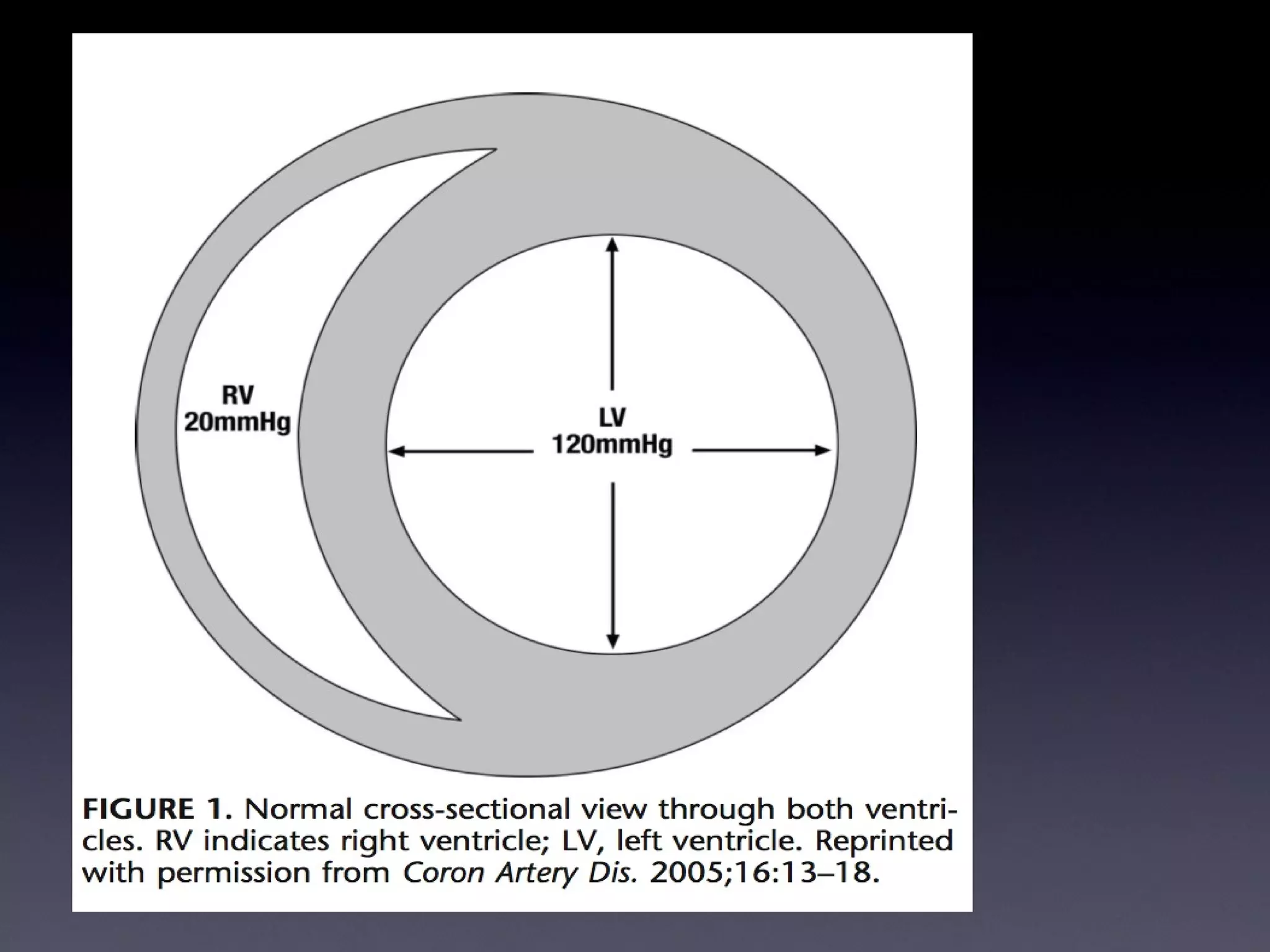
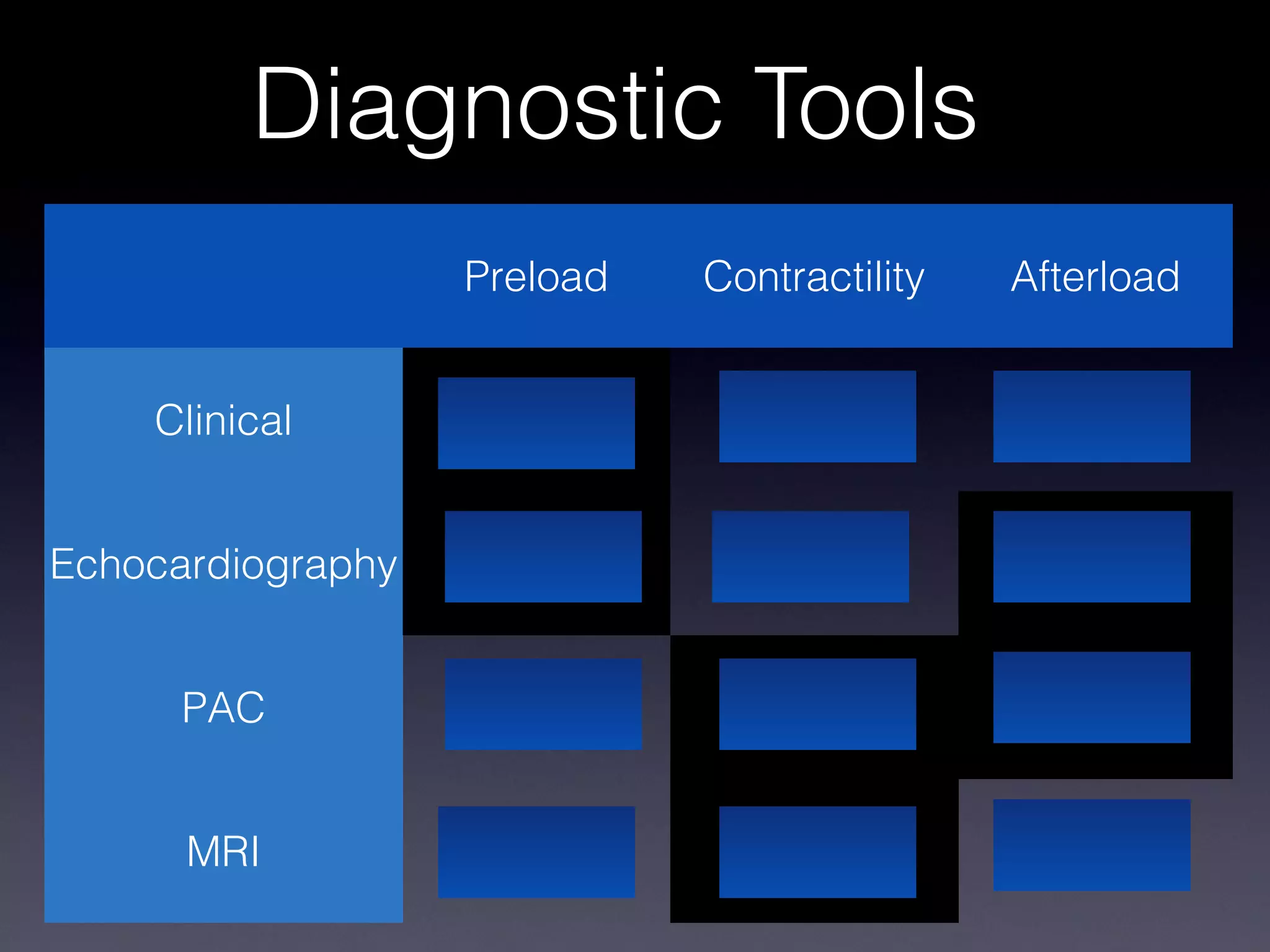
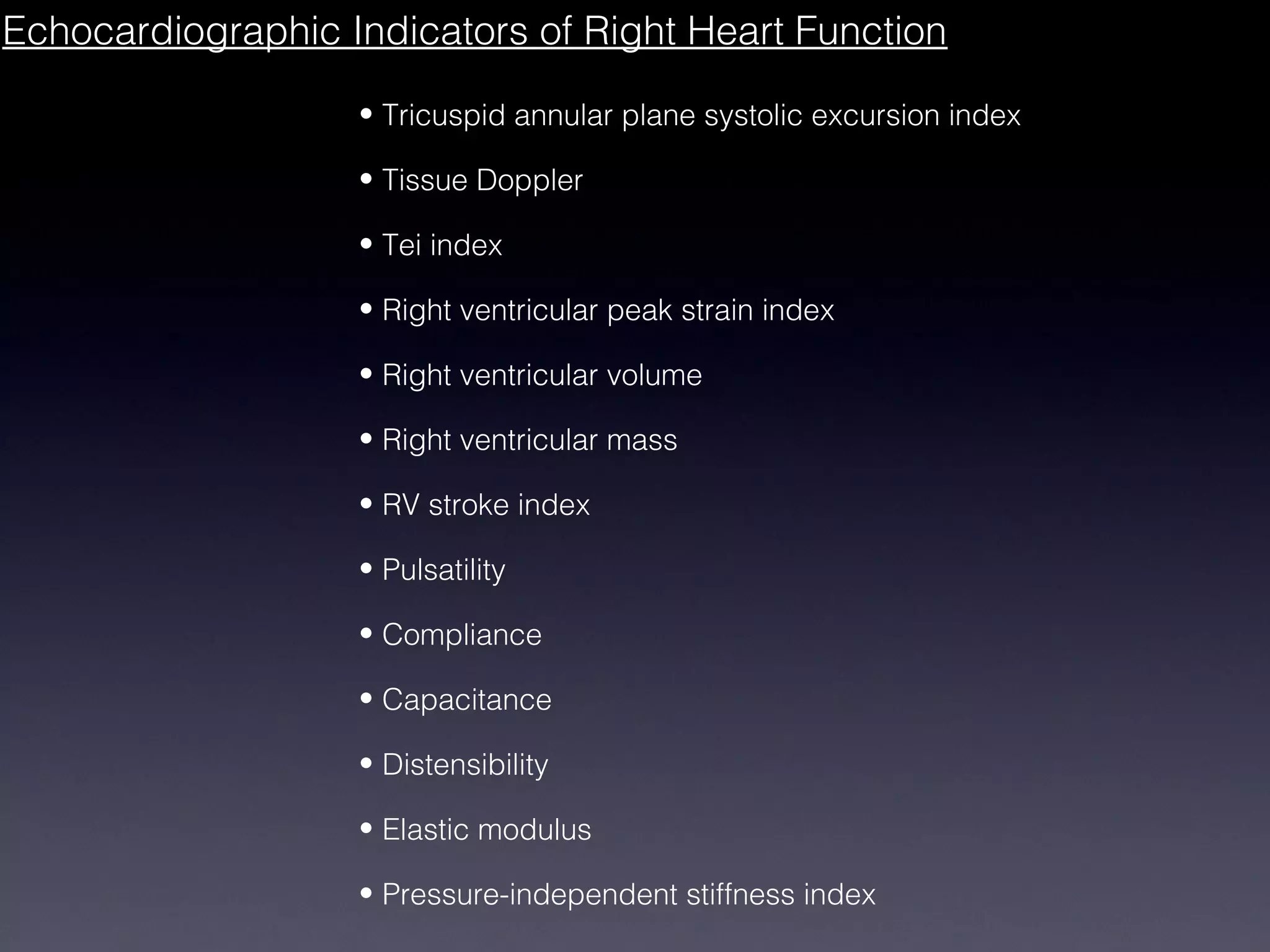
