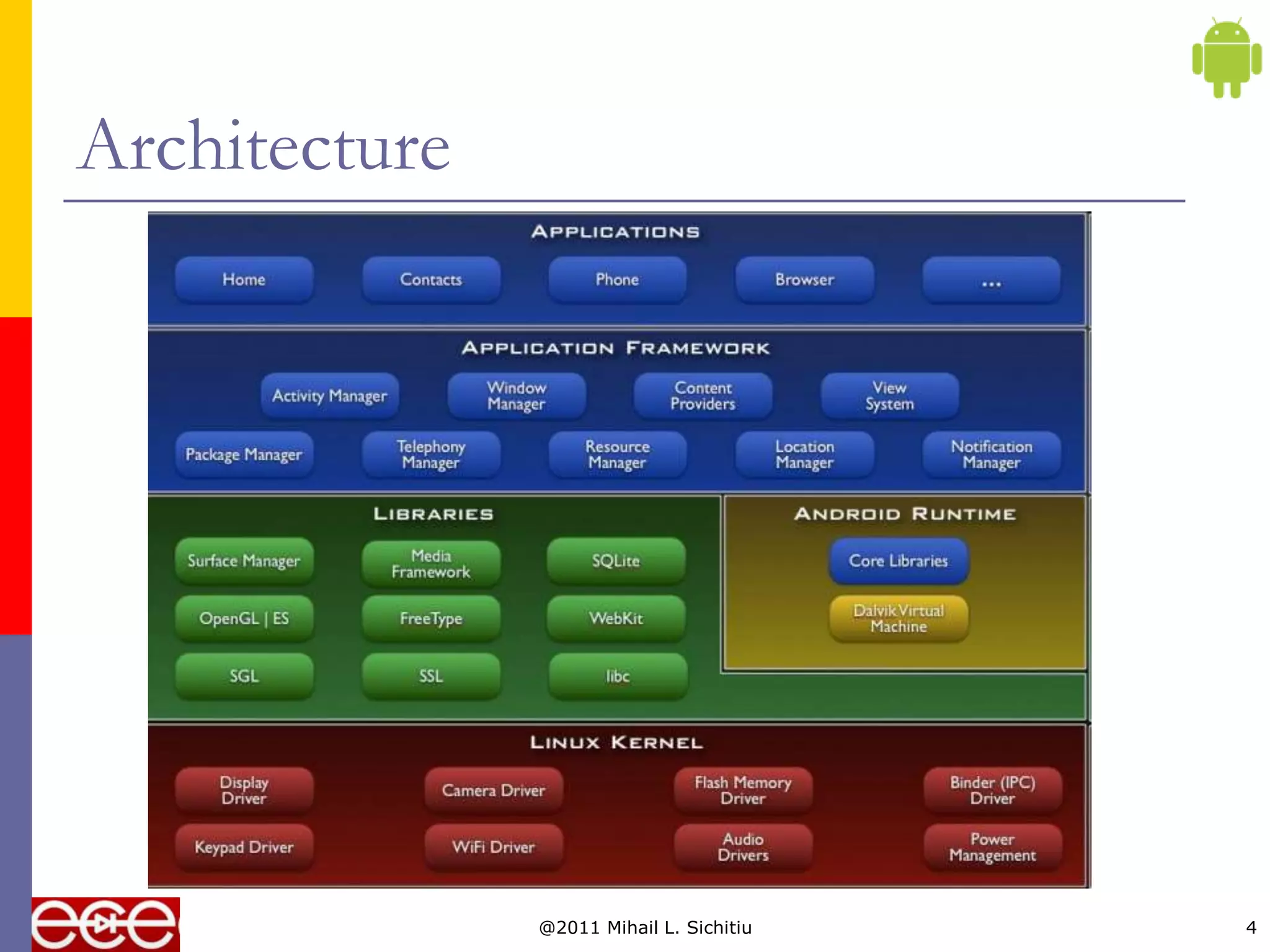
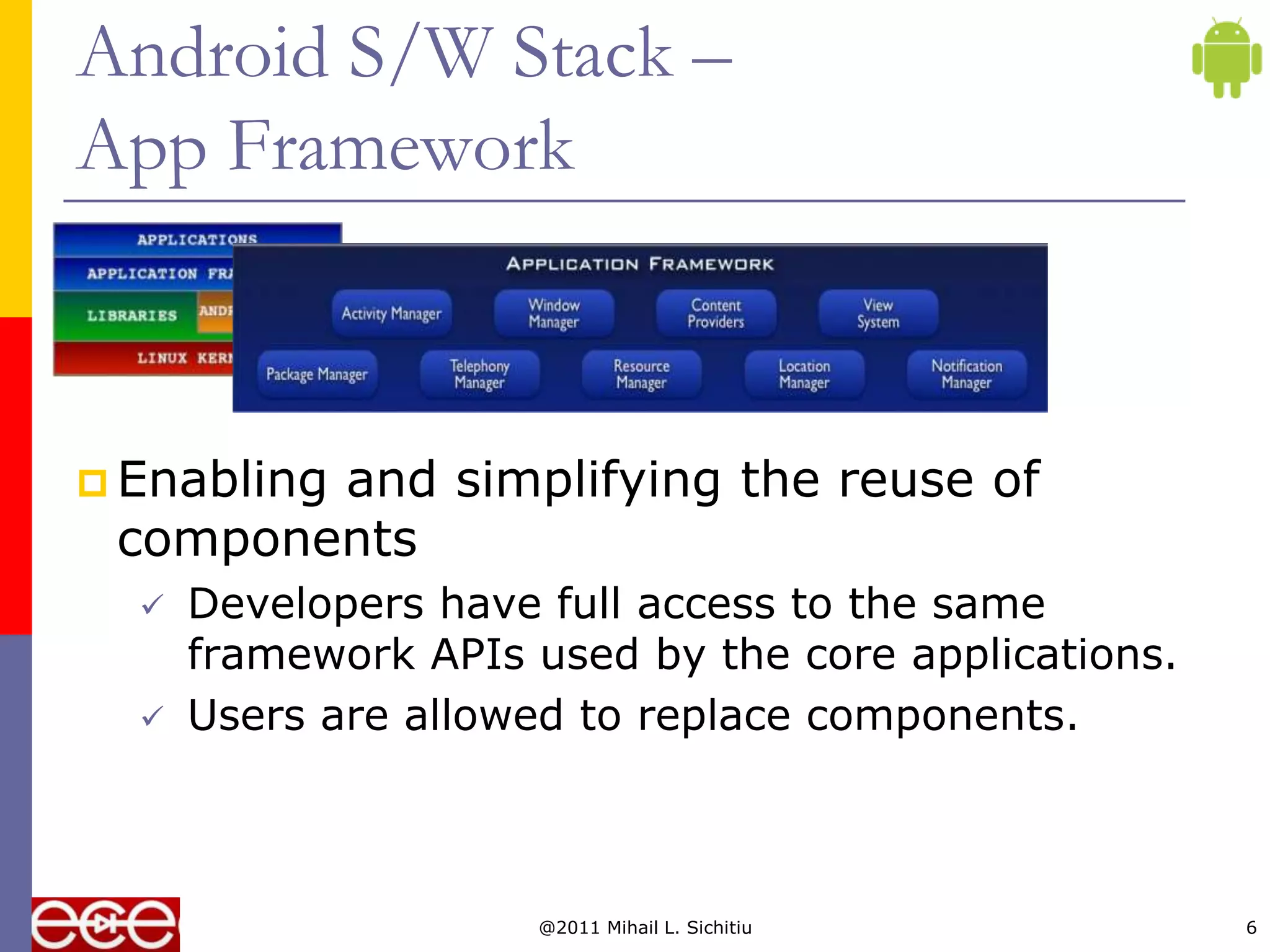
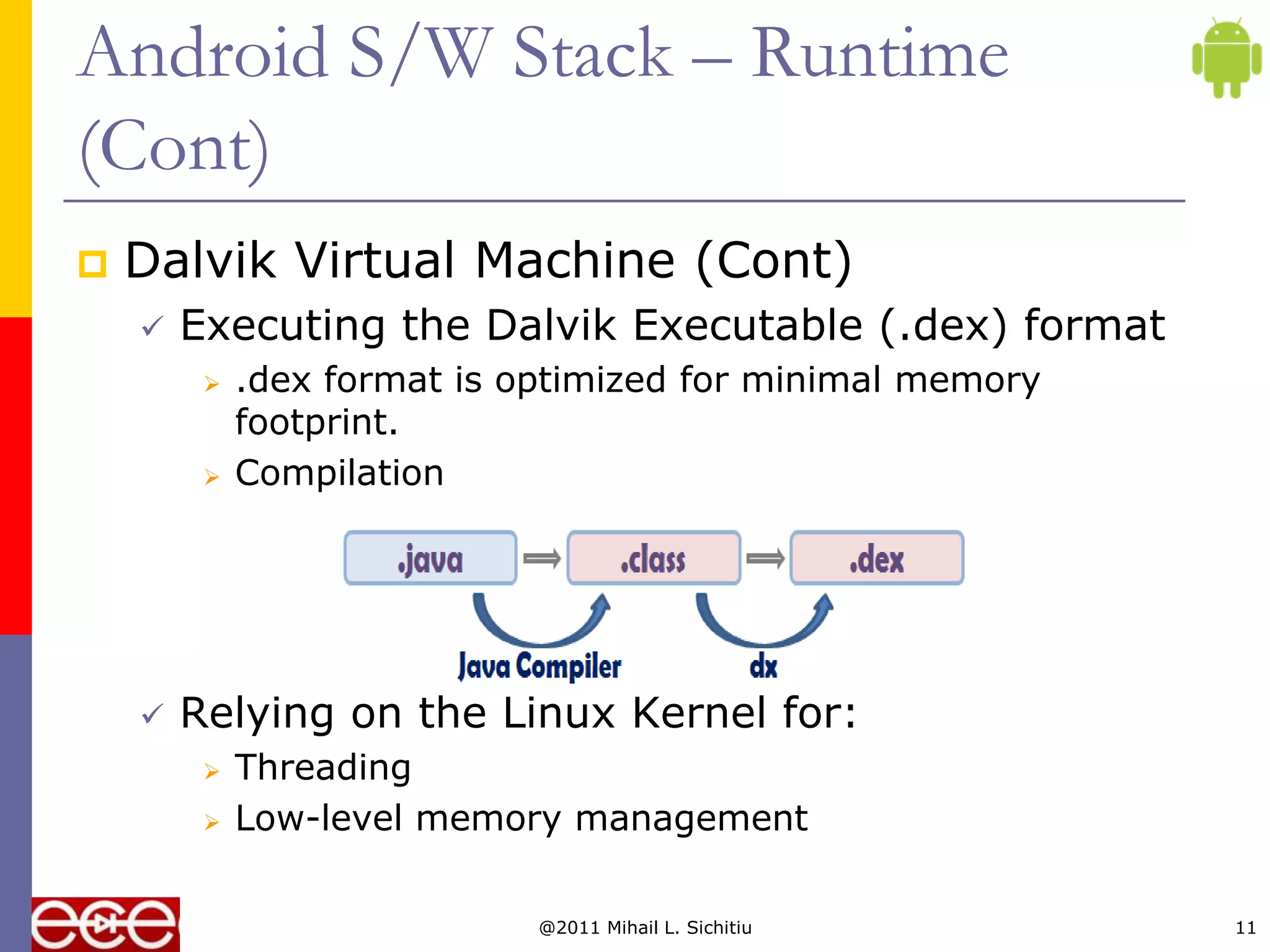
