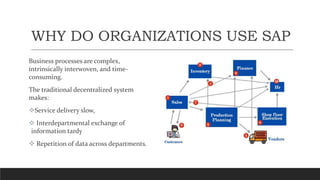
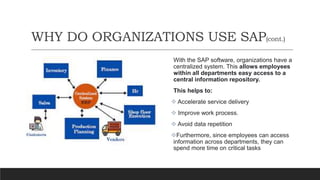
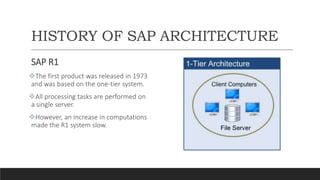
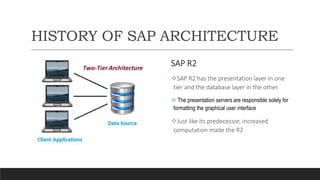
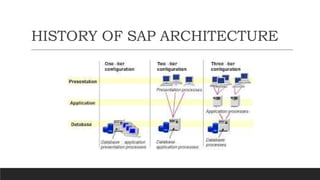
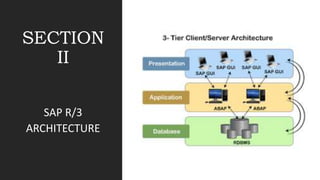
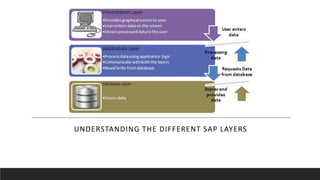
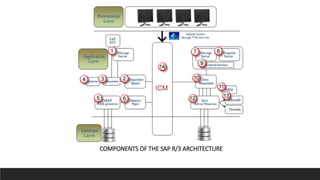
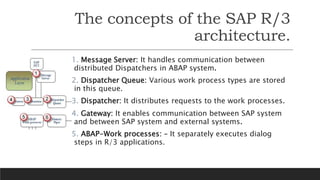
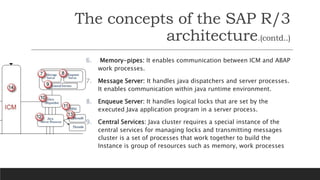
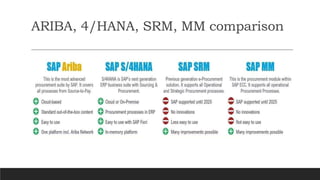
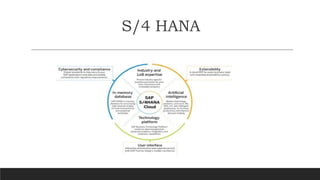
SAP is an ERP software that offers a centralized system for businesses to manage processes. It has evolved over time from a one-tier architecture to a multi-tier system with presentation, application, and database layers. The application layer is where processing occurs and includes work processes that are distributed to by dispatchers. Key SAP modules include SRM for procurement, ARIBA which SAP acquired, SOLMAN for application management, and S/4HANA which is SAP's next generation ERP that leverages new technologies.