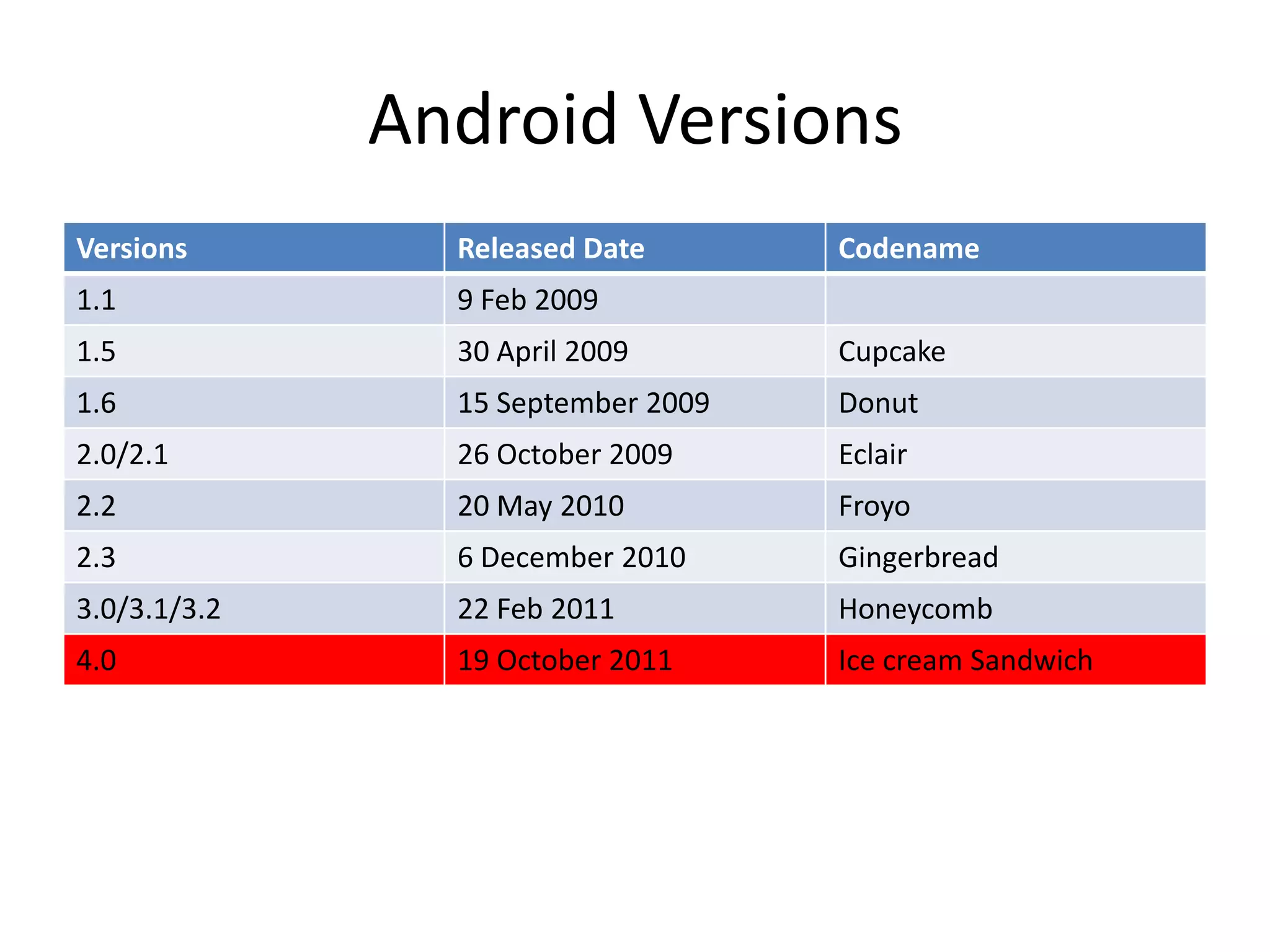
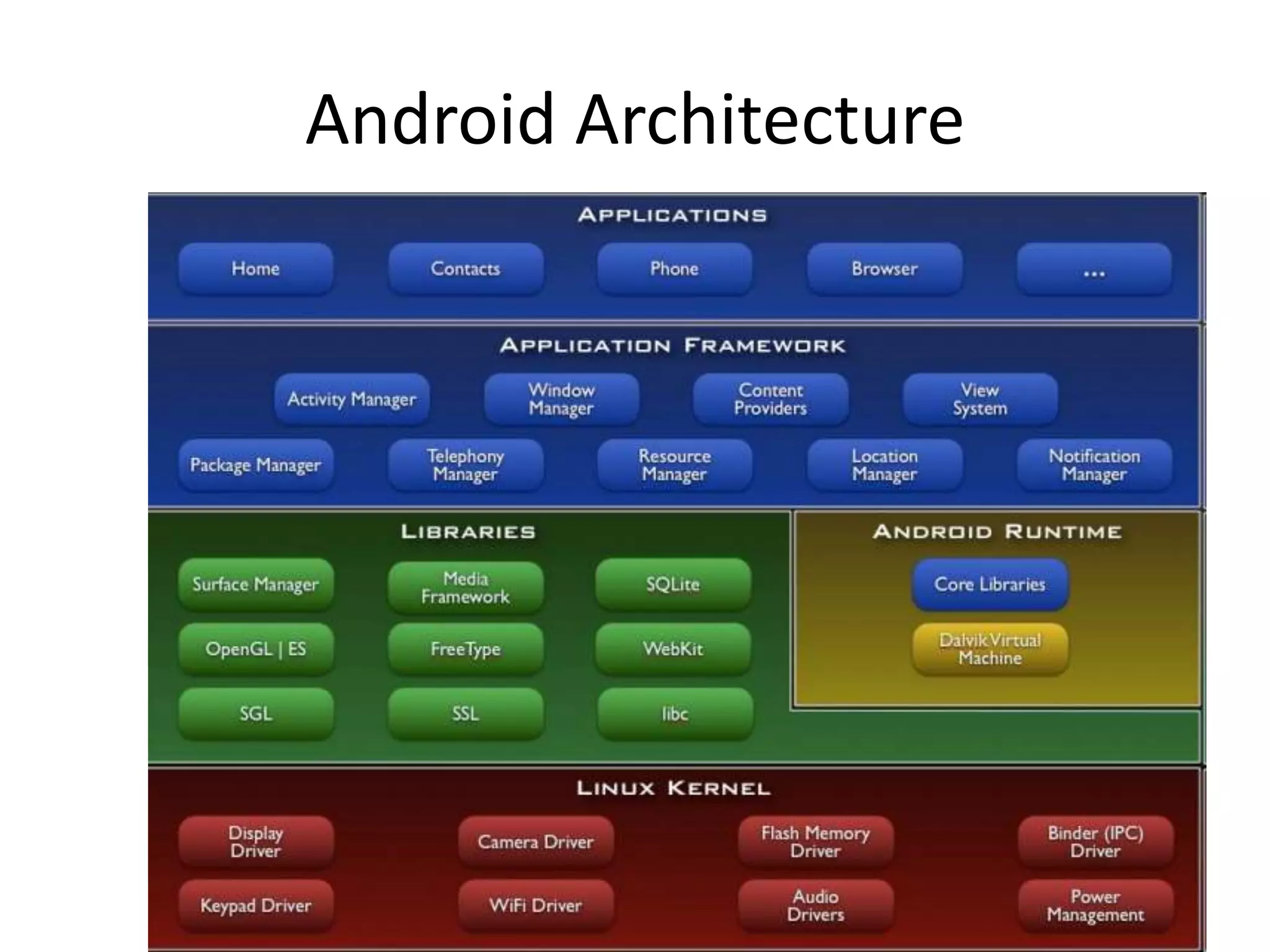
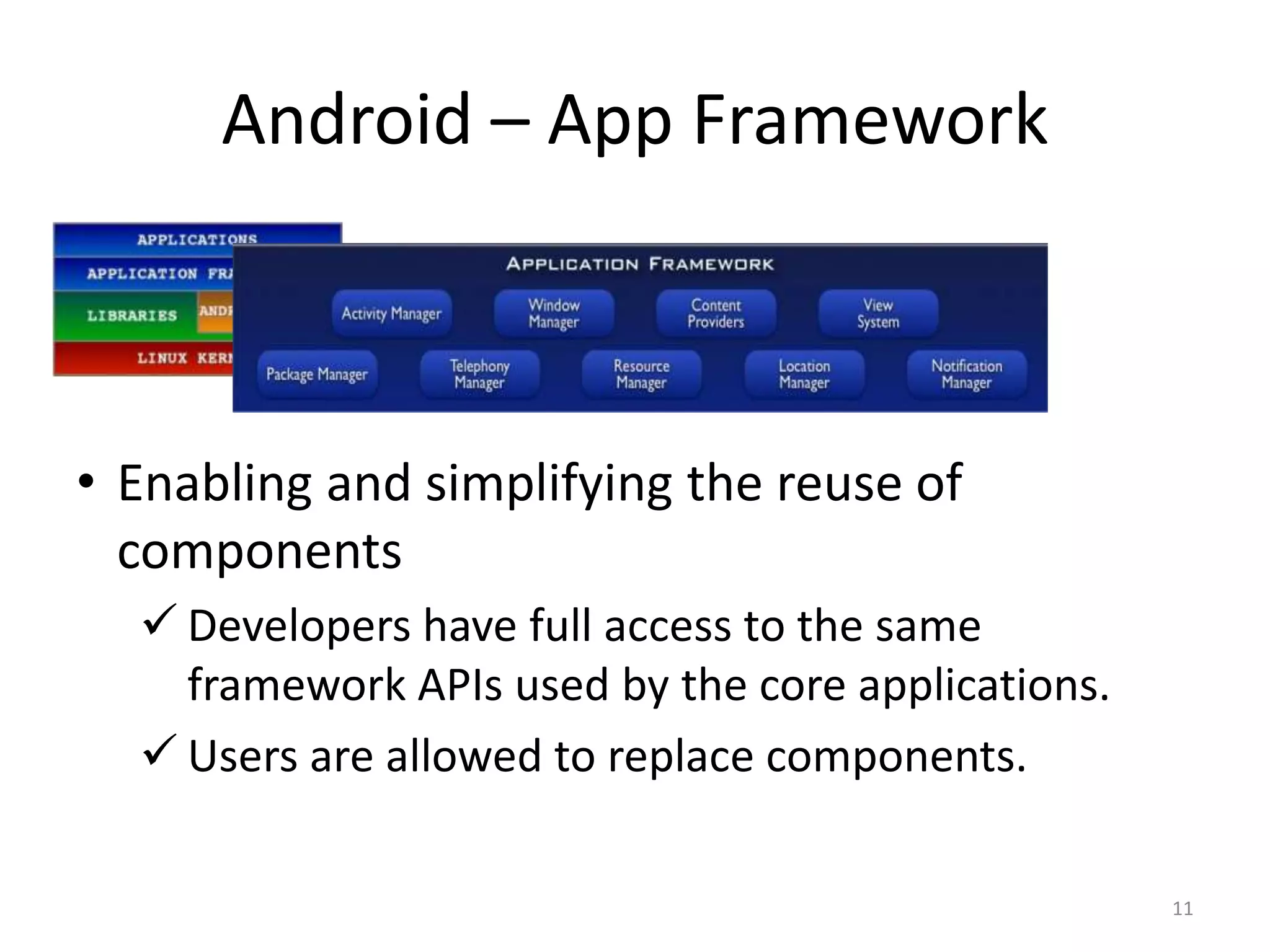
