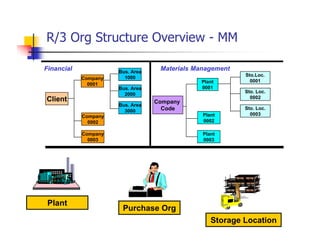
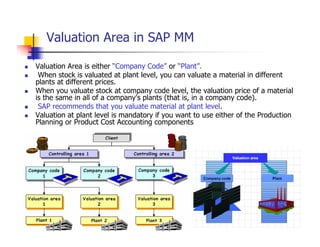
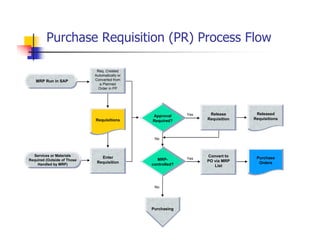
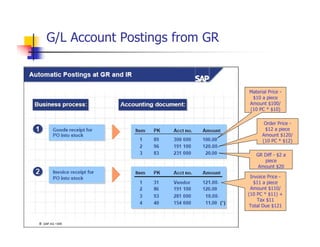
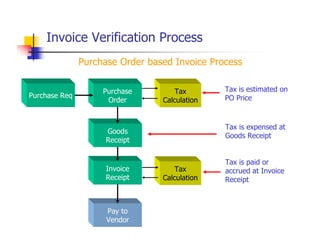
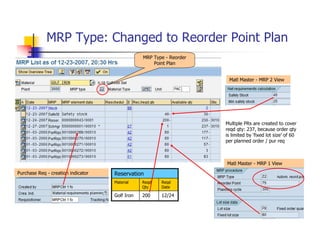
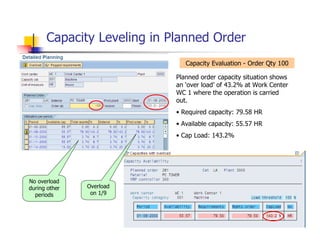
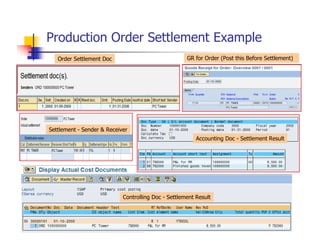
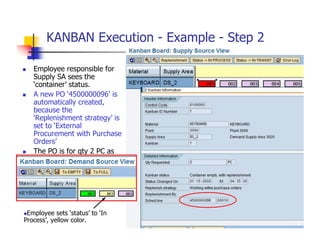
1) The document provides an overview of SAP MM and PP course material covering topics like organizational structure, valuation areas, purchase requisition process, goods receipt postings, invoice verification, MRP vs CBP, reorder point planning, configurable BOMs, capacity leveling, and production order settlement.
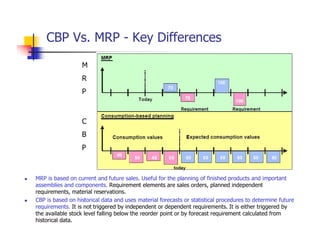
2) Key differences between MRP and CBP are outlined, with MRP being based on current and future sales/requirements, while CBP uses historical data and forecasts.
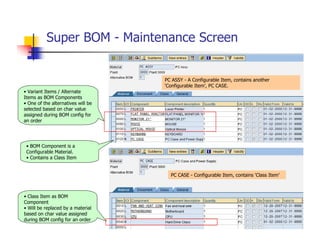
3) Configurable BOMs allow for class items and variant/alternate items as components, with characteristics determining which are selected during configuration.