 2004, has forced all
industries to closely monitor any effluents emitted to the
environment. This work focuses on the abatement of volatile
organic compounds through physical absorption using
polymeric solvents. The selection of the absorbent is governed
by the thermodynamic interactions as measured by the infinite
dilution activity coefficients among other factors. For
preliminary feasibility studies of a physical absorption
process, thermodynamic models are used to predict the
S.Ramdharee is with the Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of
Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Johannesburg,
Auckland Park, Johannesburg 2028 (e-mail: sashayr007@gmail.com;
sramdharee@csir.co.za)
M.Belaid is with the Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of
Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Johannesburg,
Doornfontein, Johannesburg 2028;(e-mail: mbelaid@uj.ac.za )
required phase equilibria. These are preferred instead of
measurements which are expensive, laborious and time
consuming. Biodiesel is one of the solvents with favourable
thermodynamic interactions with volatile organic compounds.
A. Technology Selection
The technologies used for VOC recovery are mainly
separation processes such as physical and chemical
absorption. Absorption is a separation method which involves
the removal of a compound from a contaminated gas stream
by contacting it with a suitable absorption fluid. Absorption
can be physical depending on concentration gradients or
chemical where a chemical reaction is used to enhance the
absorption process. Physical absorption follows the Nerst
partition law (1).
Absorption is a physical process, and it follows the Nerst
partition law. KN, the partition coefficient depends on
temperature. Equation (1) is valid for low concentrations and
when the species x does not change its form in the two phases
[1].
)12,(
2
1
xNK
x
x
constant (1)
B. Solvent Selection
Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils by converting the
triglyceride oils to methyl (or ethyl) esters through a process
known as transesterification. The transesterification process
reacts alcohol with the oil to release three "ester chains" from
the glycerine backbone of each triglyceride. The
transesterification of vegetable oil was first reported by
Duffy and Patrick, 1883 [2]. The selection of a suitable
scrubbing solvent for a specific waste gas stream composition
is influenced by a high absorption capacity for the separating
component, a high selectivity with reference to other gases,
low toxicity and low volatility.
J Hu, Z Du, Z Tang and E Min, 2004 [3] investigated the
suitability of biodiesel as a solvent and reported that small
quantities of non-monoalkyl esters affect solvent power. The
length of the carbon chain of the fatty acid group of biodiesel
Volatile Organic Compounds- Biodiesel
Thermodynamic Interactions Using Group
Contribution Methods.
Sashay Ramdharee, Edison Muzenda and Mohamed Belaid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f0e9debd-c8be-4624-9054-360d992bccff-151126114853-lva1-app6892/85/Sashay-Paper-1-Final-V003-1-320.jpg)
![has an effect on the solvent power of biodiesel, and the longer
the carbon chain, the weaker the solvent power. The
unsaturated fatty acid esters have a higher solvent dissolving
power than the saturated fatty esters, but the number of double
bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid esters has little effect on the
solvent power. Lastly the alcohol type also influences the
solvent power of biodiesel. The longer carbon chain of the
alcohol makes the dissolving power of biodiesel smaller.
Biodiesel is environmentally friendly, has a low volatility and
is also a renewable resource with low viscosity and good
solubility properties [4]. The largest fraction of biodiesel
consists of C16-C18 methyl esters which are readily
biodegradable. It can be produced at competitive prices [5].
C. Model Selection
Infinite dilution activity coefficients play an important role in
the analysis and design of separation processes such as
extractive and azeotropic distillation and liquid-liquid
extraction. At infinite dilution the single solute molecule is
completely surrounded by the solvent. Hence, infinite dilution
activity coefficients, (γ∞
) are useful as they give a measure of
the greatest degree of non-ideality of a mixture [6].
The most successful methods currently used for the
calculation of activity coefficients are the group contribution
methods, in which the liquid phase is considered to be a
mixture of structural groups. The most well-known and
accurate of the group contribution methods proposed is the
Universal Functional Activity Coefficient (UNIFAC) [7].
Fredenslund, Jones and Prausnitz developed the UNIFAC
model in 1975 [8]. The UNIFAC method is a semi-empirical
system for non-electrolyte activity coefficients estimation in
non-ideal mixtures. It utilizes functional groups present in the
molecules that make up the liquid mixture to compute activity
coefficients. By utilising interactions for each of the
functional groups present in the molecules, as well as some
binary interaction coefficients, the activity coefficients can be
computed [9]. In the Original UNIFAC model (Fredenslund);
the activity coefficient is expressed as the sum of the
combinatorial and residual parts respectively [10].
r
i
c
ii lnlnln
(2)
In equation (2), γcom
and γres
represent the combinatorial
(accounting for size and shape) and the residual (accounting
for energetic interactions) parts respectively. Many
modifications have been proposed to the both the residual and
combinatorial terms in order to improve the performance of
the UNIFAC model in the prediction of VLE, γ∞
and excess
enthalpies.
