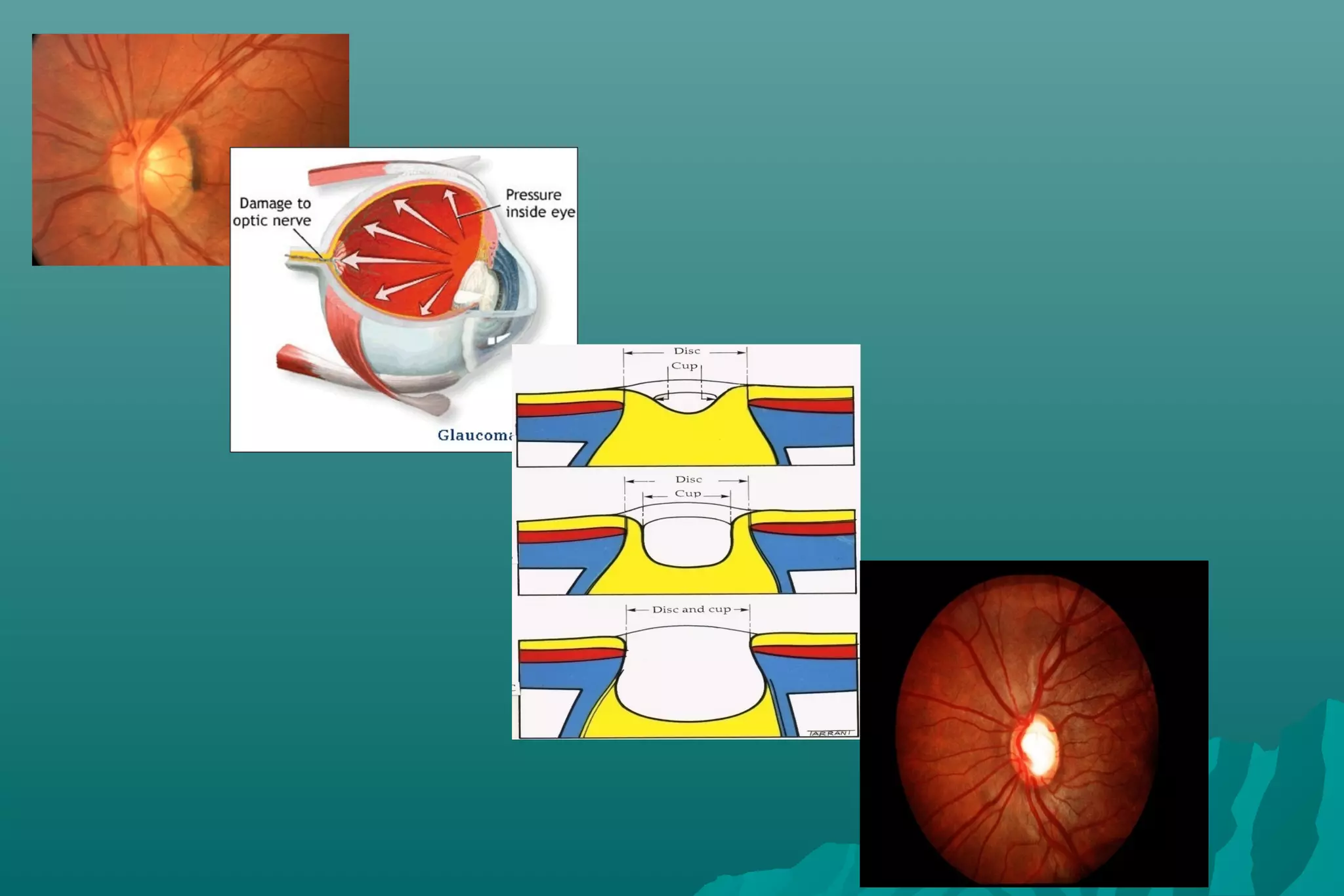
