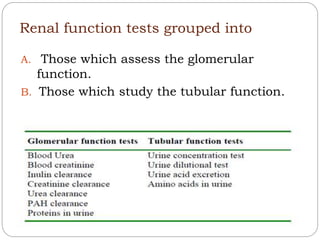
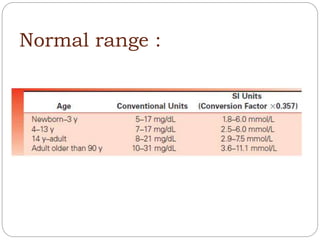
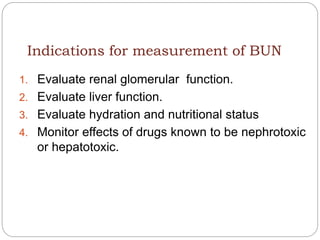
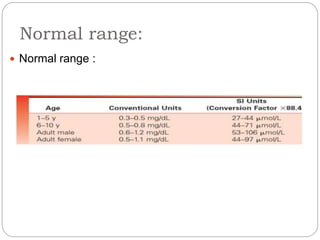
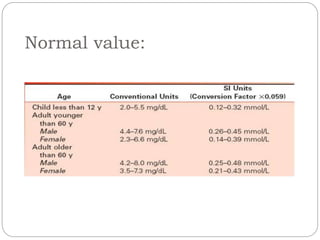
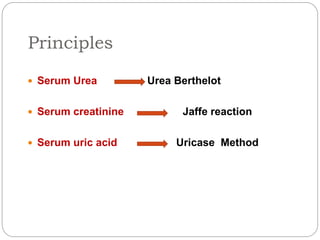
This document discusses renal function tests (RFTs) which are used to assess kidney function. RFTs are grouped into those that assess glomerular function, including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine, and those that assess tubular function, such as uric acid. BUN, creatinine, and uric acid are measured using spectrometry. BUN indicates glomerular filtration and is used to screen for renal disease. Creatinine is produced from muscle metabolism and excreted by the kidneys to assess renal function. Uric acid comes from nucleic acid breakdown and while not a primary test, can help diagnose gout or determine the cause of kidney stones.