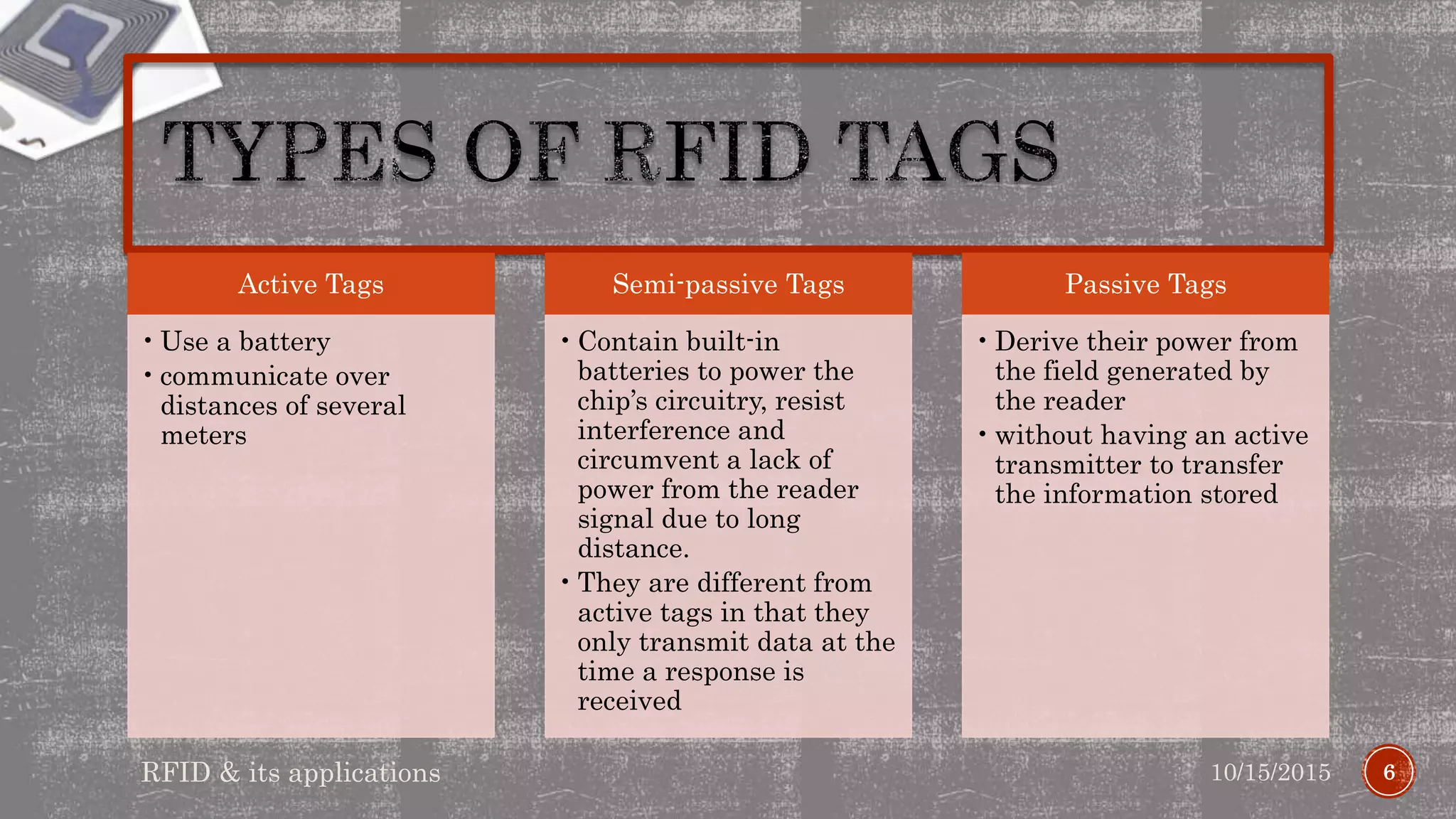
The document discusses RFID (radio frequency identification), which uses radio waves to electronically identify objects. It describes the basic components of an RFID system including RFID tags containing chips and antennas, readers, and application software. It also discusses the different types of RFID tags and their typical read ranges and data speeds. Examples of RFID applications mentioned include payment cards, electronic toll collection, access control, and supply chain/logistics.