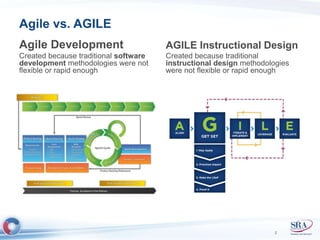
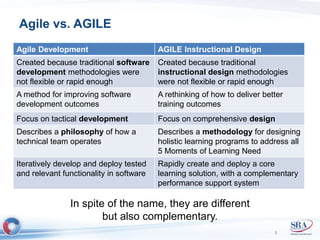
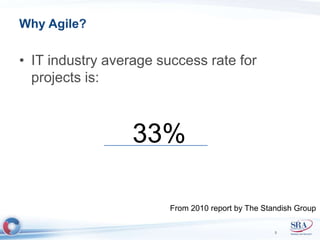
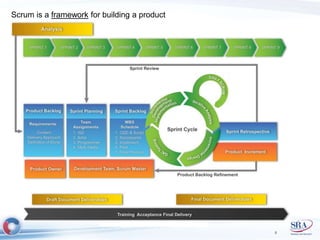
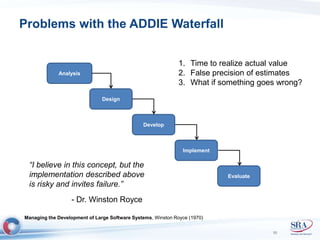
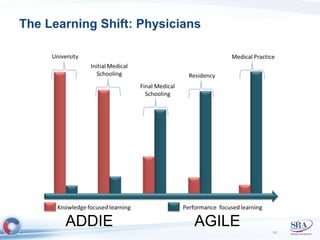
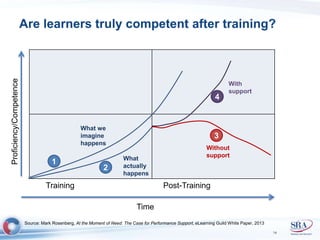
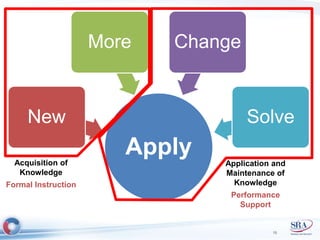
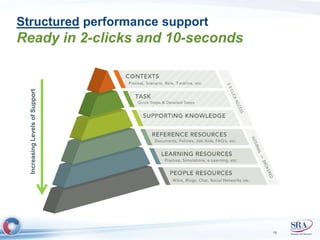
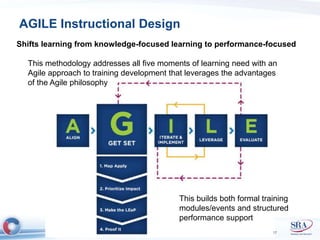
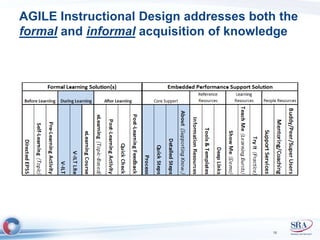
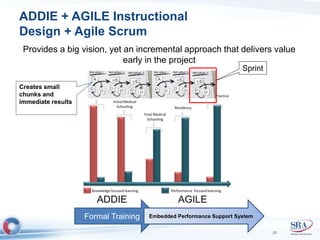
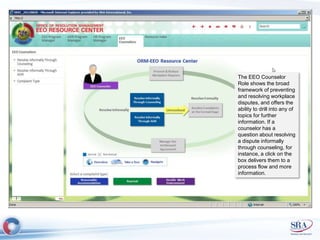
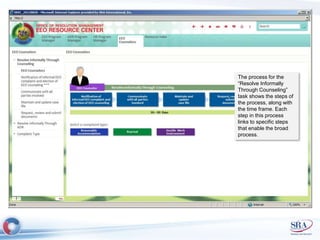
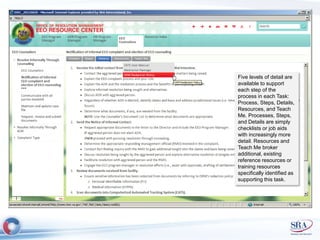
The document discusses how Agile development methods and AGILE instructional design can be used together to improve training programs. It describes how Agile was created to make software development more flexible and rapid, and how AGILE was created for the same reasons for instructional design. While they have different focuses, Agile on software tactics and AGILE on comprehensive learning, they are complementary. The document advocates using Agile values, Scrum framework, and iterative development with AGILE instructional design and the ADDIE model to create both formal training and structured performance support. This holistic approach aims to better link learning to job performance.