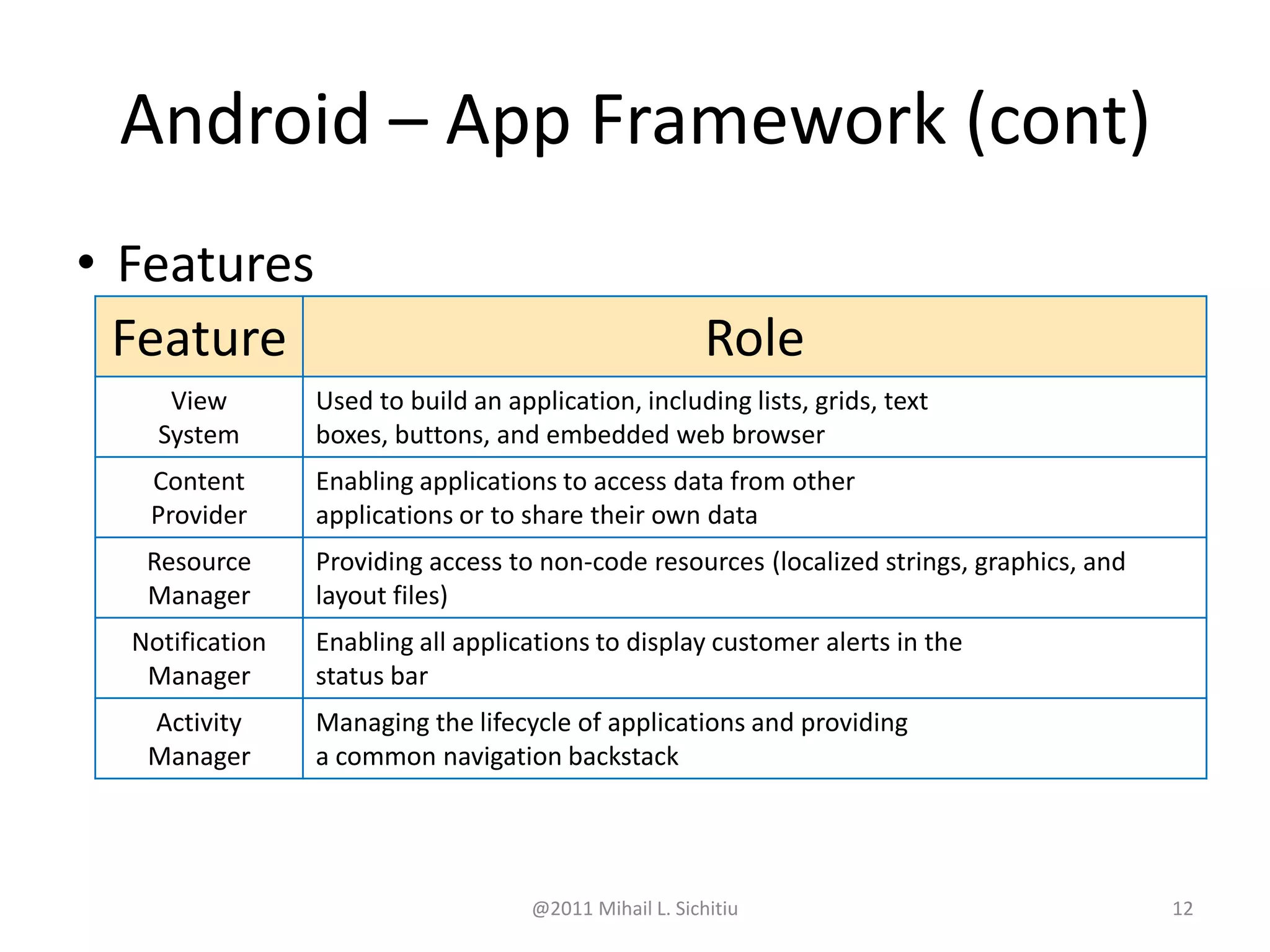
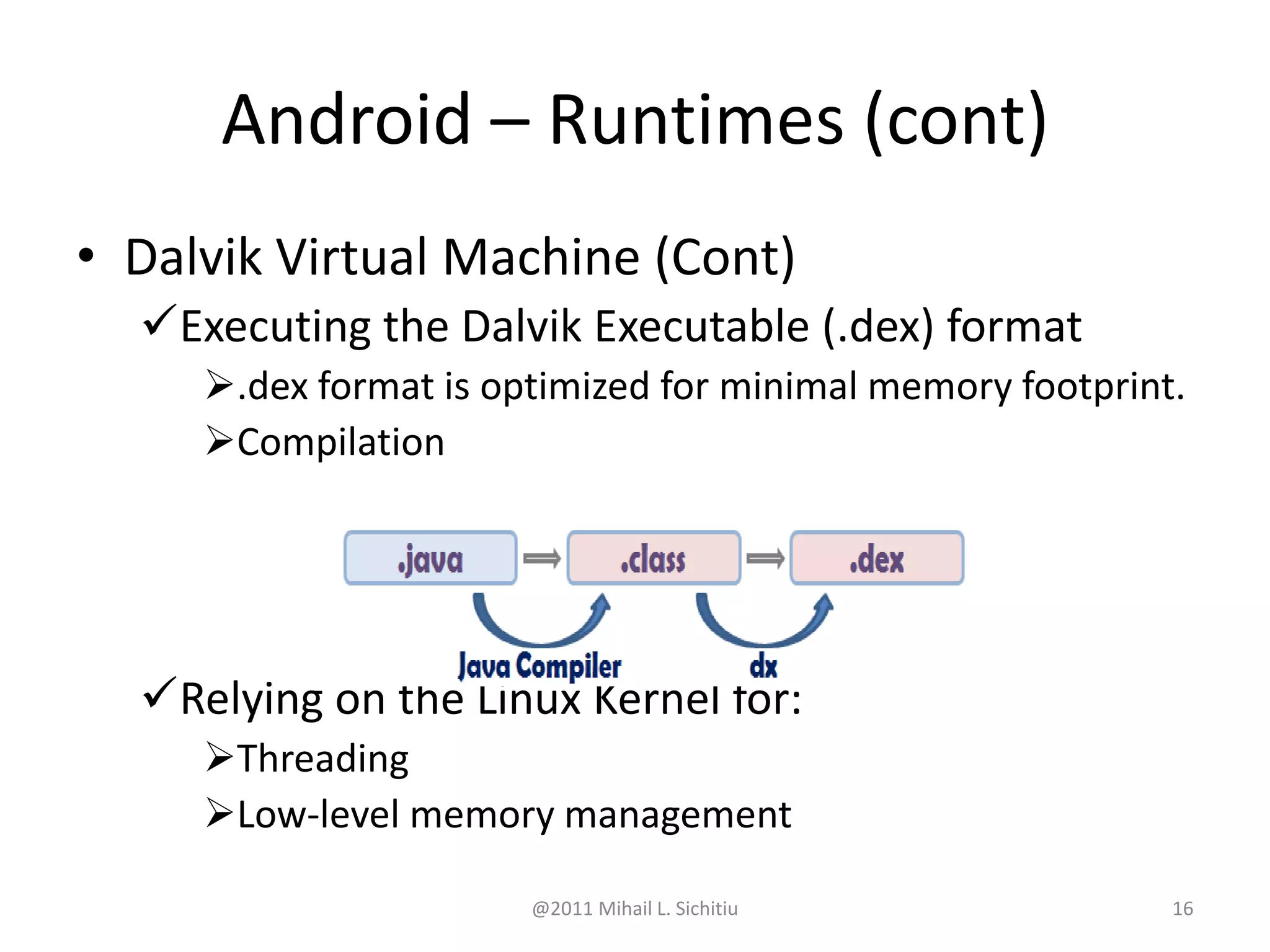
