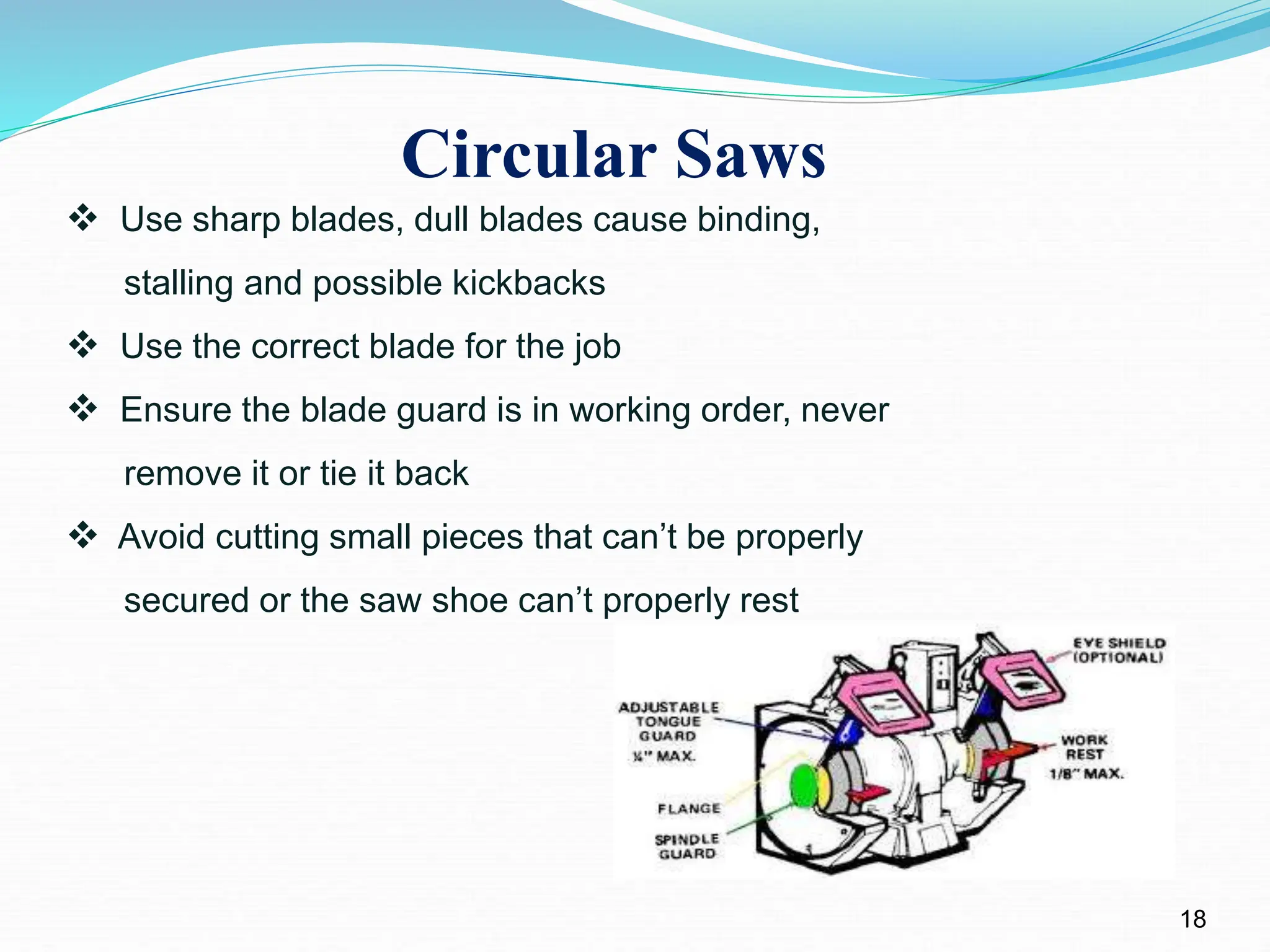
The document outlines the differences between hand tools and power tools, emphasizing that hand tools rely on human force while power tools require an external power source. It details essential safety rules for using both types of tools, including five basic precautions applicable to all, and specific guidelines for various hand tools such as hammers, chisels, and saws. Additionally, it highlights power tool safety measures and common hazards stemming from improper tool use or maintenance.