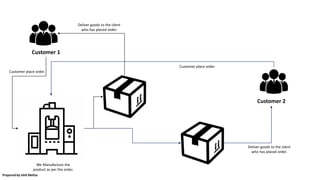
This document provides an overview of various ERP concepts using a business case scenario involving warehouse resupply, re-ordering rules, make to order, make to stock, bill of materials, advance shipping notices, pricing strategies, returns management, and automatic accounting journal entries. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these ERP concepts to address organizational challenges and optimize business processes. The document is prepared by Ishit Mehta and presents practical examples and diagrams to illustrate the principles discussed.

![Topics Covered –
• Warehouse Re-Supply.
• Re-ordering rules.
• Make to Order.
• Make to Stock.
• BOM – Bill of Materials.
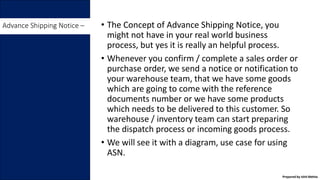
• Advance Shipping Notice.
• Price List. [Vendor / Customer]
• Returns / Scrap Management.
• Automatic Journal / Voucher entry posting.
• COGS (Cost of Goods Stock Entry).
• Multi Organization.
Prepared by Ishit Mehta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericconceptoferp-190828115427/85/Generic-concept-of-erp-2-320.jpg)





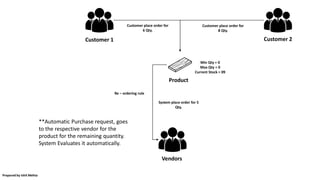

![SFG – BOM 1 [Table Head]
Raw Material –
1. Wood = 2 m
SFG – BOM 2 [Table Leg]
Raw Material –
1. Wood = 1 m
SFG – BOM Main [Table]
Raw Material –
1. Table Leg = 4 unit
2. Table Head = 1 unit
3. Glue = 1 unit
4. Screws = 8 units
5. Nut = 8 units
** Here it is a multi level BOM, where if you consider total wood consumed for one table is 6 meter. To
manufacture Table you require two other SFG. Such scenario is also know as Phantom BOM.
Prepared by Ishit Mehta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericconceptoferp-190828115427/85/Generic-concept-of-erp-13-320.jpg)
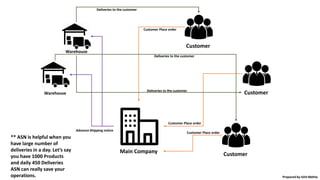
![• So we are aware, that sometime prices may change
as per the region or as per the quantity or as per
the client type. So every ERP has a concept of Price
list. While you can set both Purchase price list from
the vendors and you can also set sales price list for
the customers.
• Below are some of the examples, how can we use
ERP price lists –
• For one product you can have multiple price like Dealer /
Distributor price, & you can have customer price. Let’s
Dealer price is 10 USD & Customer price is 15 USD.
• We can also set Margin based Sales Price, for a product
or a Product Category, So for example we have one
product category as LG home appliance where we have
15% of margin for all LG Home appliance product. Once
you set cost price for any product in this category it will
add 15% into CP & will generate SP (Sales Price).
• So there can be many ways you can, setup pricing into
the ERP system.
Price List [Vendors /
Customers] –
Prepared by Ishit Mehta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericconceptoferp-190828115427/85/Generic-concept-of-erp-16-320.jpg)