II. GROUP CONTRIBUTION METHODS
The group contribution method uses the principle that the
some simple aspects of structures of chemical components are
always the same in many different molecules. For example,
all organic components are built from carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen, nitrogen and halogens etc. This coupled with a
single, double or triple bonds means that there are only ten
atom types and three bond types with which we can use to
build thousands of molecules. The next more complex
building blocks of the components are the functional groups
which are themselves built of a few atoms and bonds.
Group contribution methods are used to predict the properties
of pure components and mixtures by using group properties.
This reduces the amount of data required radically. Therefore,
instead of requiring the properties of millions of components,
only the data for a few groups are required.
The group contribution concept has been used to estimate
various chemical properties of pure compounds such as
densities, heat capacities and critical constants [11]. Since the
early applications of group contribution methods, they have
been developed and applied to calculate activity coefficients
of the components in a liquid mixture. When considering
mixtures of molecules in terms of the fundamental groupings
of atoms, the following aspects should be accounted for: the
organization of the molecules in the solution and in the
standard state, the restrictions imposed on these interactions
by the organization of the groups into molecules and the
interaction of various groups which can occur in the solution
and in the standard state.
The advantage of group contribution methods is that it allows
for systematic interpolation and extrapolation of VLE data for
many chemical mixtures. It also offers an appropriate way of
predicting properties of mixtures for which experimental data
is limited. When considering such mixtures it is not necessary
to measure the intermolecular interactions as they can be
calculated from known group interaction parameters [12].
However, these are found from experimental data not
necessarily with the same molecules as those in the
investigated mixture, but containing the same functional
groups.
A. Original UNIFAC model (Fredenslund et al.,
1975)
In this model, the infinite dilution activity coefficient is
expressed as the sum of the combinatorial and residual
contributions:
r
i
c
ii lnlnln
(3)
In equation (3),
c
iln is the combinatorial part accounting for
differences in the size and shape of the molecules and
r
iln is
the residual that accounts mainly for the effects arising from
energetic interactions between groups present in solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f0e9debd-c8be-4624-9054-360d992bccff-151126114853-lva1-app6892/85/Sashay-Paper-1-Final-V003-2-320.jpg)
![For the combinatorial part:
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
ic
i q
z
xx
1ln
2
1lnln (4)
In equation (4), i , i is the molar weighted segment and area
fractional components for the ith
molecule in the total system, z
being the coordination number respectively. ri and qi are
calculated from the group surface area and volume
contributions as in (6) and (7) respectively
j
jj
ii
i
rx
rx
(5)
k
k
i
ki Rvr (6)
k
k
i
ki Qvq (7)
j
jj
ii
i
qx
qx
(8)
The residual part is calculated as in (9)
)ln(lnln i
kk
k
i
k
r
i v (9)
m
n
nmn
mkm
m
mkmkk Q
ln1ln (10)
In (10), k is the activity of an isolated group in a solution
consisting only of molecules of type i. The calculation of the
residual activity coefficient ensures that the condition for the
limiting case of a single molecule in a pure component
solution is obeyed by ensuring that the activity is equal to 1.
m is the summation of the area fraction of group m, over all
the different groups and is somewhat similar in form, but not
the same as i . mn is the group interaction parameter and
is a measure of the interaction energy between groups. Xn is
the group mole fraction.
In (11), m is the group parameter
n
nn
mm
m
xQ
xQ
(11)
(12), mx is the group mole fraction.
nj
j
i
n
j
j
i
m
m
xv
xv
x
,
(12)
mn ,
the group interaction parameter is calculated using (13)
T
amn
mn exp (13)
In (13), mna represents the net energy of interaction between
groups’ m and n and has the units of SI Kelvin [13].
