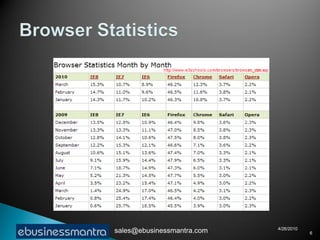
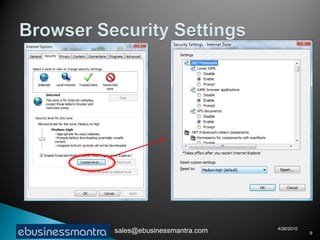
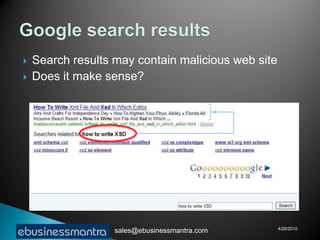
A web browser is software that displays web pages and allows users to navigate between them. It takes URL requests, communicates with web servers to retrieve content, and renders received files and scripts to display webpages to the user. Common functions of browsers include fetching webpages and embedded content like images, running client-side scripts, and handling cookies and other data used to maintain state across webpage visits.