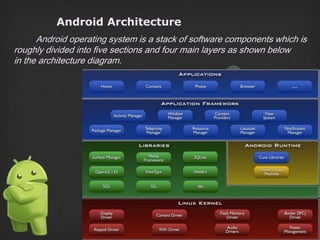
Android is an open source software stack that was developed by Android Inc. and later acquired by Google. It includes an operating system, middleware, and key applications. The software stack consists of five main sections - applications, application framework, libraries, runtime, and the Linux kernel. It allows developers to write once and run on multiple device types.