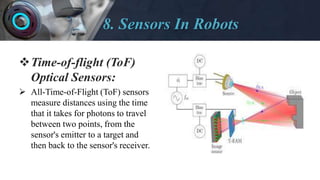
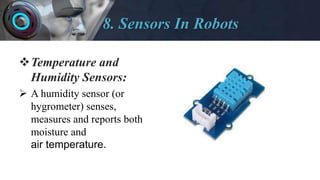
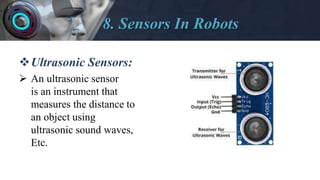
The document provides an overview of robotics including:
- Defining robotics as a field that uses electronics, mechanics, and computer science.
- Stating the purpose of robots is to perform tasks traditionally done by humans.
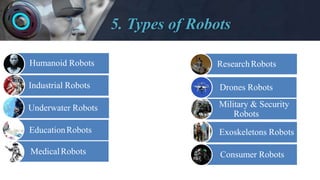
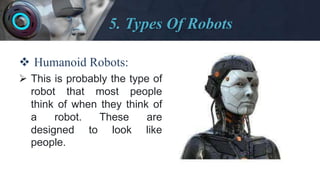
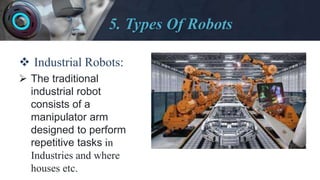
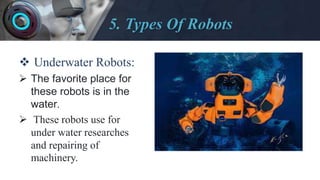
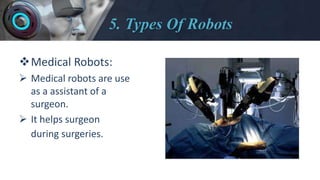
- Describing some of the major types of robots like industrial, medical, consumer, and military robots.
- Outlining three laws of robotics related to not harming humans and obeying orders.
- Noting robots use sensors and AI to perform tasks and are controlled through various methods.