B. Modified UNIFAC (Larsen et al., 1981)
Larsen presented a modified version of the UNIFAC (Lyngby
modified UNIFAC) in which the Staverman-Guggeheim
combinatorial part was changed to a Flory-Huggings
combinatorial part with a modified volume fraction. He also
introduced temperature dependant group interaction
parameters. This model allows for the simultaneous
presentation of VLE and excess enthalpies. It is also capable
of presenting liquid-liquid equilibria using the modified
UNIFAC-VLE parameters with the same quality as the
original UNIFAC with LLE based parameters of Magnusses,
1982 [14]. The combinatorial term and the group interaction
parameters of the residual part were modified according to
(14) and (15):
i
i
i
icomb
i xx
1lnln (14)
In (14), i the segment fraction of component (i) calculated
from (15).
jj
ii
i
rx
rx 3
2
(15)
The interaction parameter mn in the residual part is
calculated from (16).
T
TT
T
T
TcTTba mnmnmn
mn
)ln()(
exp
0
0
0
(16)
In (16), 0T is taken as a reference temperature equal to
298.15K (25o
C)
C. Modified UNIFAC (Bastos et al., 1988)
The Modified UNIFAC (Bastos et al., 1988) only modifies the
combinatorial part of the Original UNIFAC of Fredenslund et
al, 1975 [15]
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
ic
i q
z
xx
1ln
2
1lnln (17)
In (17), i is calculated from (18):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f0e9debd-c8be-4624-9054-360d992bccff-151126114853-lva1-app6892/85/Sashay-Paper-1-Final-V003-3-320.jpg)

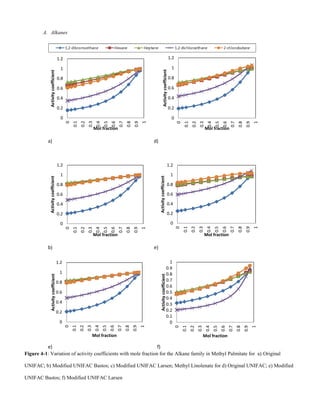
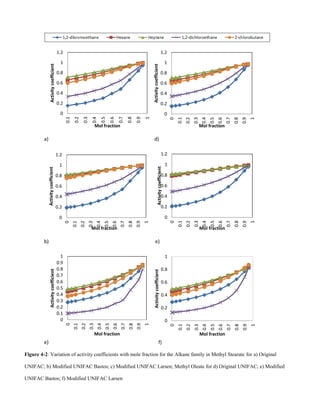


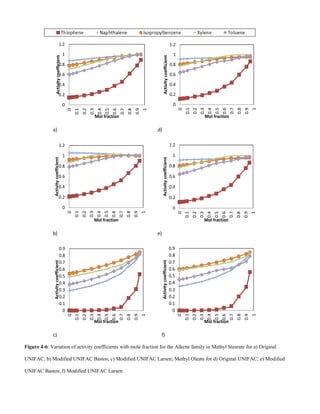
![C. Alkenes
The low activity coefficients of alkene VOCs in Figs 4-5 and
4-6 are due to the polarizing effect caused by the delocalised
electron cloud around the benzene molecule. Spectroscopic
evidence shows that all bond lengths are equal and
intermediate between single and double bond lengths and that
the benzene molecule is flat [16]. The solubility of alkenes
decrease with increase in VOC molecular weight due to the
increase in Van der Waals forces between solute – solute
interactions, Figs 4-5 and 4-6.
-Interactions of alkenes in saturated/unsaturated esters
Solubility decreases with increase in unsaturation in the ester
hydrocarbon chain, Figs 4-5 and 4-6. A lot of energy is
required for solute – solvent bond formation. The low
solubility can also be attributed to cis-formation of the
unsaturated double bonds.
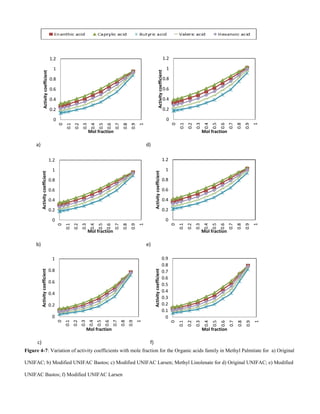
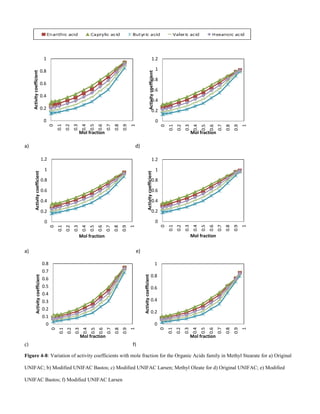
D. Organic acids
For organic acids, solubility decreases with increase in VOC
molecular weight, Figs 4-7 and 4-8. This could be due to the
increase in Van der Waals forces bewteen solute – solute
molecules. Hence more energy is required to overcome the
the attractive forces to allow for solute – solvent interactions.