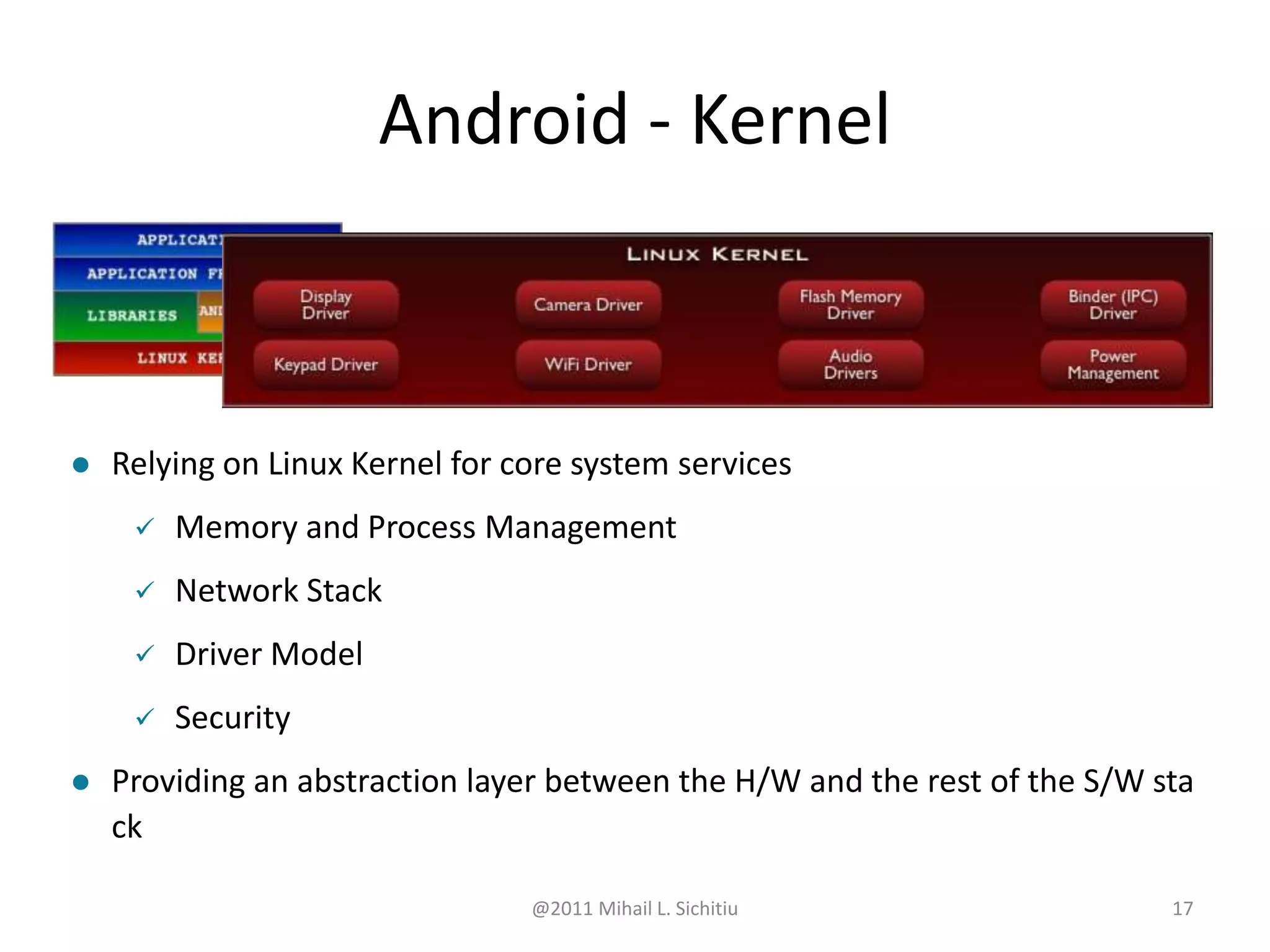
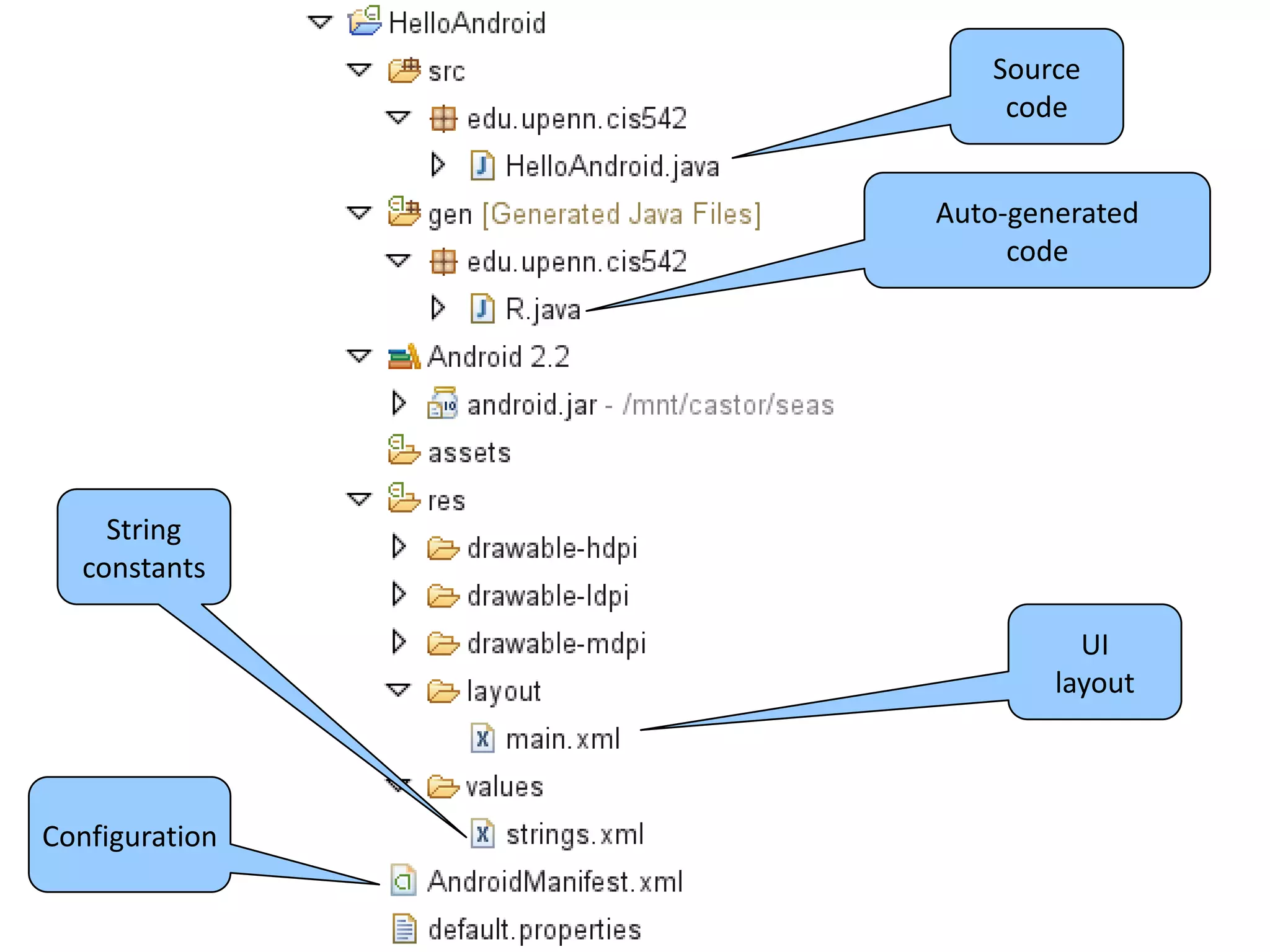
Android is an open source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications for mobile devices. It allows developers to write managed code in Java for the Dalvik virtual machine. The Android software development kit provides tools and APIs to develop and debug apps using standard Java libraries and Android specific ones. Apps are packaged and distributed through the Android Market which is preinstalled on Android devices.