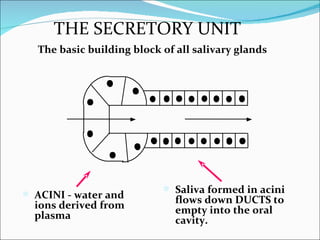
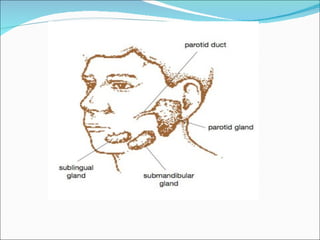
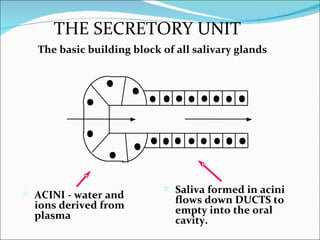
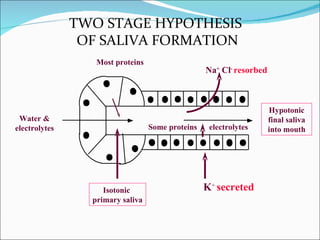
The document summarizes key information about saliva, including its composition and functions. Saliva is produced in the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands and contains water, electrolytes, enzymes, mucus, and immunoglobulins. It begins digestion of carbohydrates and lipids, lubricates food for swallowing, and protects teeth from decay through its antibacterial properties and pH buffering. Saliva production is controlled by both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems.