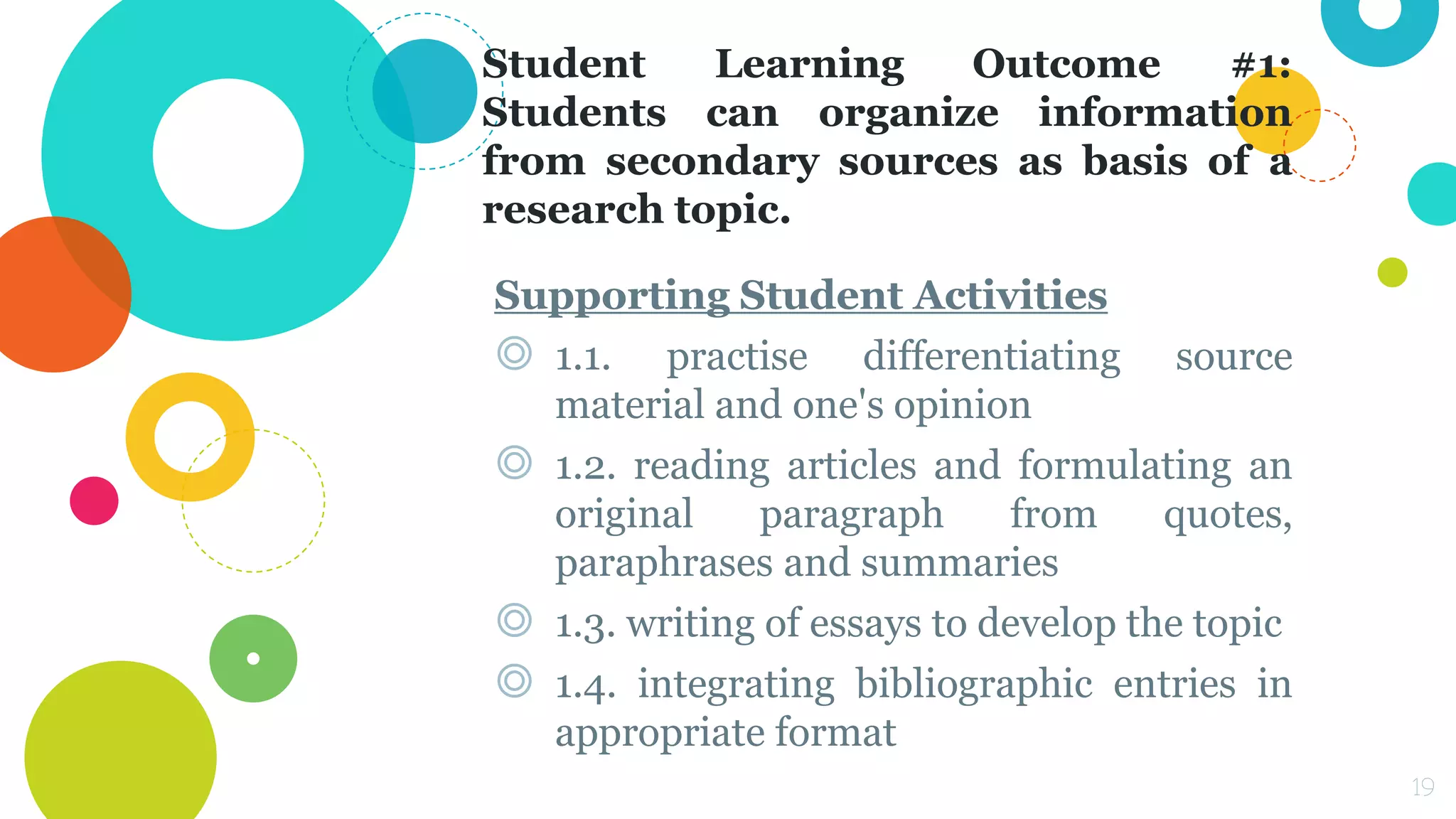
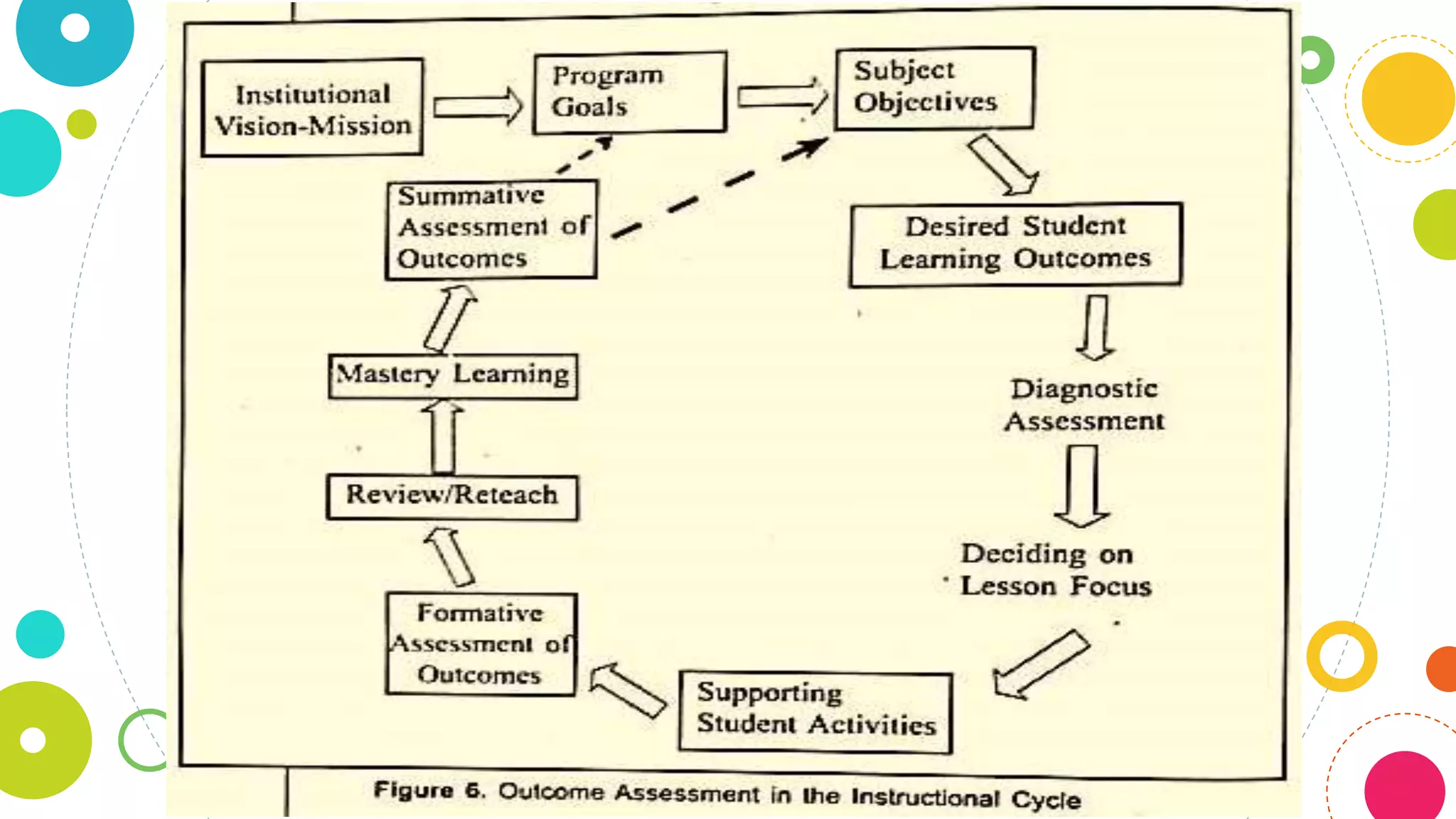
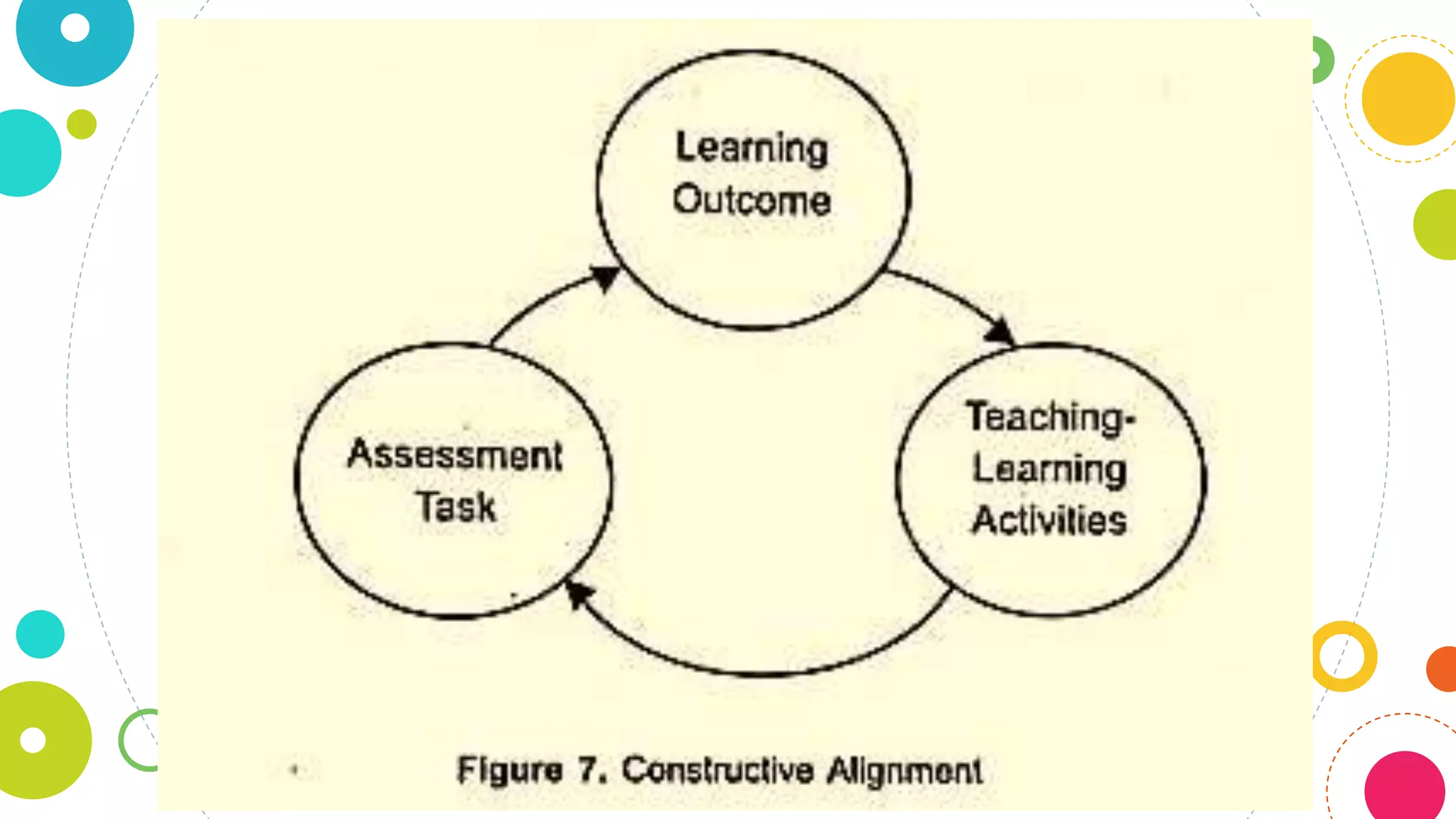
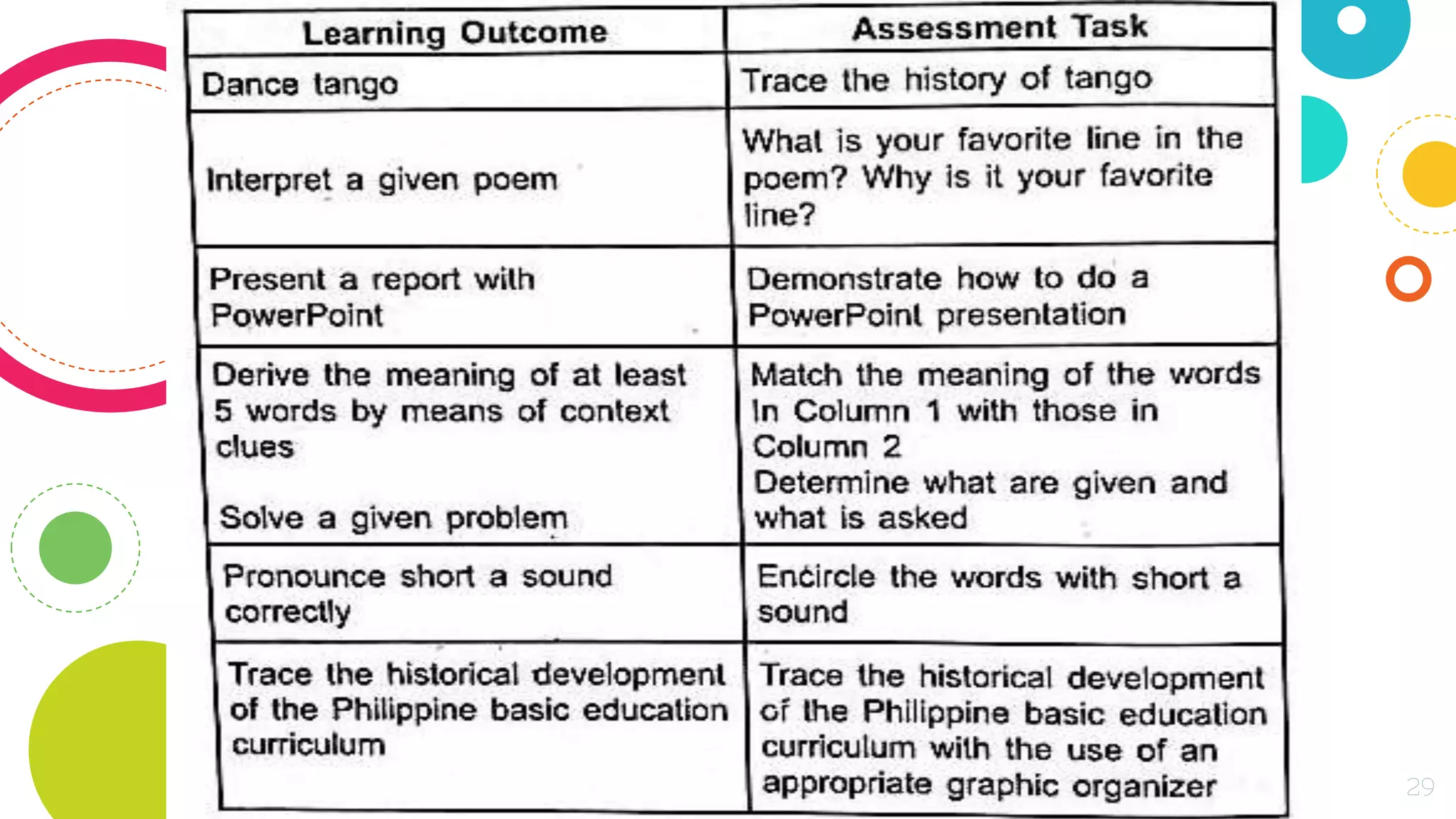