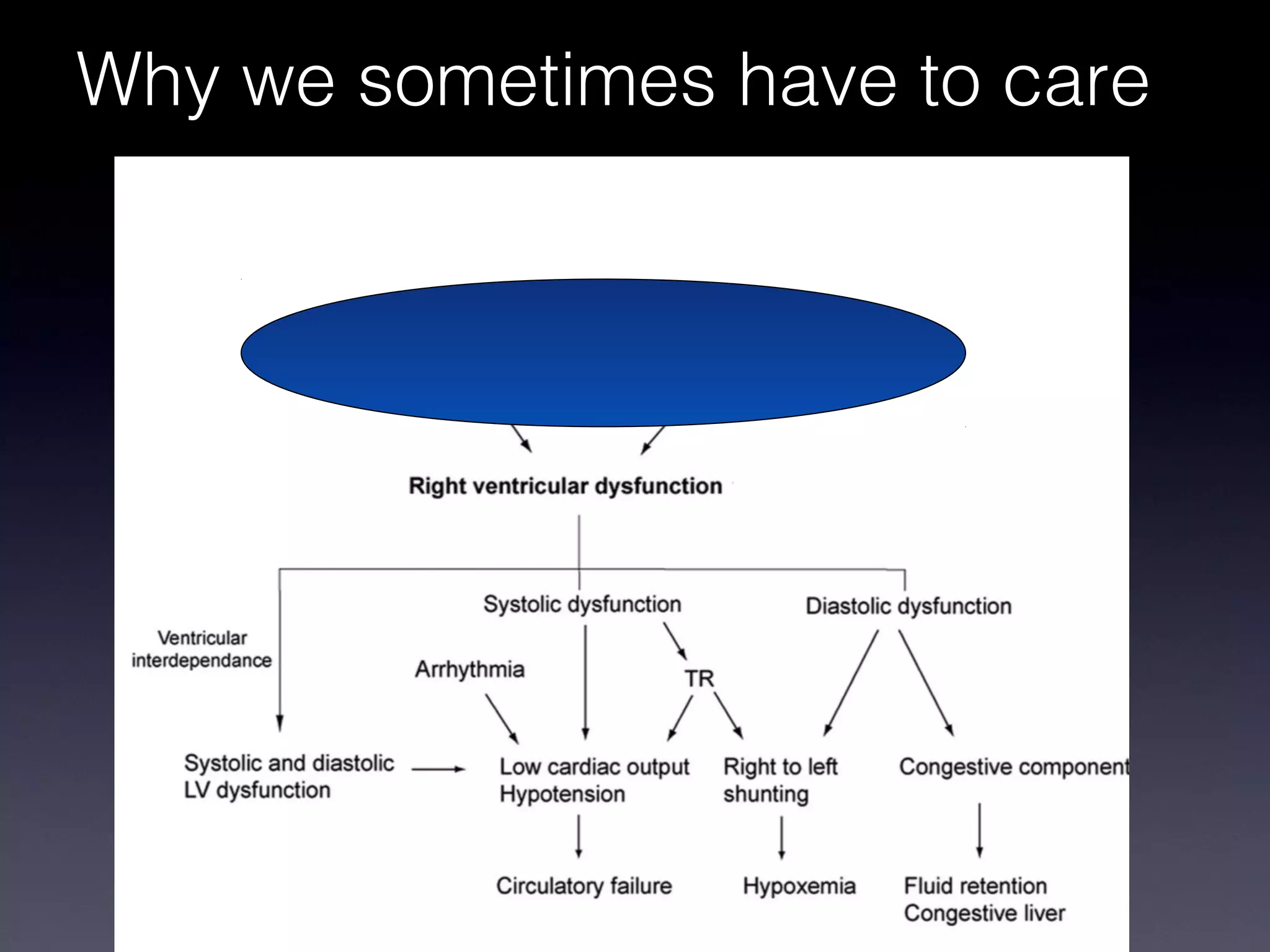
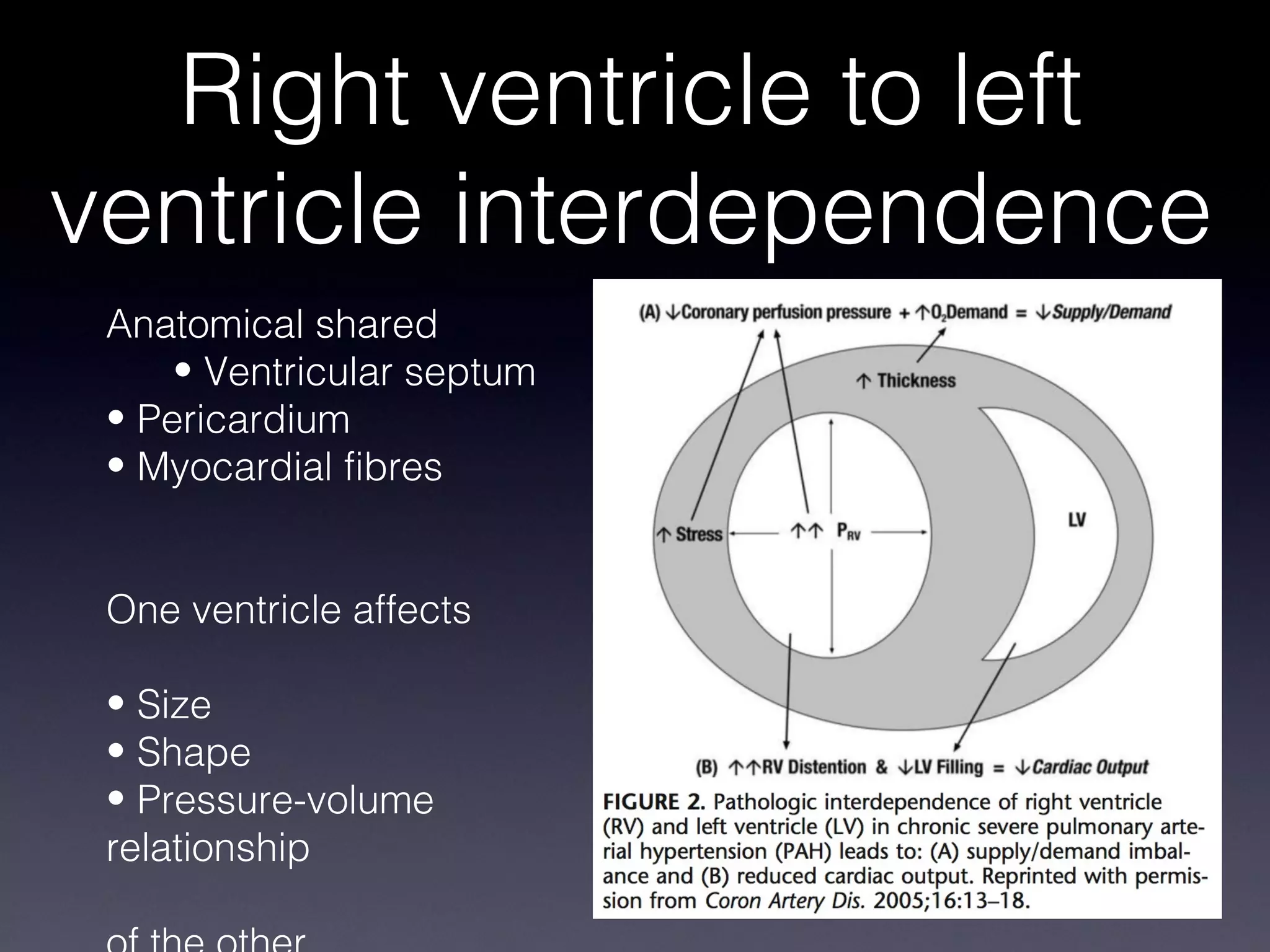
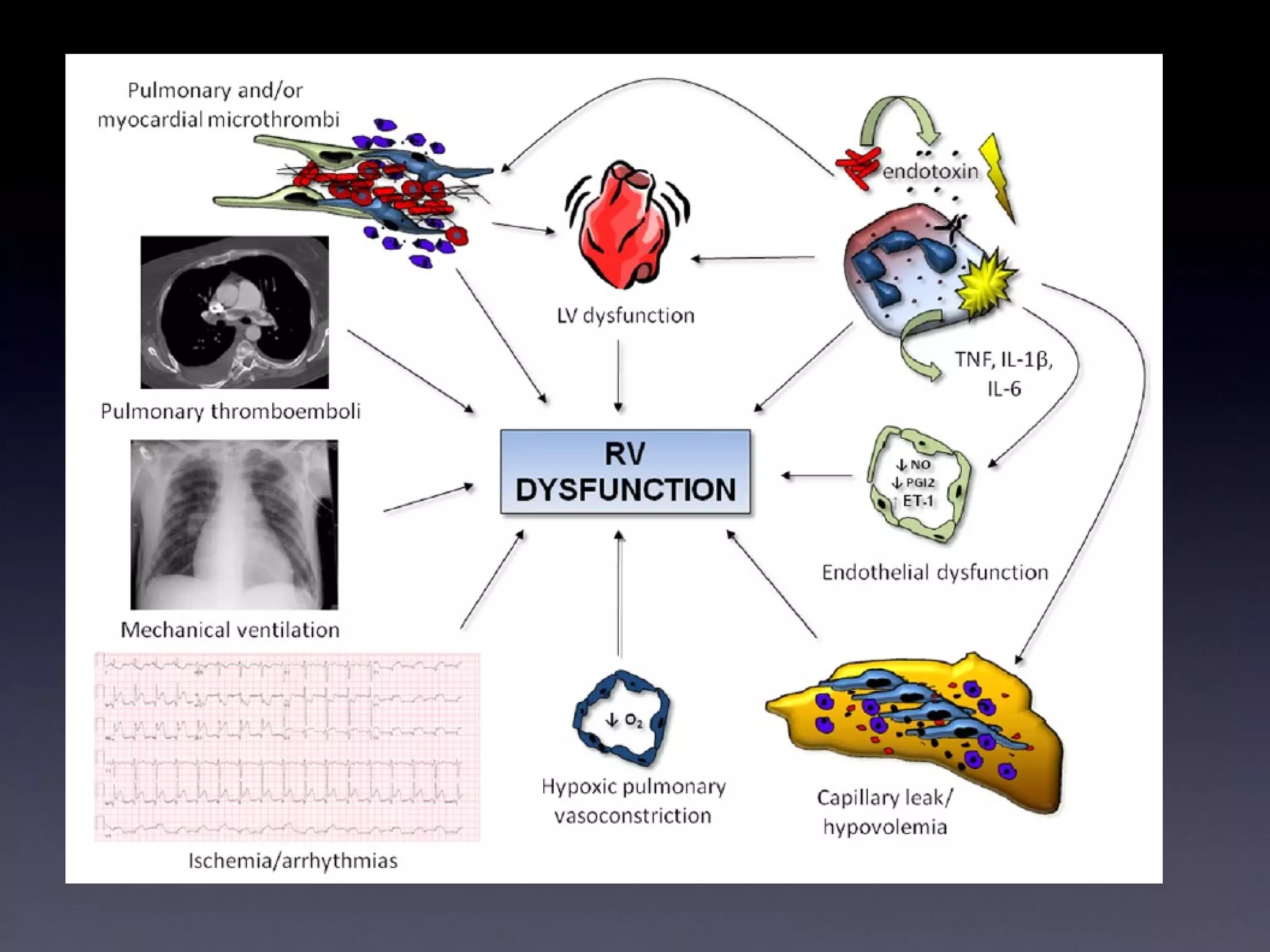
