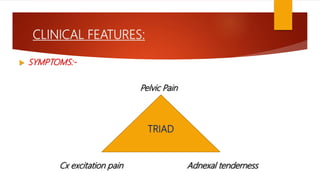
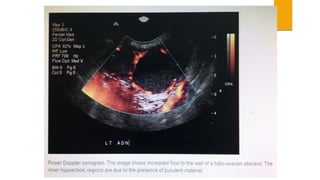
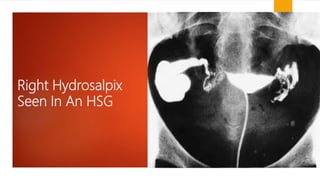
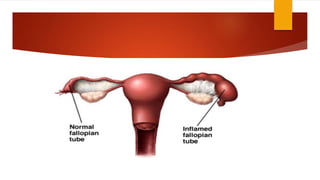
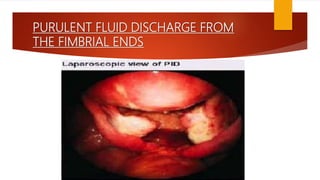
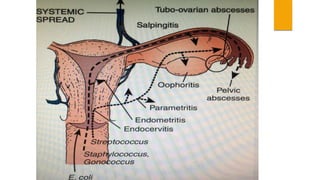
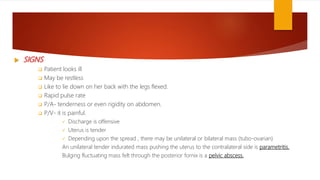
This document provides an overview of acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). It discusses the definition, epidemiology, risk factors, microbiology, pathogenesis, stages, clinical features, diagnostic criteria, investigations, management, complications, prevention of reinfection, and follow up of PID. PID is caused by the ascending spread of microorganisms from the cervix to the upper genital tract organs. It is commonly caused by sexually transmitted organisms like N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis. Clinical features include lower abdominal and pelvic pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge. Management involves antibiotic therapy based on CDC guidelines to treat infection and prevent complications like infertility.




























![TO PREVENT REINFECTION:
1. Educating the patient to avoid reinfection and the potential hazards of it.
2. The patient should be warned against multiple sexual partners.
3. To use contraception[ barrier].
4. The sexual partner or partners are to be traced and properly investigated to
find out the organisms and treated effectively.
If sexual partner have got non gonococcal urethritis, they should be treated
with
- tetracycline 500mg 6 hourly or Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 7 days.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutepelvicinflammatorydisease-180806154337/85/Acute-pelvic-inflammatory-disease-48-320.jpg)








![TREATMENT:-
[PROPHYLACTIC+CURATIVE]
PROPHYLAXIS:-
a) To maintain asepsis and antiseptic measures during labour.
b) To avoid traumatic and difficult vaginal deliveries.
c) To use prophylactic antibiotic when labour is delayed following
rupture of membranes or when there are intrauterine
manipulations like forceps or manual removal of placenta.
d) To encourage family planning acceptance to prevent the
unwanted pregnancies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutepelvicinflammatorydisease-180806154337/85/Acute-pelvic-inflammatory-disease-59-320.jpg)
![TREATMENT:-
[PROPHYLACTIC+CURATIVE]
CURATIVE:-
a) HOSPITALIZATION
b) TRIPLE SWABS are to be taken- one from high
vagina, one from the endocervix and the third from
the urethra and are sent fro culture , drug sensitivity
and gram staining.
Swabs are to be taken prior to bimanual
examination.
c) VAGINAL and RECTAL examinations are then made
to note the extent of pelvic infection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutepelvicinflammatorydisease-180806154337/85/Acute-pelvic-inflammatory-disease-60-320.jpg)








![TREATMENT:
[PROPHYLACTIC + CURATIVE]
PROPHYLACTIC:
-preoperative cleaning of vagina with antiseptic lotion,
-perfect hemostasis during surgery and
-leaving behind the vault open in infected cases could reduce the postoperative
infection.
-Metronidazole 500mg IV 8hrly and ceftriaxone 1g IV given during the operation
and 1-2 doses after the operation.
CURATIVE :
Antibiotics and drainage of pus through the vault.
Adnexal abcess requires urgent exploration and removal of the infected mass.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutepelvicinflammatorydisease-180806154337/85/Acute-pelvic-inflammatory-disease-69-320.jpg)