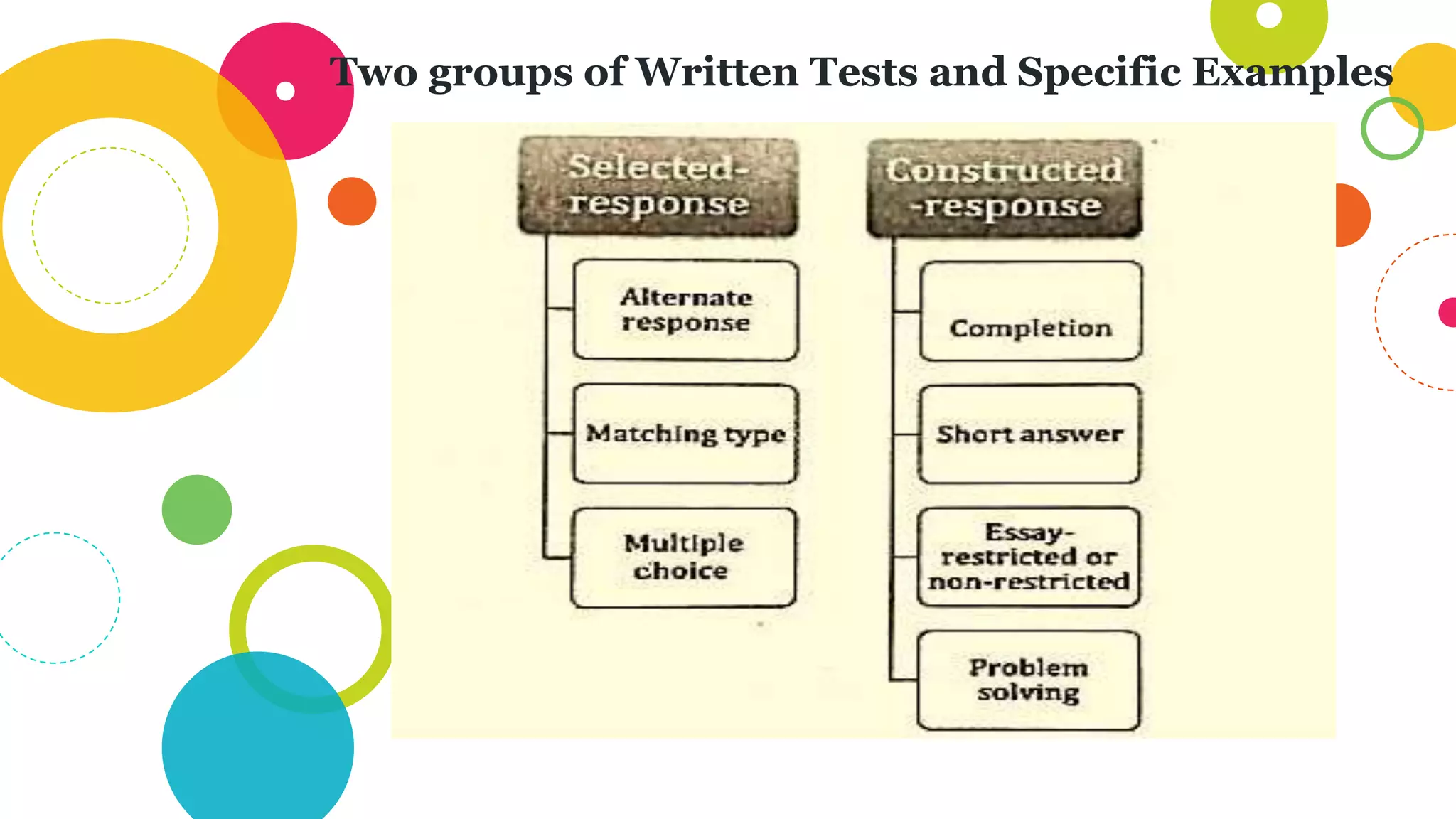
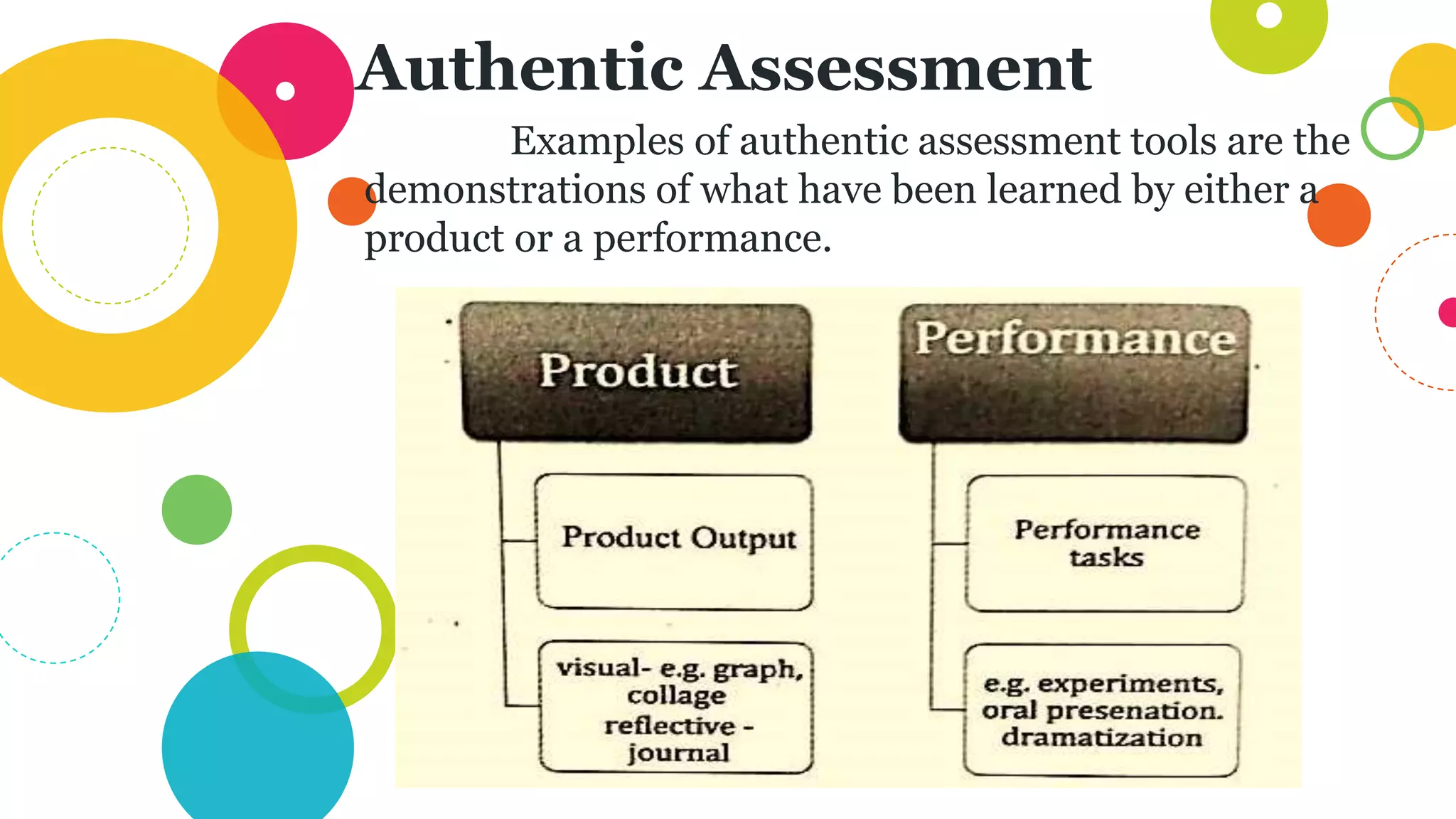
The document discusses assessing student learning outcomes through various assessment methods and tools. It begins by defining outcome assessment as gathering information on whether instruction is achieving desired student learning outcomes. It then provides 13 principles of good practice in assessing outcomes, such as ensuring alignment between outcomes, instruction, and assessment. Various assessment methods and tools are described, including traditional paper-and-pencil tests and authentic assessments involving student products or performances. The concept of constructive alignment between outcomes, instruction, and assessment tasks is also explained.