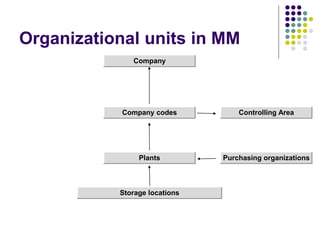
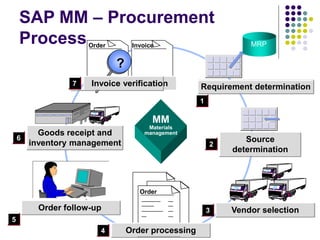
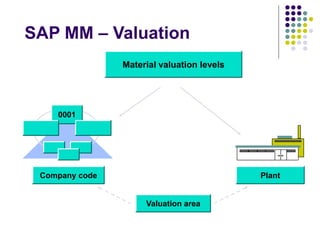
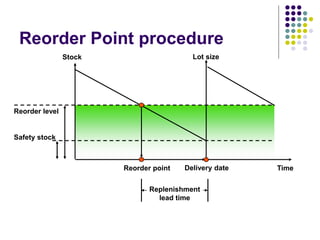
This document provides an overview of SAP MM (Materials Management) including key concepts like the procurement process, inventory management, invoicing, valuation, materials requirements planning, and implementation milestones. It describes the basic functions of MM like master data setup, purchasing documents, goods movement, invoice verification, and price planning. It also gives examples of how procurement is different for stock and non-stock items, and how materials requirements are planned and replenished through purchase orders and requisitions.