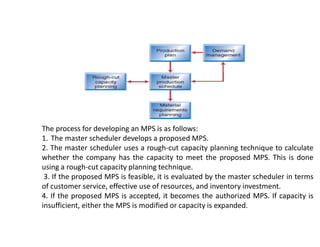
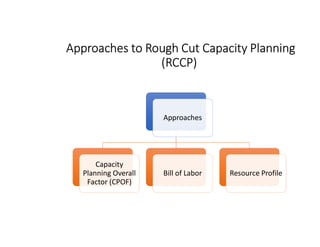
Rough cut capacity planning (RCCP) is a technique used to test the feasibility of a master production schedule (MPS) by comparing the workload it places on critical resources to those resources' demonstrated capacities. The RCCP process involves developing a list of resources needed to meet the MPS quotas, calculating the workload on each resource, and allowing the company to modify capacity or the MPS if needed. RCCP helps identify potential problems before implementing the MPS and initiates actions to adjust mid- to long-term capacities.