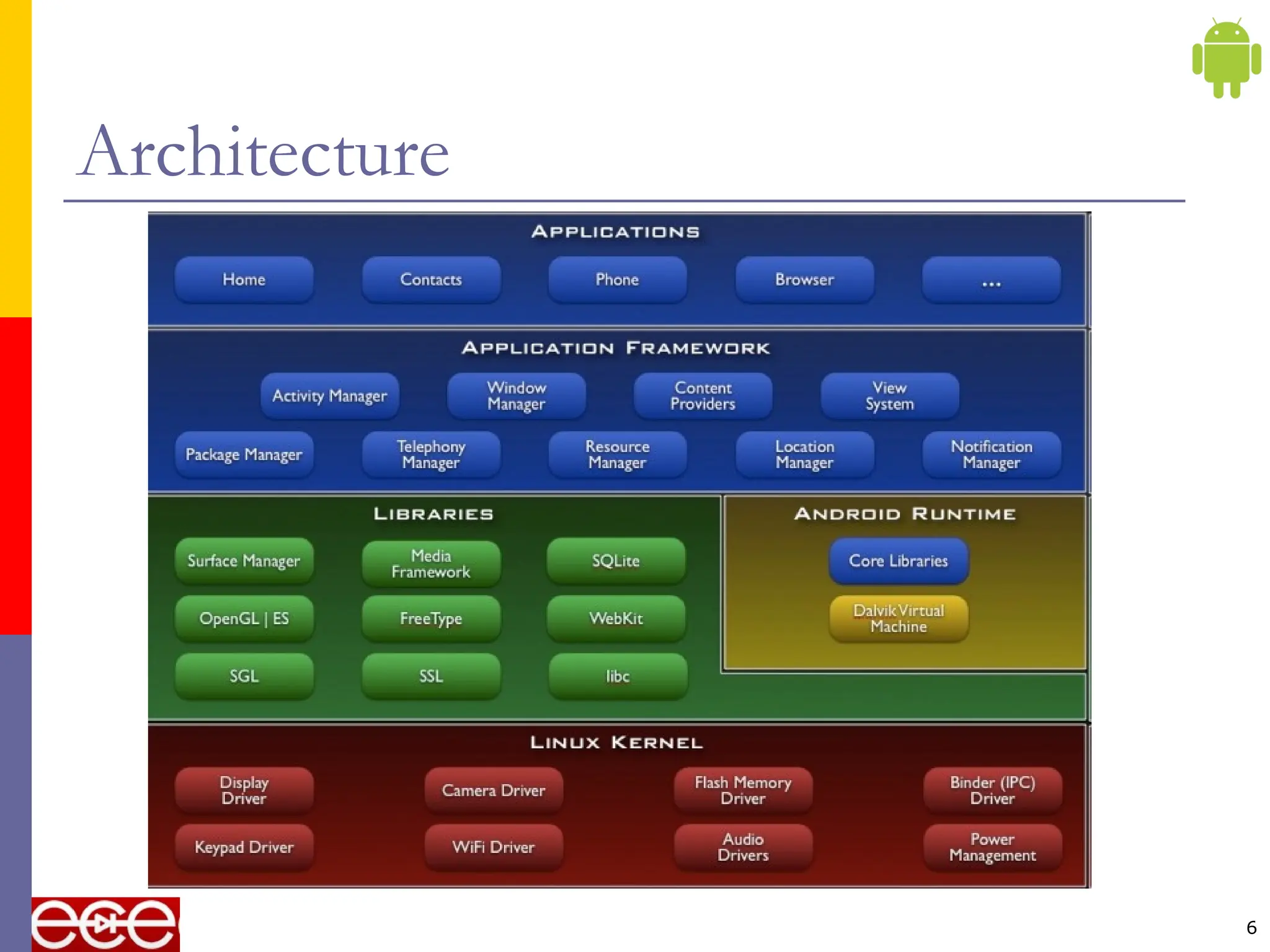
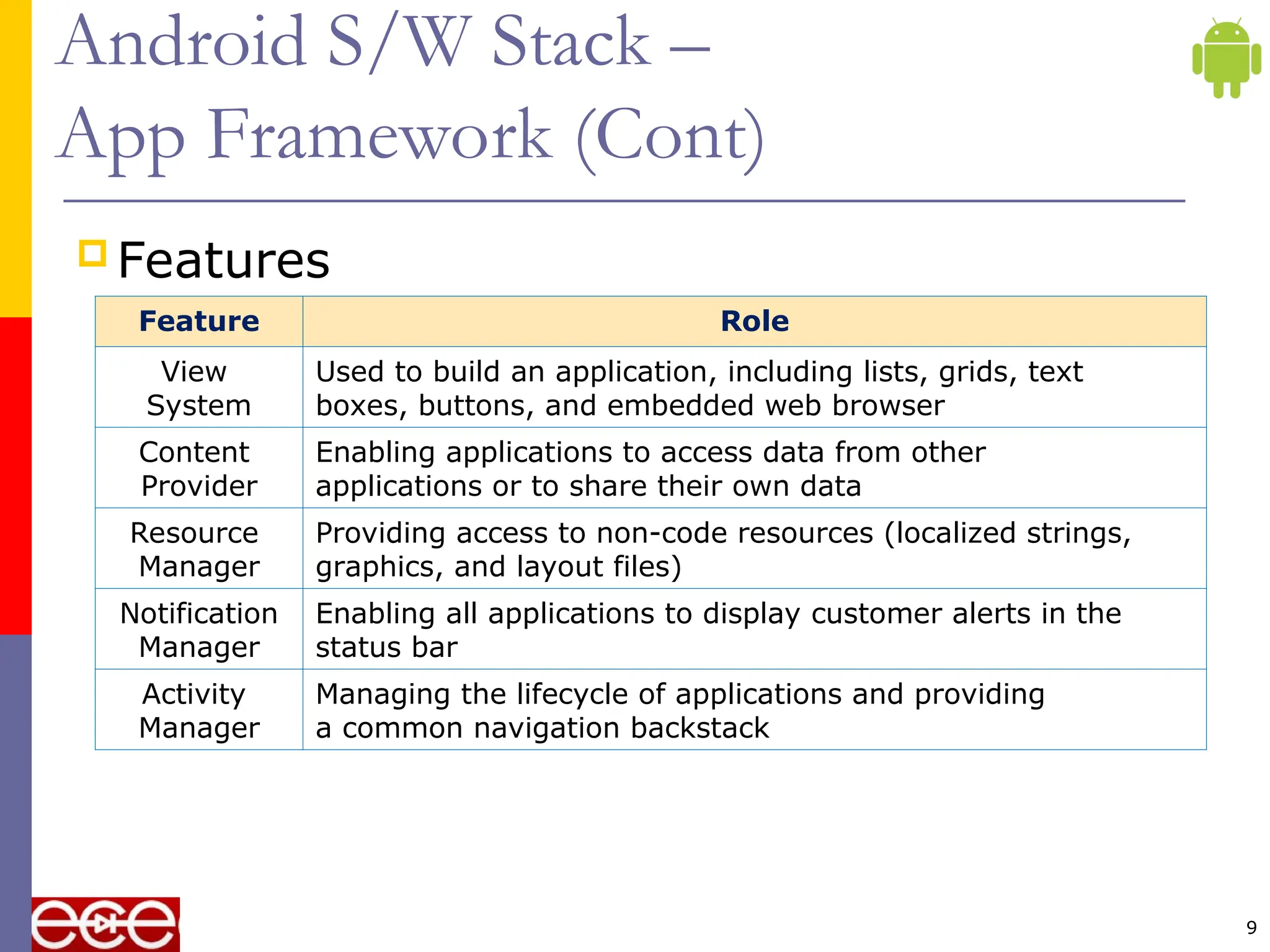
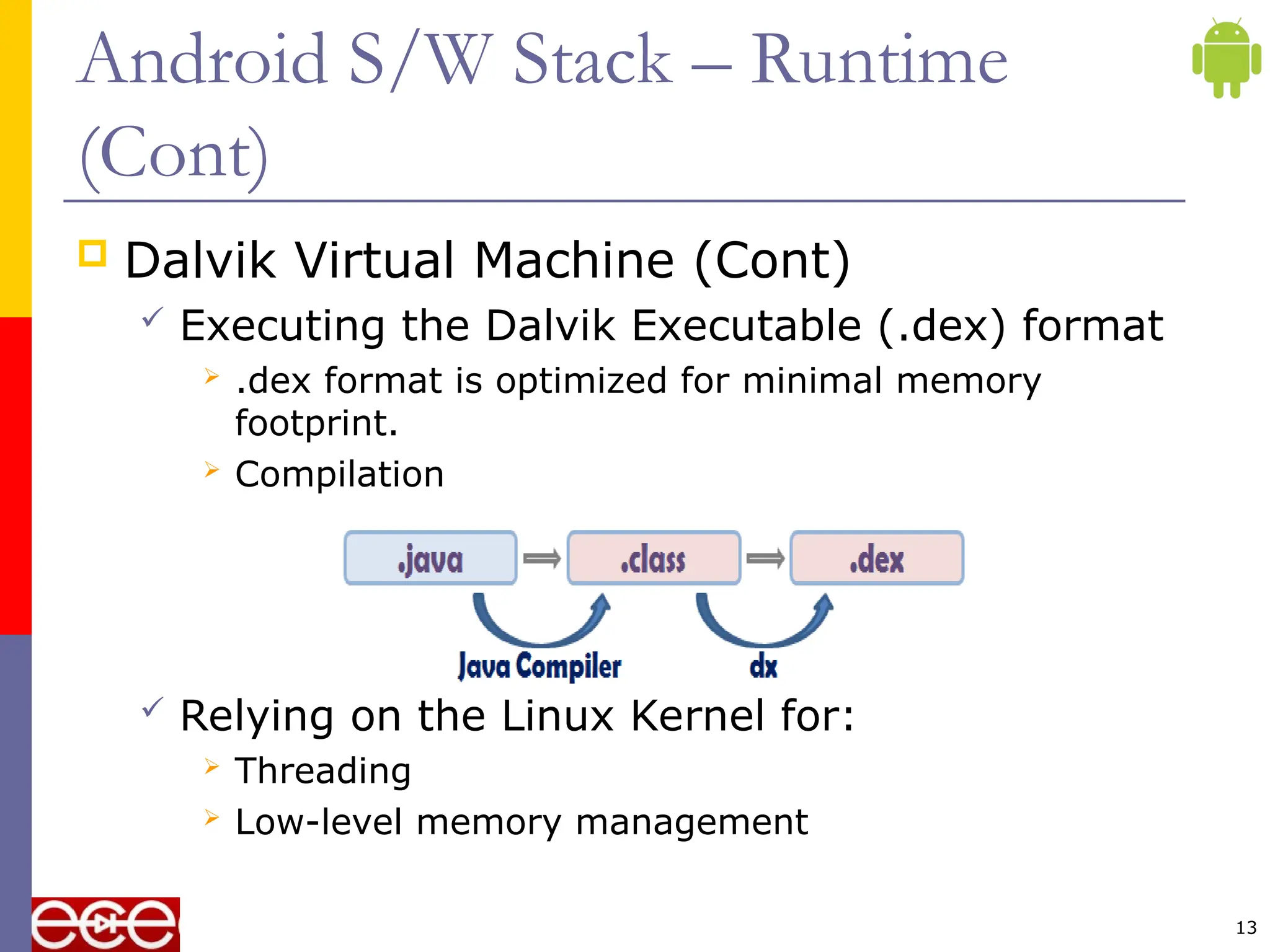
The document provides an overview of the Android platform, highlighting its components including the operating system, middleware, and applications. It discusses the architecture of Android's software stack, including the application framework, libraries, runtime, and the reliance on the Linux kernel for core services. Additionally, it notes that Android supports a variety of devices, including smartphones and tablets, and emphasizes the Open Handset Alliance's role in developing open standards for mobile devices.