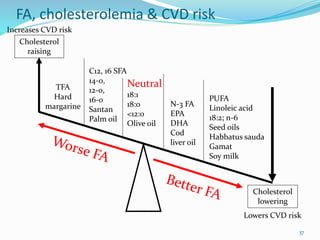
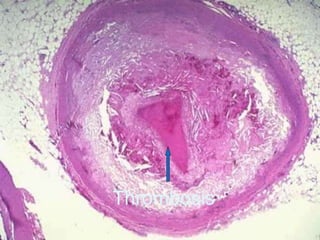
This document summarizes information about myocardial infarction (MI), also known as a heart attack. It discusses the causes of MI as being due to blockage of the coronary arteries, usually from atherosclerosis. It describes the symptoms of MI and risk factors such as age, sex, genetics, hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking. Treatment options for MI mentioned include coronary artery bypass graft surgery, percutaneous coronary intervention such as angioplasty and stenting, and fibrinolysis to break up blood clots in the heart.






![Myocardial Infarction
Women may experience
fewer typical symptoms
than men, most
commonly shortness of
breath, weakness, a
feeling of indigestion,
and fatigue.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myocardialinfarctionfpa-170315100813/85/Sakit-Jantung-7-320.jpg)
![Myocardial Infarction
] A sizeable proportion of
myocardial infarctions
(22–64%)[3] are "silent",
that is without chest
pain or other symptoms
Common - Elderly,
Diabetes Mellitus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myocardialinfarctionfpa-170315100813/85/Sakit-Jantung-8-320.jpg)