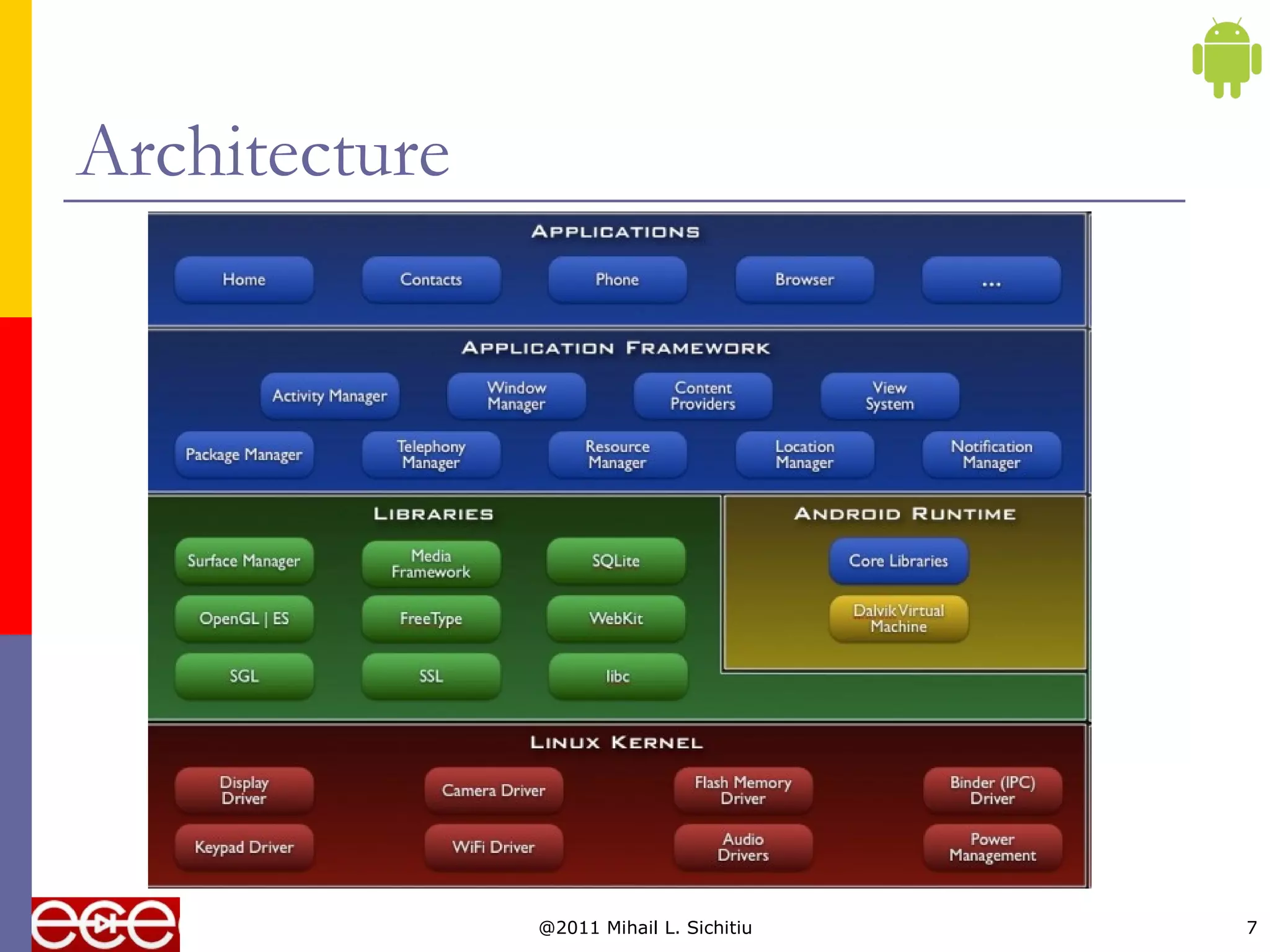
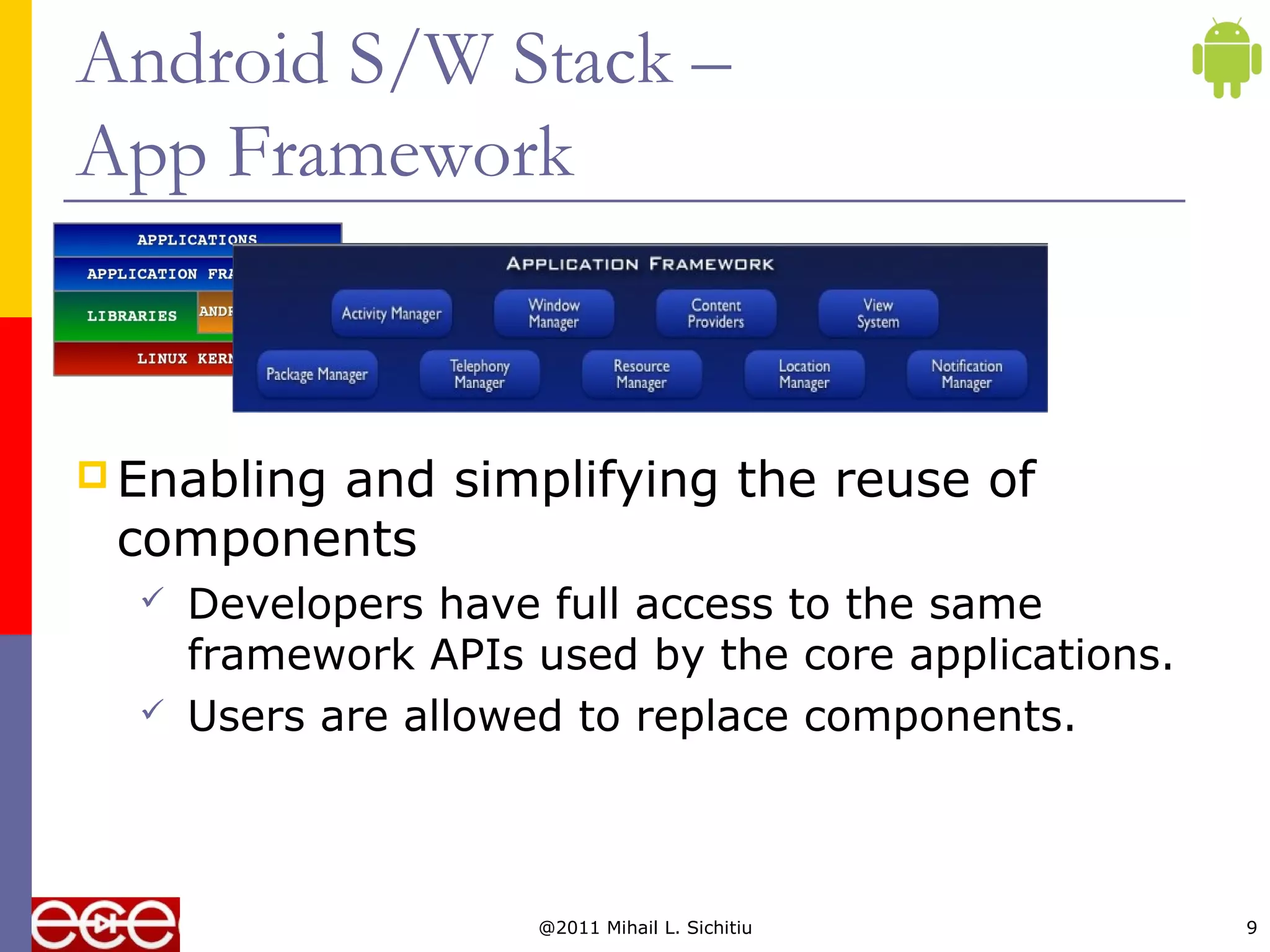
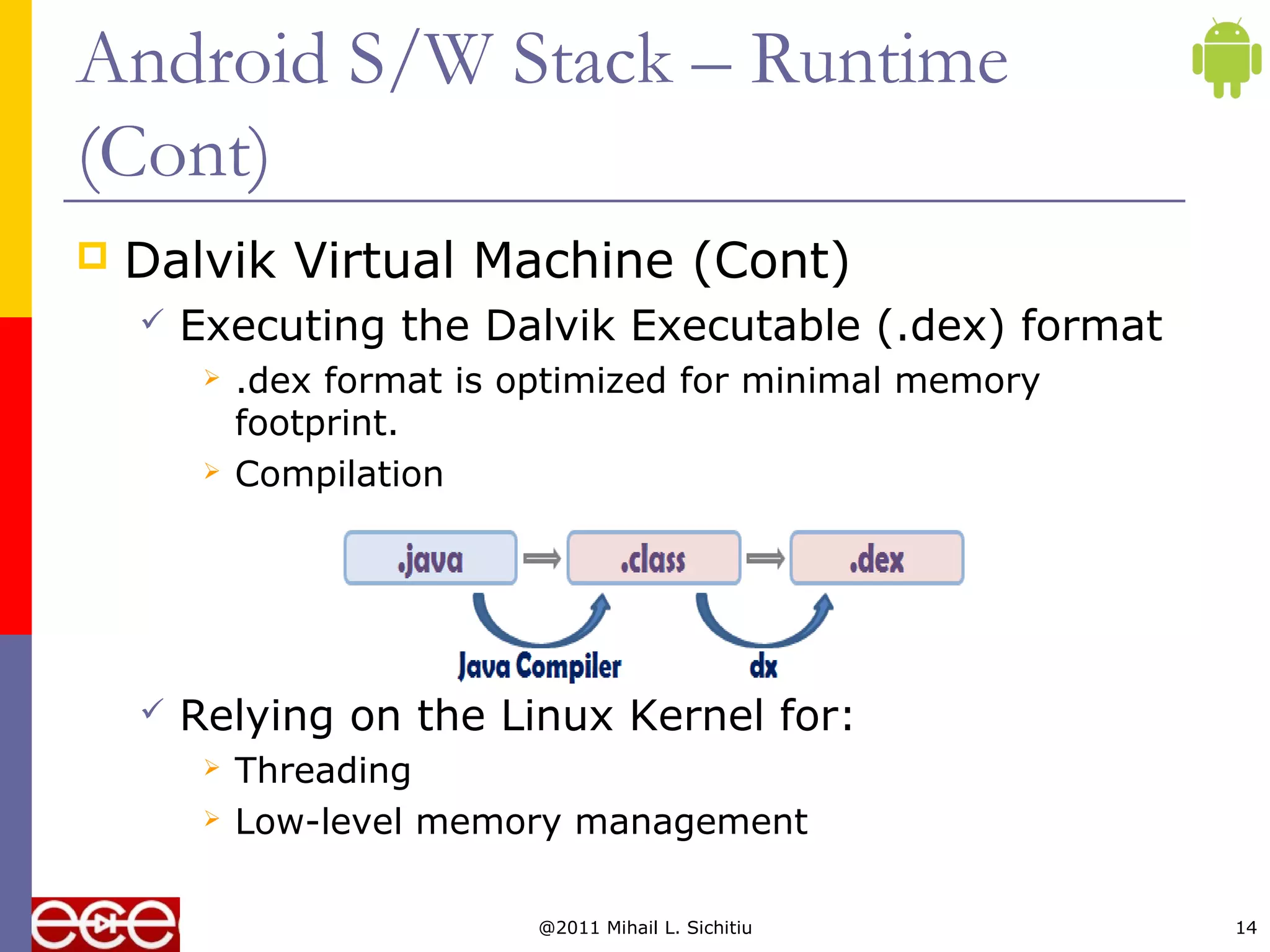
This document provides an overview of the Android platform, including its software stack and architecture. It describes Android as an open source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware and applications. It also discusses the Open Handset Alliance of companies that develop Android, some popular Android phones and tablets, Android's growing market share, and the key components of Android's software stack such as the application framework, libraries, Dalvik virtual machine, and reliance on the Linux kernel.