Solubility also decreases with an increase in unsaturation of
the solvent.
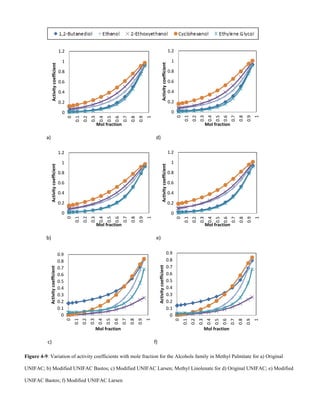
E. Alcohols
An increase in Van der Waals forces of attraction with
increased alcohol chain length accounts for the decrease in
solubility with increase in solute molecular weight, Figs 4-9
and 4-10.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f0e9debd-c8be-4624-9054-360d992bccff-151126114853-lva1-app6892/85/Sashay-Paper-1-Final-V003-10-320.jpg)
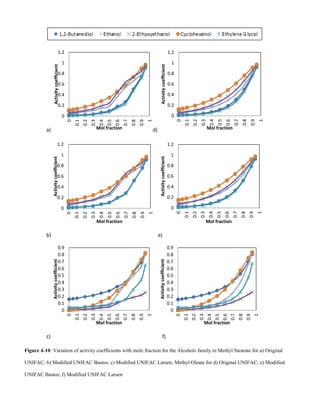
![V.CONCLUSION
This paper discusses the interactions of 25 volatile organic
compounds with biodiesel. The Original UNIFAC:
Fredenslund et al, 1975; Modified UNIFAC: Bastos et al,
1988 and the Modified UNIFAC (Larsen et al., 1981) were
used to compute the desired phase equilibria. Biodiesel was
found to be thermodynamically suitable for the physical
absorption of the selected VOCs.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors wish to acknowledge University of Johannesburg
and the CSIR for the financial and technical support.
REFERENCES
[1] N.P. Cheremisinoff,. Handbook of Air Pollution Prevention and
Control, Elsevier Science, 2002
[2] Biodiesel [online]. 2012 [cited 2012 Sept]. Available from URL:
http://www.wikipedia.com
[3] Jianbo H, Zexue D, Zhong Tang, E Min. Study on the Solvent Power of
a New Green Solvent: Biodiesel. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 7928-
7931
[4] K. Bay, H. Wanko, J. Ulrich,. Absorption of Volatile Organic
Compounds in Biodiesel: Determination of Infinite Dilution Activity
Coefficients by Headspace Gas Chromatography, Chem. Eng. Res.
Des,2006, Vol. 84, 22–27
[5] Wilson A, Canas M, Uriel EG, Julian D., Comparison of different cubic
equations of state and combination rules for predicting residual
chemical potential of binary and ternary Lennard–Jones mixtures:
Solid-supercritical fluid phase equilibria. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2005,
42–50
[6] Voustas E.C, D.P Tassios., Prediction of infinite dilution activity
coefficient in binary mixtures with the UNIFAC. A critical evaluation.
Ind Eng. Chem Res.1996,35,1438-1445
[7] Herber RP, Soares RP,. Assessing the reliability of predictive activity
coefficient models for molecules consisting of several groups. Braz. J.
Chem Eng 2013, Vol 30, 1
[8] Activity coefficient [online]. 2012 [cited 2012 Sept]. Available from
URL: http://www.wikipedia.com
[9] H.K Hansen, P. Rasmussen, A. Fredenslund, M. Schiller, J. Gmehling,.
Vapor-Liquid Equilibria by UNIFAC Group Contribution. 5. Revision
and Extension, Ind. Eng. Chem., 1991, Vol. 30,2355–2358
[10] Fredenslund, A. Jones, R. L., Prausnitz,. J. M. Group Contribution
Estimation of Activity Coefficients in Non-ideal Liquid Mixtures.
AIChE J. 1975, 21, 1086
[11] Soave Redlich Kwong EOS- Department of Energy and Mineral
processing. [online]. 2012 [cited 2012 Sept]. Available from URL:
http://www.eme.psu.edu
[12] Somaieh S, Marc A. Dub,. Biodiesel: a green polymerization solvent.
