This document summarizes two case studies presented at an immunohematology workshop on March 27, 2019.
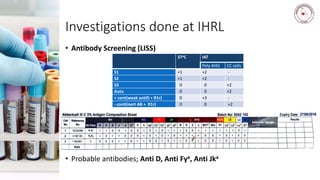
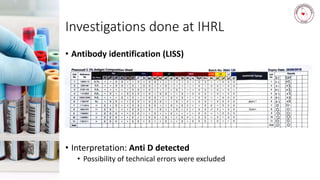
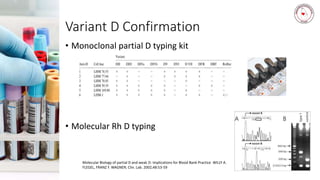
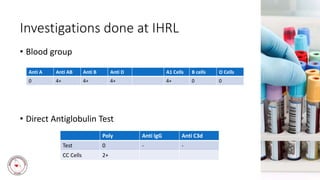
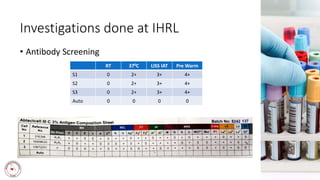
Case 1 involves a 28-year-old woman who experienced postpartum hemorrhaging. Testing found she was RhD positive with anti-D antibodies, indicating a previous sensitization event. Further testing identified her as R1r phenotype and a compatible blood unit was issued.
Case 2 involves a 78-year-old man in need of surgery who was found to have a pan-reactive antibody. Phenotyping identified anti-Hr0 (Rh17), a rare antibody. Finding compatible blood was difficult as his phenotype was not found in his family. Autologous donation was suggested due to the r