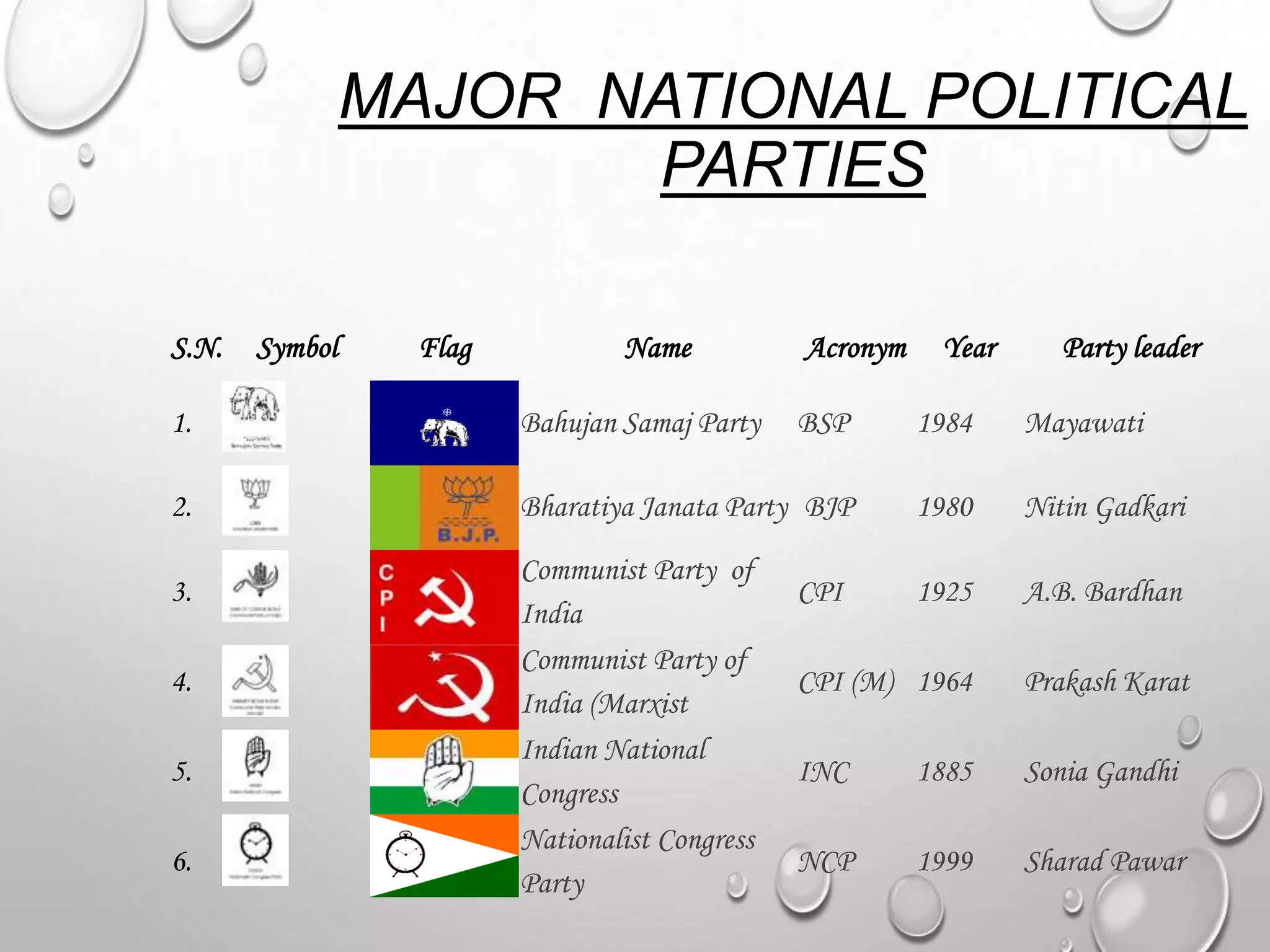
Political parties are groups that contest elections and seek to hold power in government. They agree on policies and programs to promote collective good. The main components of a political party are leaders, active members, and supporters. Most Indians are critical of political parties and blame them for problems in democracy. Political parties are necessary to give citizens choices and form stable governments. The two types of political parties in India are national parties and state/regional parties. Political parties play important roles like contesting elections, forming governments, shaping public opinion, and providing access to government programs. While ruling parties govern and address people's concerns, opposition parties scrutinize the government and prevent abuse of power. The major national political parties in India are the Bharati