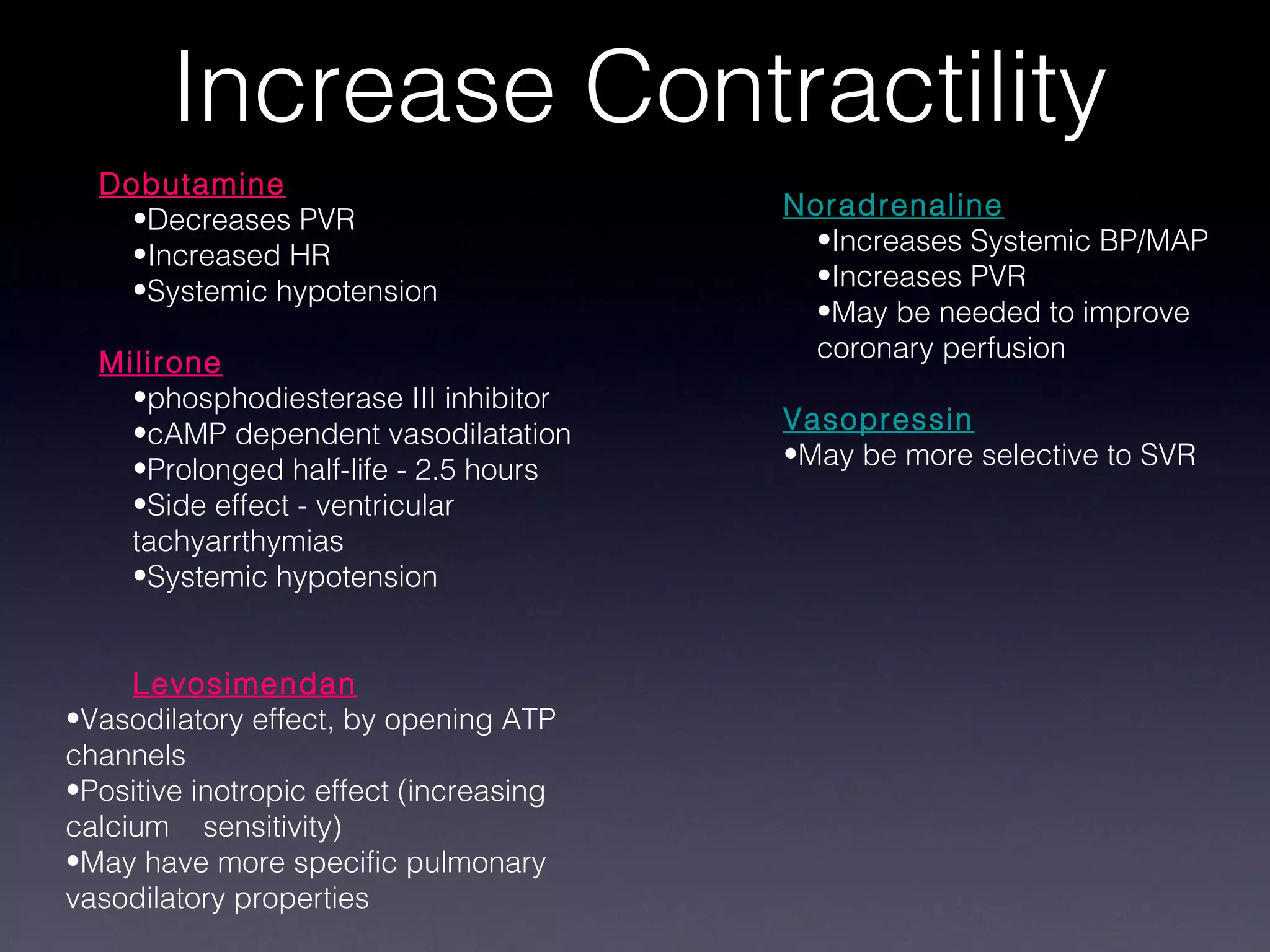
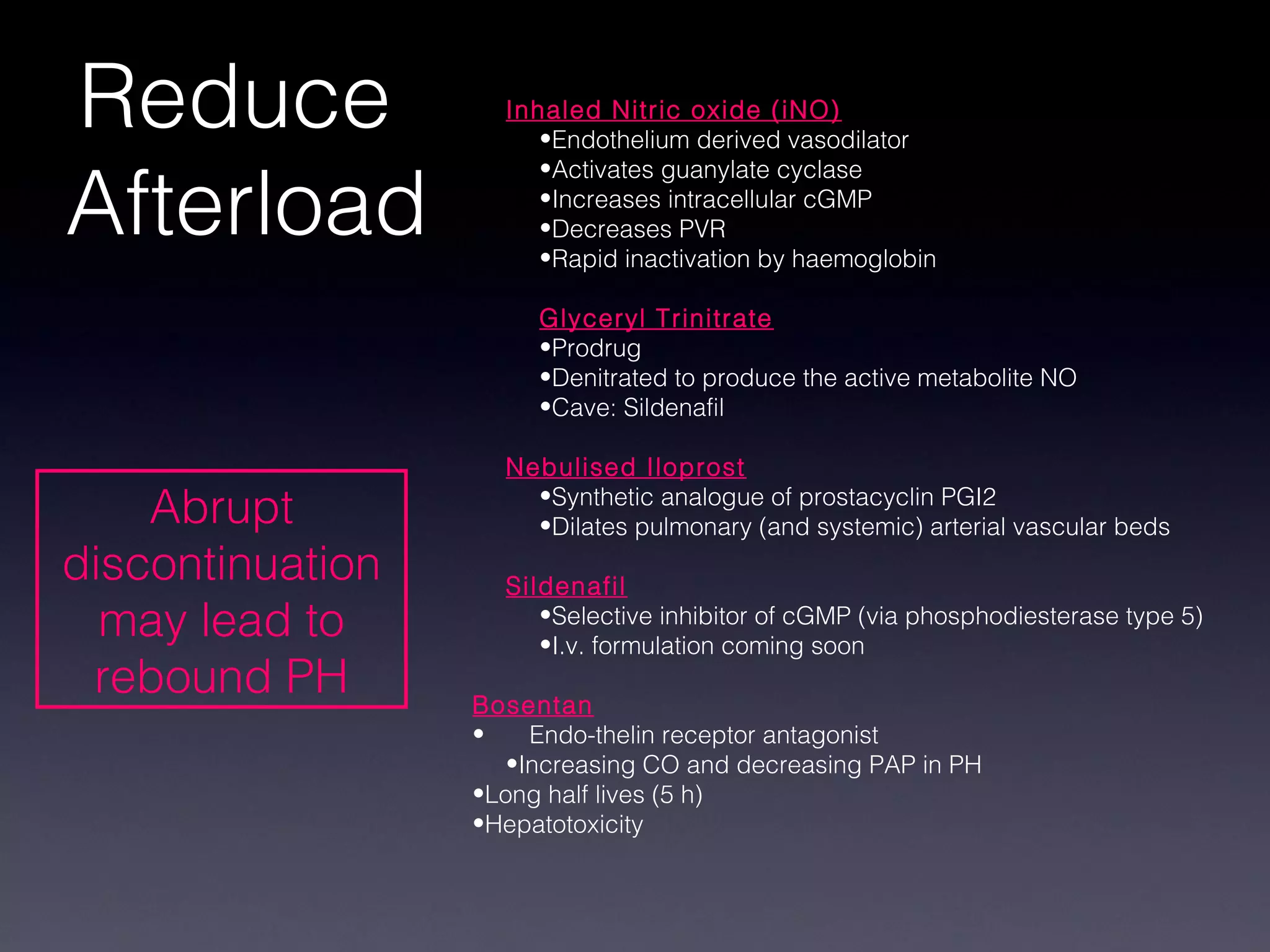
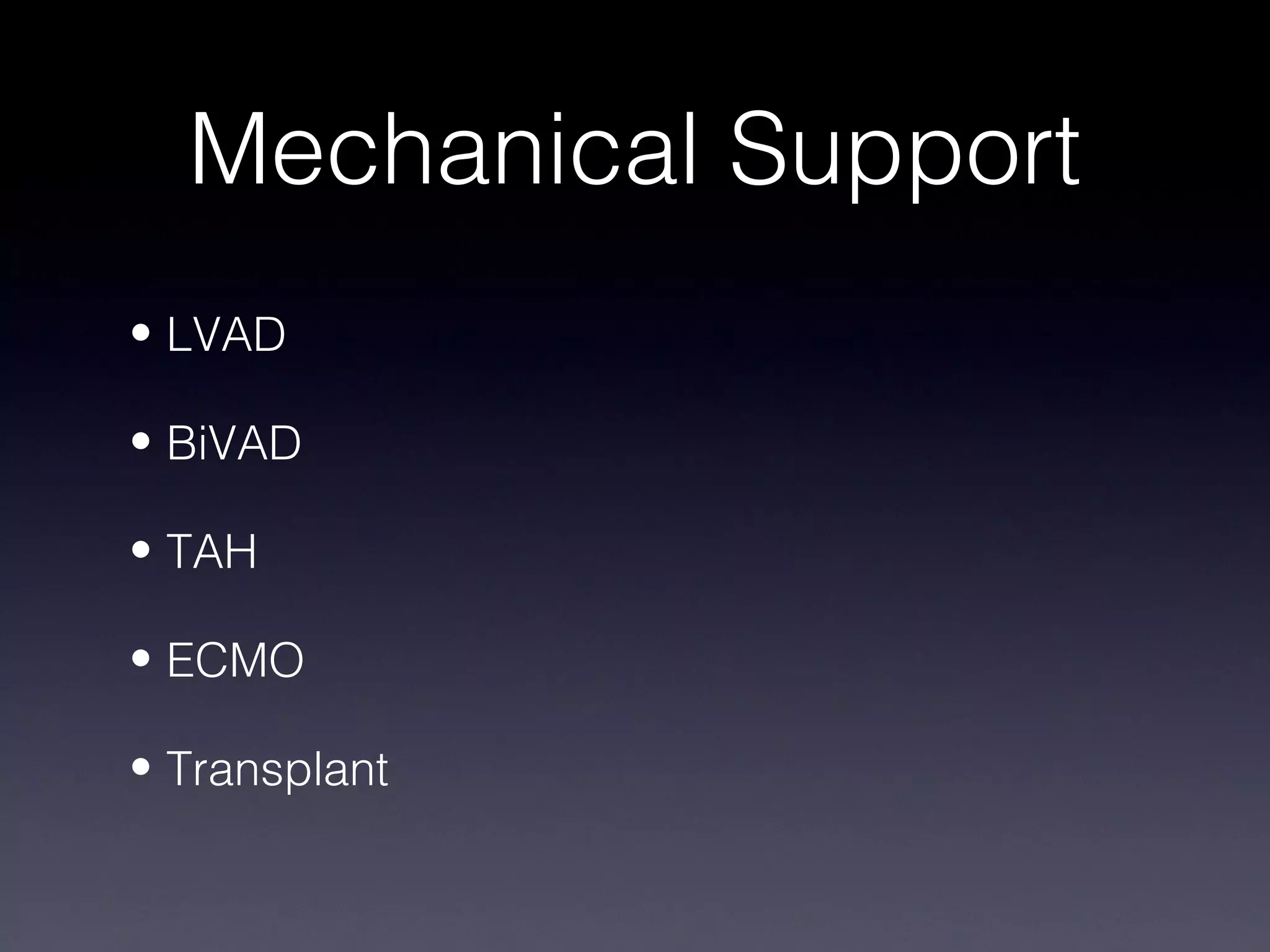
This document discusses treatment of right heart failure. It begins by explaining how the right heart is both similar and different to the left heart in its structure and function. It notes that right heart failure can be difficult to diagnose and monitor due to its complex geometry. The document then discusses why right heart failure sometimes requires treatment, focusing on conditions like pulmonary hypertension. It concludes by outlining approaches to treating right heart failure, such as treating the underlying cause, optimizing preload and contractility, reducing afterload, and considering mechanical support in severe cases.