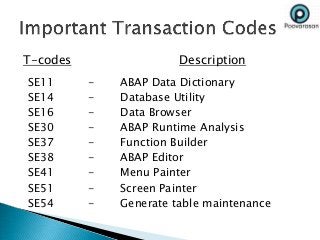
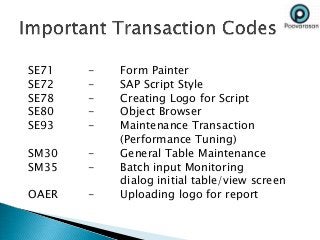
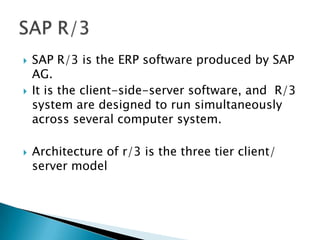
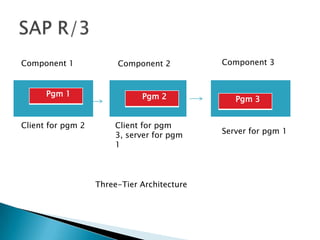
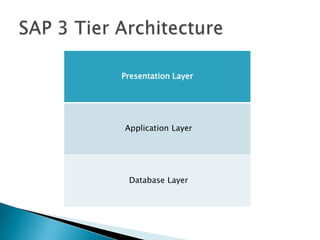
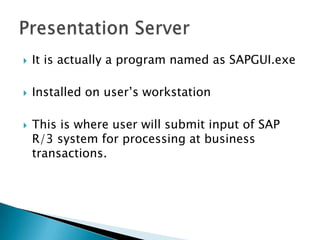
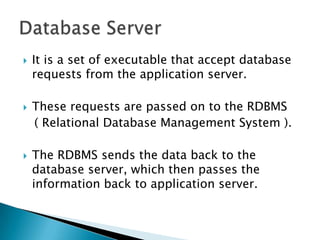
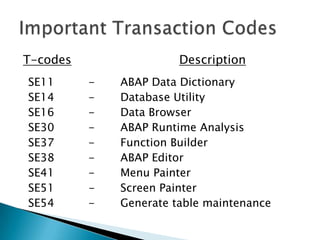
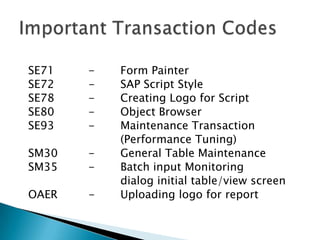
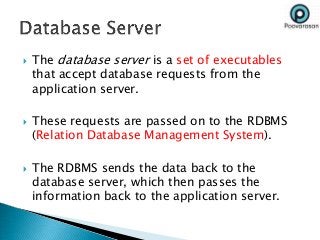
ERP software combines data from various business functions into a single system with a unified database and simplified infrastructure. SAP R/3 is a major ERP software from SAP. The SAP GUI runs on user workstations and provides an interface for submitting transactions. An application server processes requests and communicates with the database server which accesses the relational database. SAP consists of key business modules like financials, human resources, materials management and more. Common transaction codes in SAP include SE11 for data dictionary, SE30 for runtime analysis and SM30 for table maintenance.




![ Financials and controlling [FICO]
Human Resources [HR]
Materials Management [MM]
Sales and Distribution [SD]
Production Planning [PP]
Quality Management [QM]
Plant Maintenance [PM]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofsap-140319135205-phpapp01/85/Basics-of-sap-13-320.jpg)