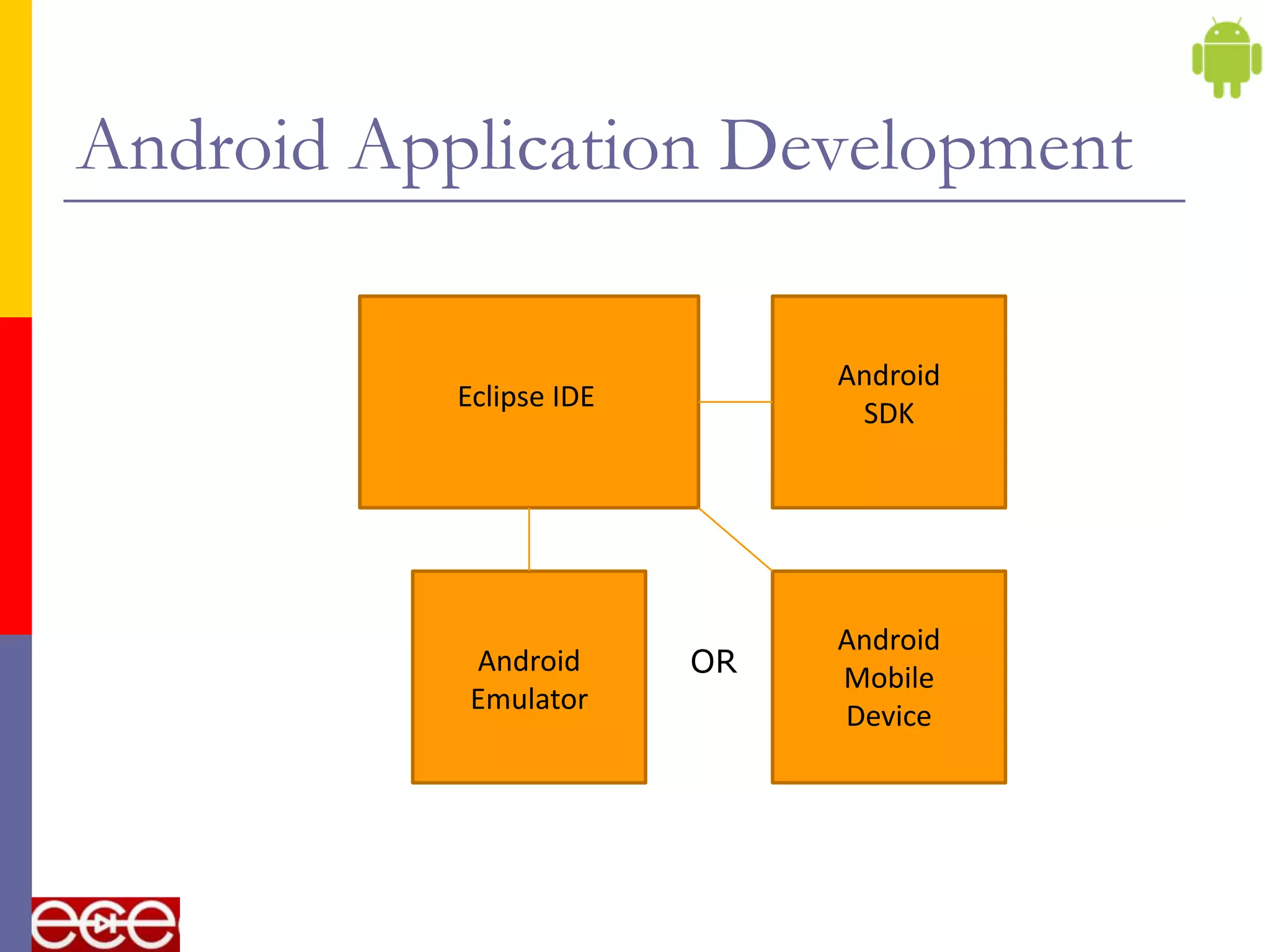
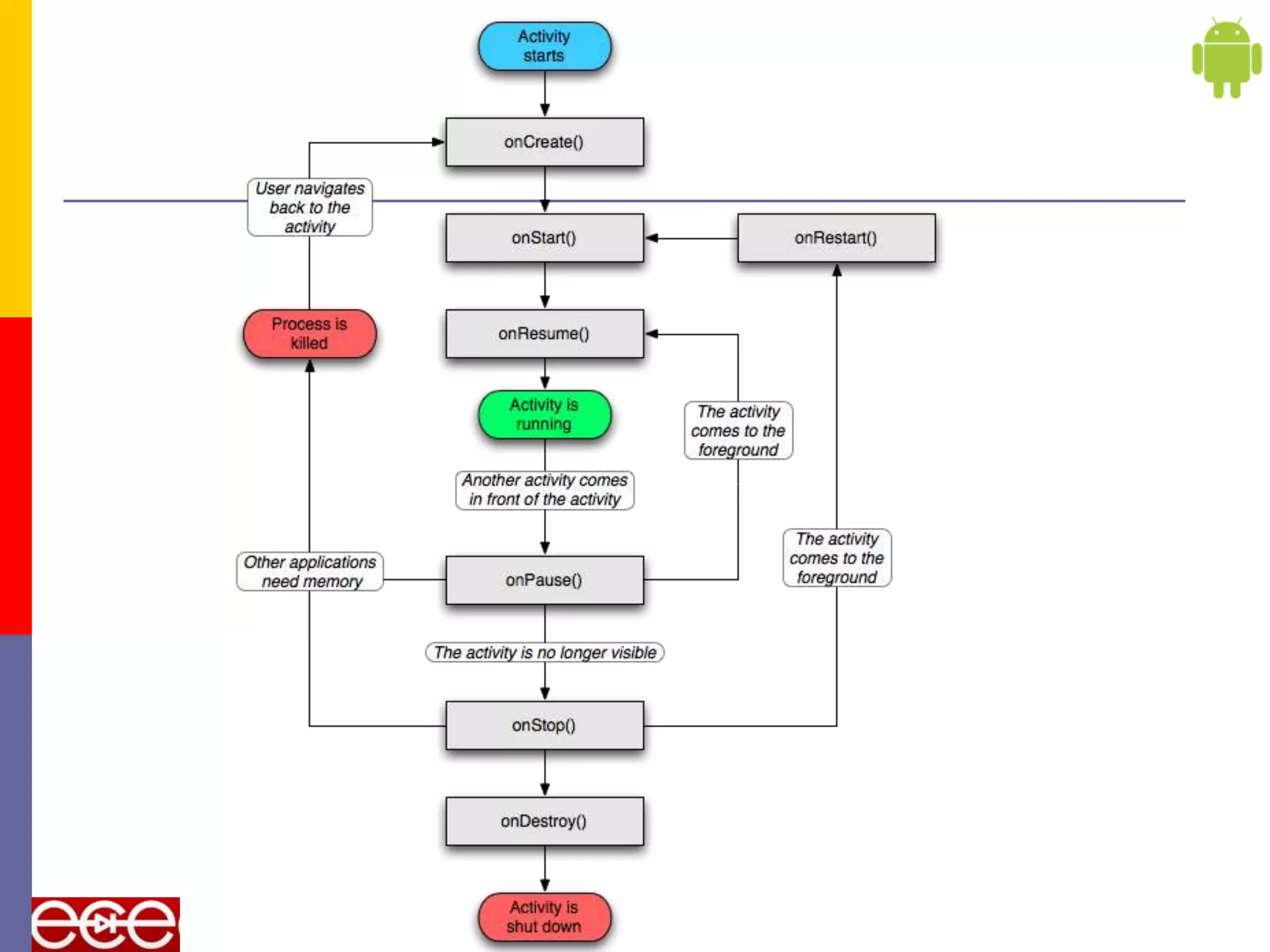
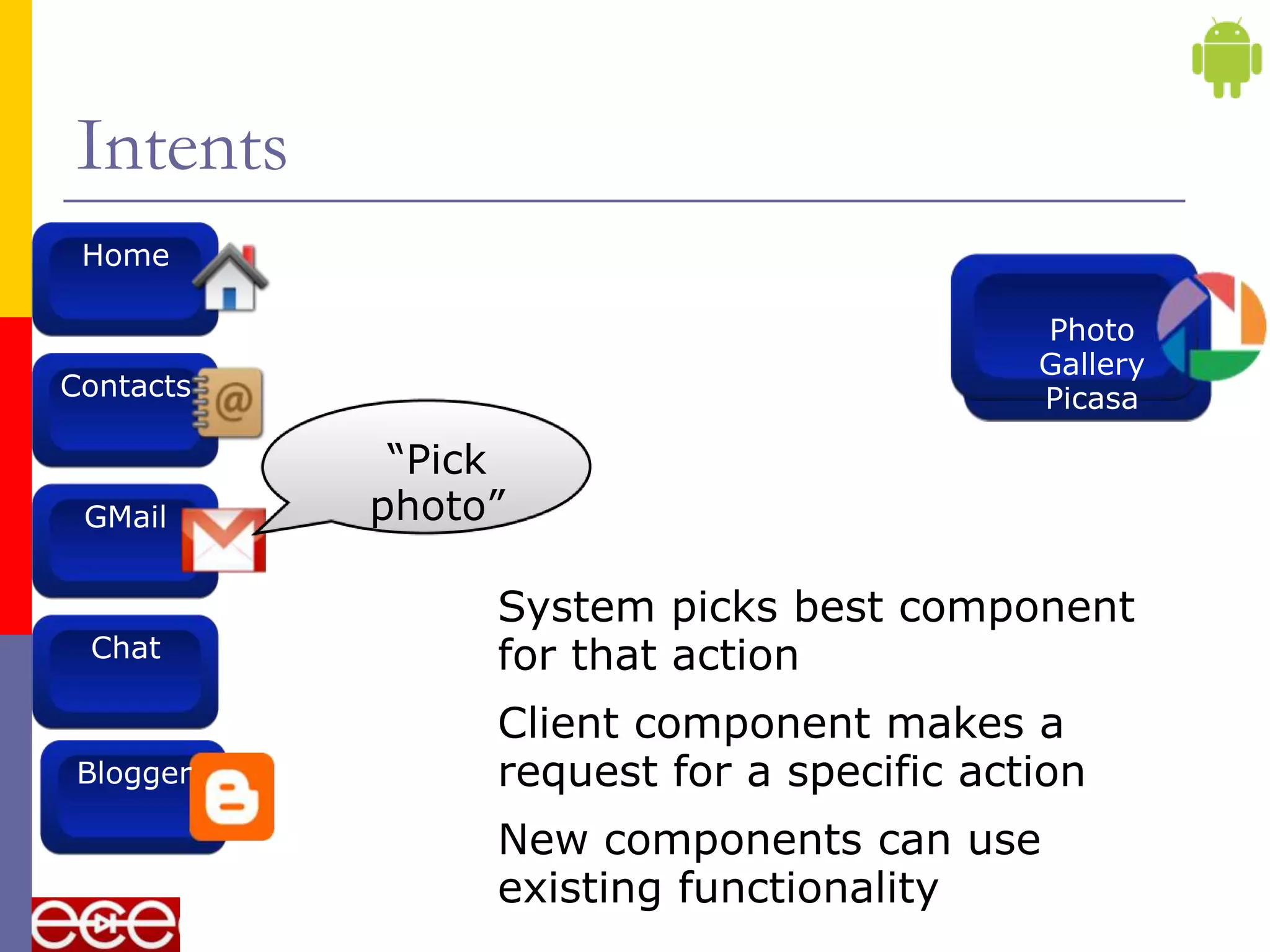
Android is an open source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware, and key applications for mobile devices. It was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, a consortium of 47 technology companies. The Android software stack consists of applications, an application framework, libraries, a runtime, and the Linux kernel. It provides core applications like email, SMS, calendar, maps, and a browser. All applications are written using the Java programming language.