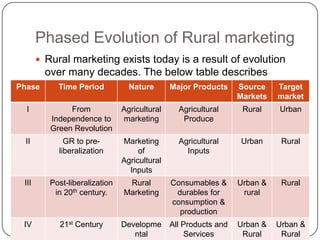
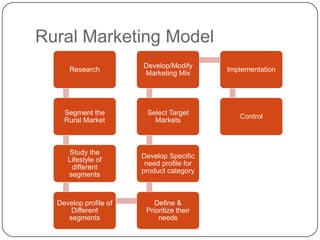
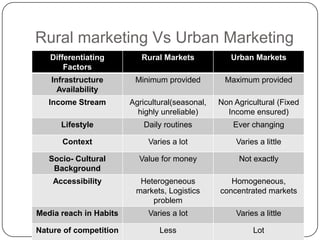
Rural marketing is defined as developing, pricing, promoting, and distributing rural-specific goods and services to satisfy consumer demand and achieve organizational objectives. It involves all aspects of the market structure including pre- and post-harvest operations for farm commodities in rural areas. Rural marketing has evolved over decades from agricultural marketing to marketing of agricultural inputs to current marketing of all products and services to both urban and rural consumers. The rural marketing model involves segmenting the rural market, selecting target markets, developing profiles of segments, defining and prioritizing their needs, developing or modifying the marketing mix, implementing plans, and controlling the process. Rural and urban markets differ in factors like infrastructure availability, income sources, lifestyles, socio-