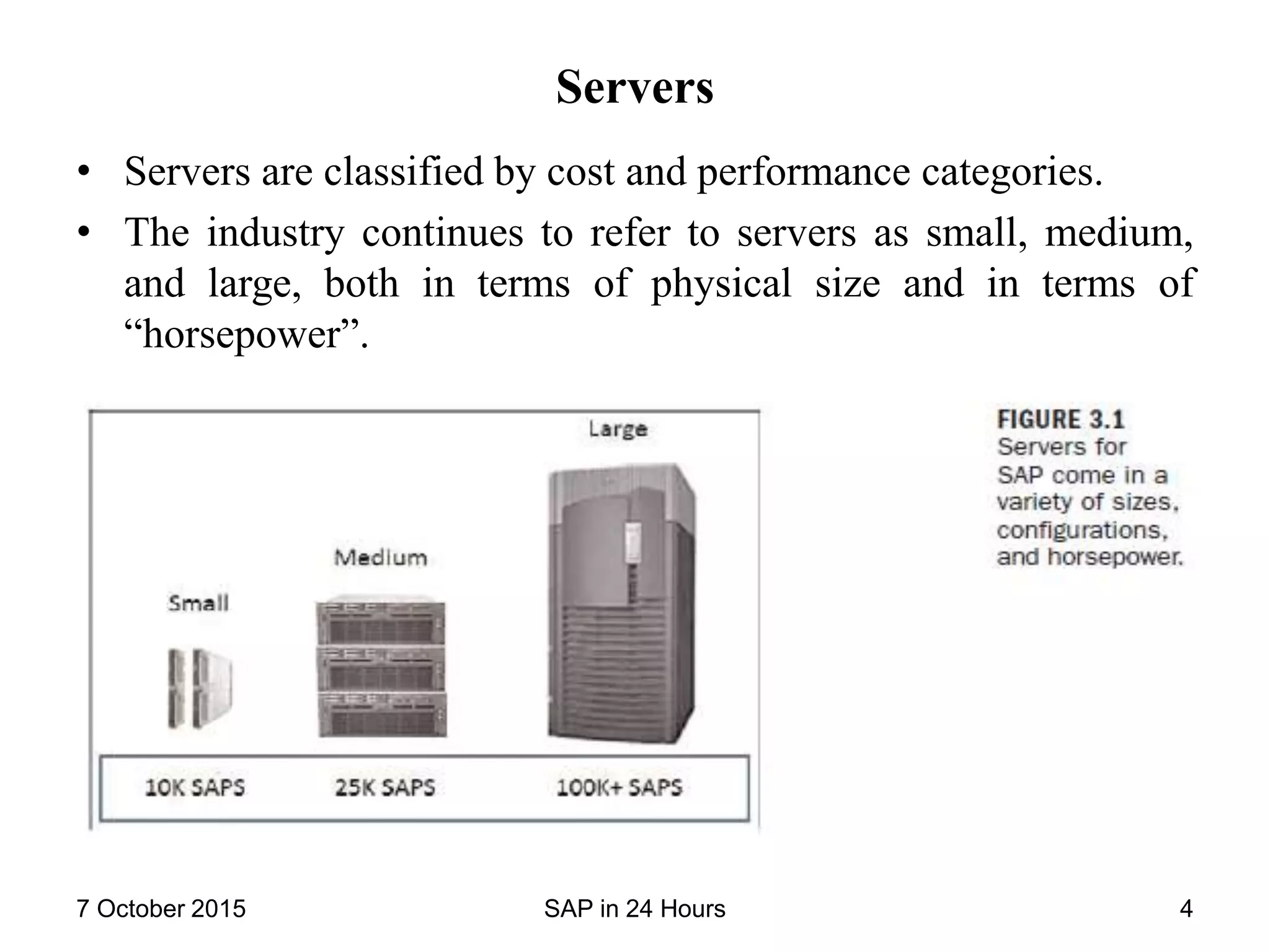
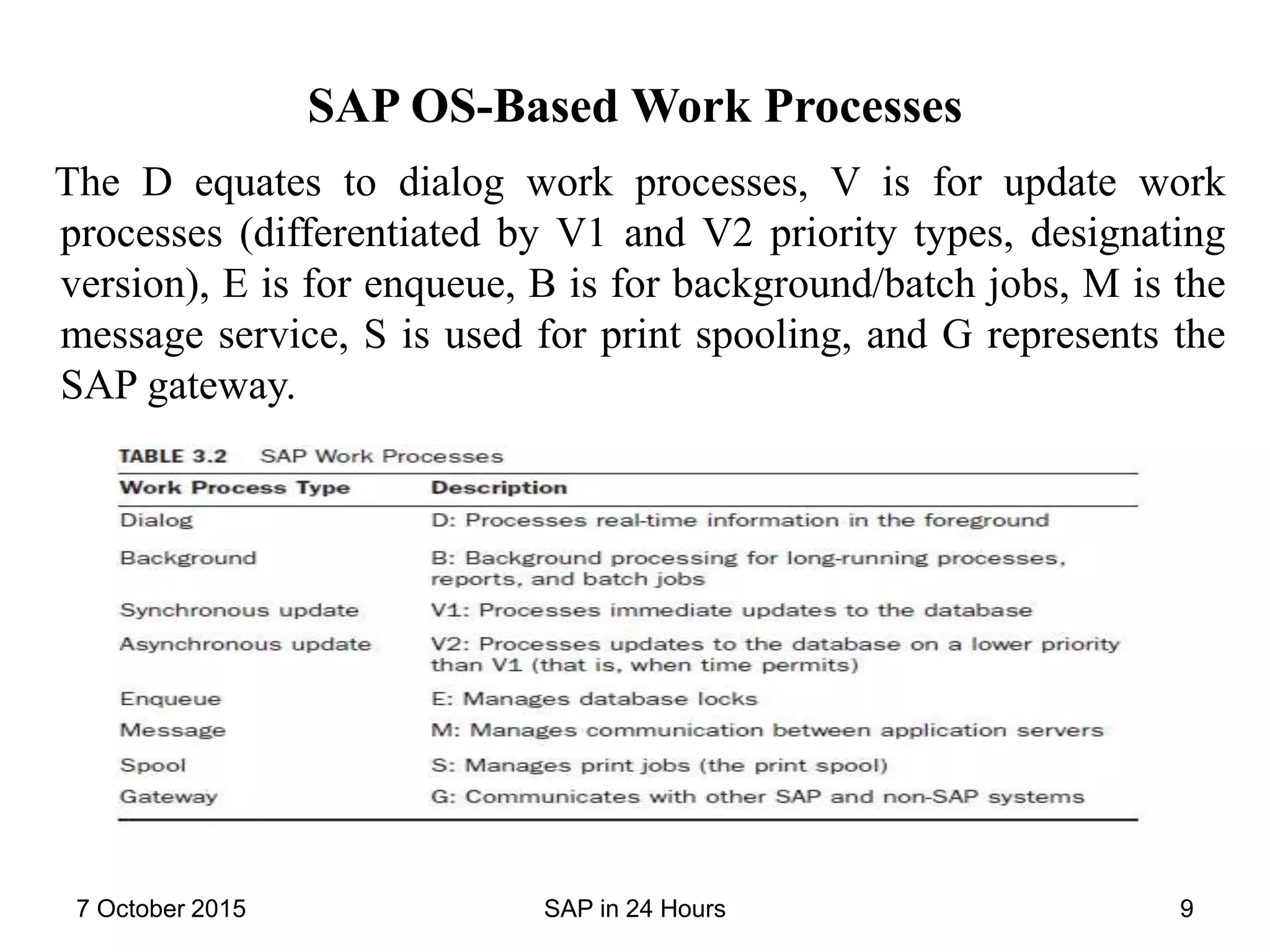
The document provides an overview of SAP technology basics including hardware, operating systems, databases, and application technologies that underpin SAP systems. It discusses the layers of technology such as servers, storage, networks, operating systems, databases, and SAP-specific processes and profiles. It also summarizes the SAP implementation process including configuration teams, integration, testing, security, and accessing the new SAP system through the SAPGUI or web browser.