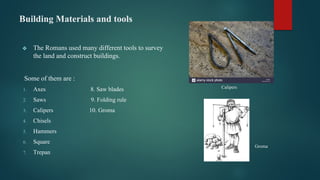
The document details the features of Roman architecture, emphasizing the influence of Greek and Etruscan styles while highlighting advancements like the arch and vault. Important architectural examples include the Colosseum, Pantheon, and Maison Carrée, showcasing unique construction techniques and materials used by the Romans. Additionally, it covers tools employed in construction, Roman roads, and public baths as significant aspects of Roman architectural heritage.