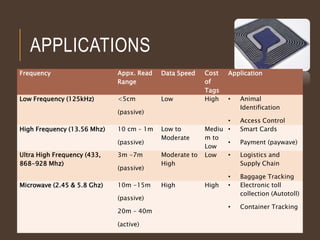
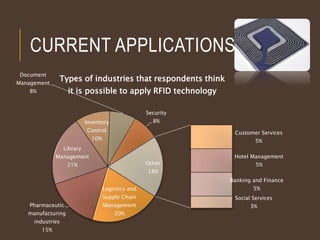
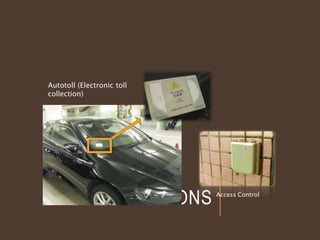
This document discusses RFID technology and its applications. It begins with an introduction to RFID, describing its components and different tag types. Applications that were discussed include logistics, inventory control, libraries, and electronic toll collection. The document also summarizes the results of an online survey on opinions of RFID. It concludes that RFID provides benefits like contactless reading and updating data, though costs remain higher than barcodes and standards are still being developed.