The Royal Society of Chemistry, Green Chem., 2008, 10, 321–326
[13] Larsen, B. L. Rasmussen, P. Fredenslund,. UNIFAC Parameter Table
for Prediction of Liquid-Liquid Equilibria. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process
Des. Dev. 1981, 20, 331
[14] H.O. Paksoy, S. Örnektekin, B. Bilgin, Y. Demirel,. The Performance
of UNIFAC and Related Group Contribution Models Part I. Prediction
of Infinite Dilution Activity Coefficients, Thermochimica Acta, 1996,
Vol. 287, 235–249
[15] Bastos, J.C. Soares,. M. E., Medina, A. G. Infinite Dilution Activity
Coefficients by UNIFAC Group Contribution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.
1988, 27, 116
[16] Graham Solomoins TX,. Organic Chemistry Solomons 6th Edition.
August, 1995, Chap 14, 614-654
S. Ramdharee: The author was born in 1984 in
Newcastle, Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa. This
author became a member of ECSA (Engineering
Council of South Africa) in 2010. He successfully
completed a NDip: Chemical Engineering at Durban
University of Technology, Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa in 2007. After
which he pursued a BTech: Chemical Engineering at the same institution in
2008, graduating Cum Laude, with the Deans Merit award for being the top
student in year 2008, and also received the award for Mathematics, Statistics
and Physics Year 2008. Currently he is studying towards a MTech: Chemical
Engineering at the University of Johannesburg, Gauteng, South Africa and
completing the PMP®
certification with the American based Project
Management Institute.
He has worked at African Amines: Junior production engineer; Karbochem
ltd: Junior projects engineer; International Furan Technology: Chemical
engineer; Sasol Synfuels: Senior as-built auditor; Sasol Synfuels: Process
technologist; National Cleaner Production Centre of South Africa: Regional
project manager: Energy systems optimization.
Mohamed Belaid obtained Msc Chemical
Engineering, UKZN South Africa (2001), BSC
Industrial Chemical Engineering, Engineering of
organic processes (1994), University of Blida,
Algeria, currently is doing PhD at Wits University
(South Africa). Mohamed is a senior lecturer at the
University of Johannesburg, worked as a lecturer at
the University of Kwazulu Natal for over 8 years, a
quality control Engineer for Energy Engineering PTY
(South Africa) for two years and Elangeni oil and soap (South Africa) for a
period of two years, process Engineer (SAIDAL, antibiotic company, Algeria)
for one year.
Mr. Belaid is a member of SAIChE (2003, South Africa institute of
Chemical Engineers) and He is a research member at the department of
Chemical Engineering, authored and contributed to various publications, both
journals and conferences proceedings in environmental engineering,
separation processes, mineral processing, fluidized beds, activated carbon and
engineering Education
Edison Muzenda is a Full Professor of Chemical
and Petroleum Engineering, and Head of
Chemical, Materials and Metallurgical
Engineering Department at Botswana
International University of Science and
Technology. He is also a Visiting Professor in the
Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of
Engineering and Built Environment, University of
Johannesburg. He was previously a Full Professor
of Chemical Engineering, the Research and
Postgraduate Coordinator as well as Head of the Environmental and Process
Systems Engineering and Bioenergy Research Groups at the University of
Johannesburg. Professor Muzenda holds a PhD in Chemical Engineering from
the University of Birmingham, United Kingdom. He has more than 16 years’
experience in academia which he gained at various institutions including the
National University of Science and Technology, Zimbabwe, University of
Birmingham, University of Witwatersrand, and most importantly the
University of Johannesburg. Through his academic preparation and career, He
has held several management and leadership positions such as member of the
student representative council, research group leader, university committees’
member, staff qualification coordinator as well as research and postgraduate
coordinator. Edison’s teaching interests and expertise are in unit operations,
multi-stage separation processes, environmental engineering, chemical
engineering thermodynamics, professional engineering skills, research
methodology as well as process economics, management and optimization. He
is a recipient of several awards and scholarships for academic excellence. His
research interests are in green energy engineering, integrated waste
management, volatile organic compounds abatement and as well as phase
equilibrium measurement and computation. He has contributed to more than
280 international peer reviewed and refereed scientific articles in the form of
journals, conferences books and book chapters. He has supervised more than
30 postgraduate students and over 250 Honours and BTech research students.
He serves as reviewer for a number of reputable international conferences and
journals. Edison is a member of several academic and scientific organizations
including the Institute of Chemical Engineers, UK and South African Institute
of Chemical Engineers. He is an Editor for a number of Scientific Journals
and Conferences. He has organized and chaired several international
conferences. He currently serves as an associate Editor of the South African](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f0e9debd-c8be-4624-9054-360d992bccff-151126114853-lva1-app6892/85/Sashay-Paper-1-Final-V003-17-320.jpg)
