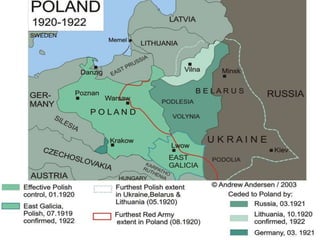
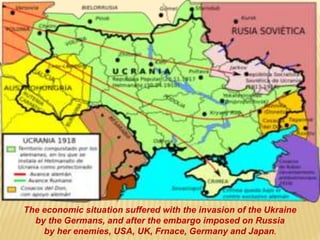
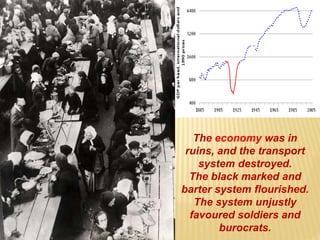
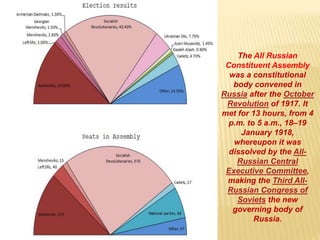
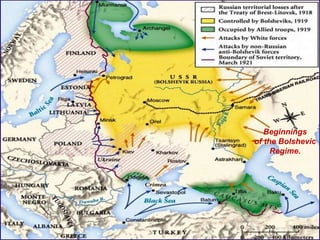
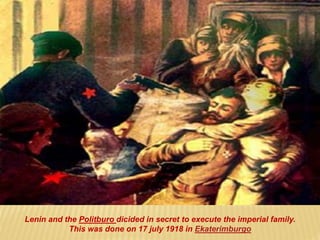
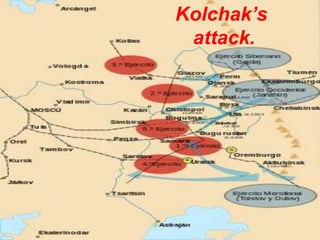
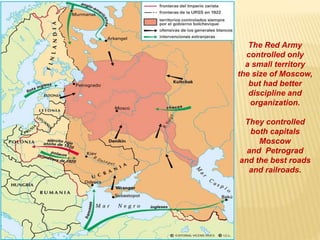
1) After the Bolshevik revolution in Russia, revolutions and protests arose across Europe in response, but most were suppressed, such as in Germany, Hungary, and Italy. 2) The Russian Civil War began as the Bolsheviks consolidated power and eliminated opposing factions, leading to violence, starvation, and economic ruin in Russia. 3) The White Army, consisting of monarchists, liberals, and non-Bolshevik socialists, formed to combat the Red Army and tried to restore pre-revolution governments, gaining control of parts of Russia.