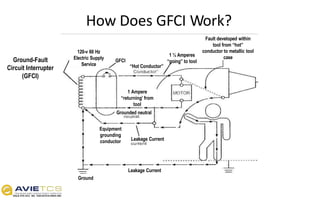
Workers using hand and power tools may be exposed to flying or falling objects, dust, fumes, and electrical or explosive hazards. Proper safety precautions include inspecting tools for damage, using the right tool for each job, guarding moving parts, wearing personal protective equipment, and receiving training on hazardous tools. Power tools like saws, drills, and sanders require additional precautions such as disconnecting tools when not in use, avoiding accidental starting, and securing workpieces.