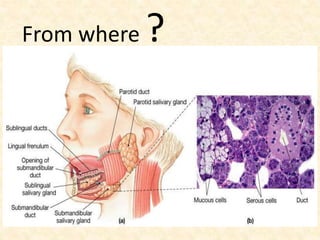
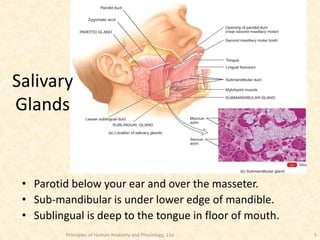
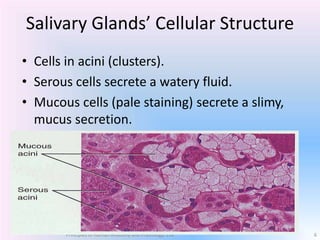
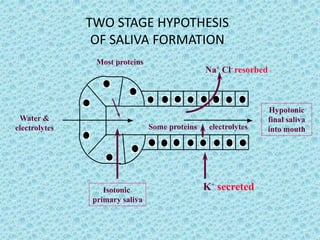
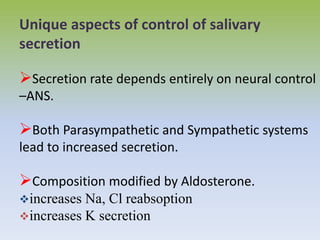
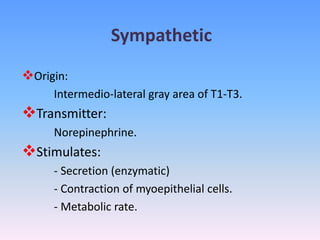
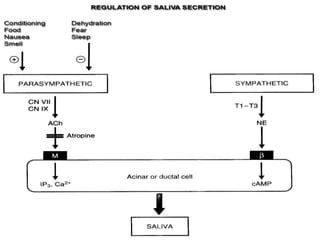
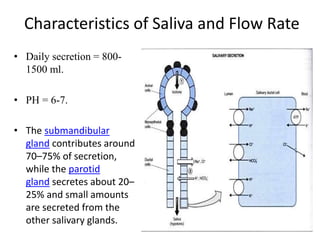
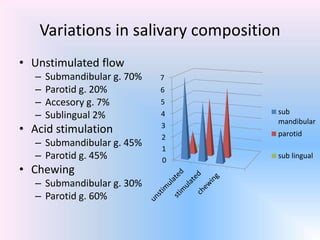
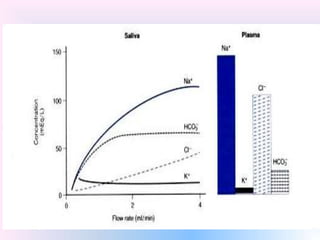
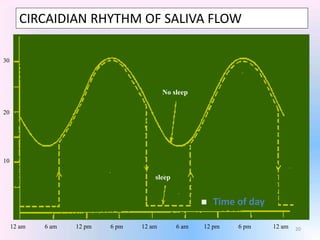
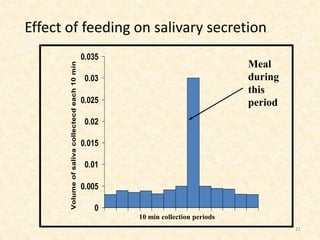
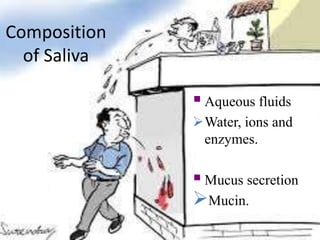
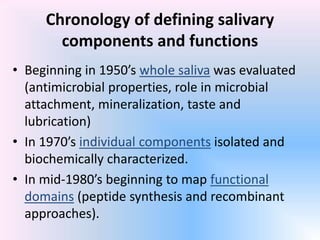
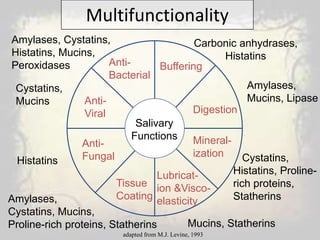
Saliva is produced in salivary glands and contains water, enzymes, mucus and antibacterial components. It has several functions including lubrication, digestion of carbohydrates, remineralization of teeth, and maintaining pH balance. Saliva production is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and varies throughout the day, increasing during eating. The major salivary glands are the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. Saliva supports oral health through its antibacterial properties and ability to regulate the pH environment in the mouth.