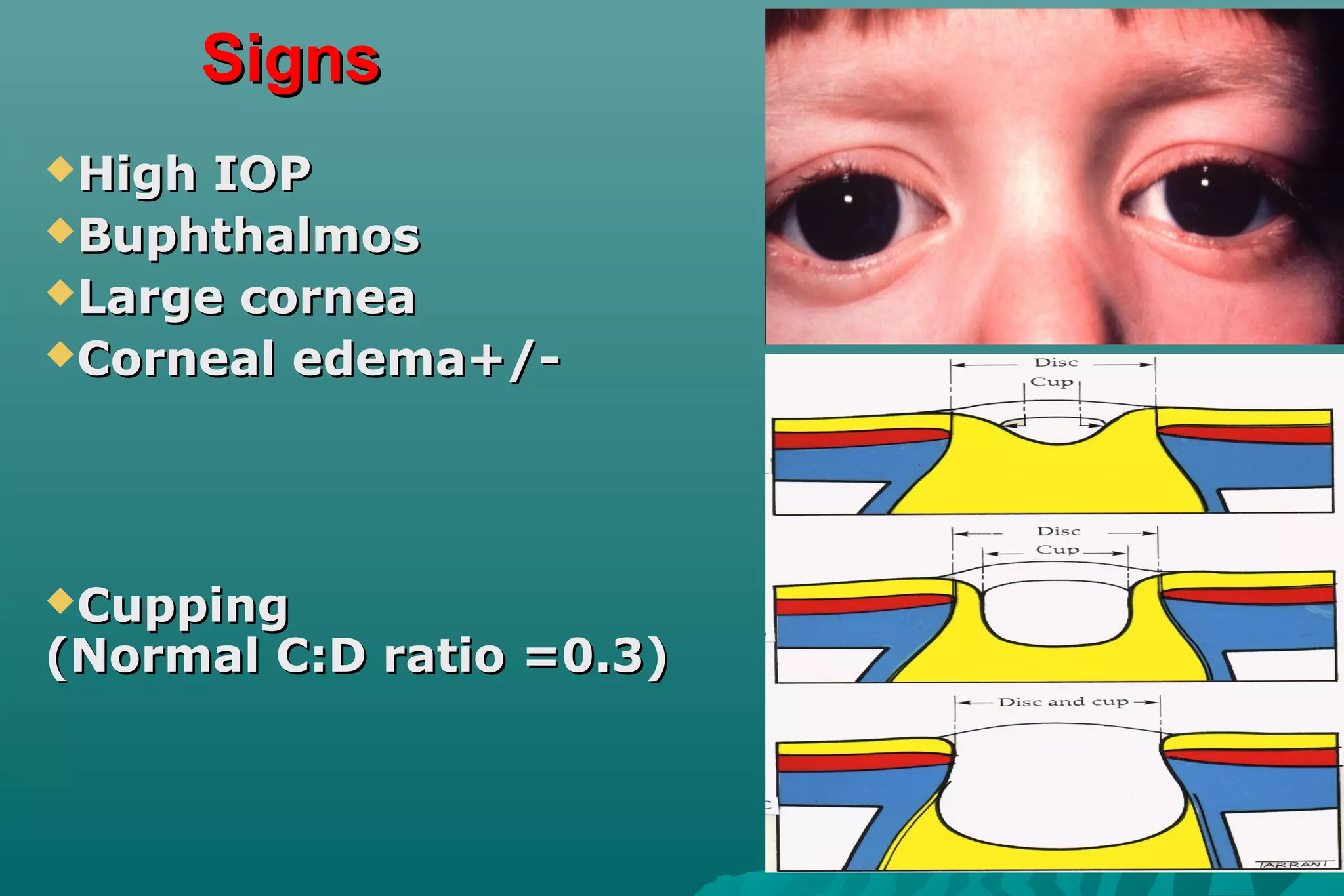
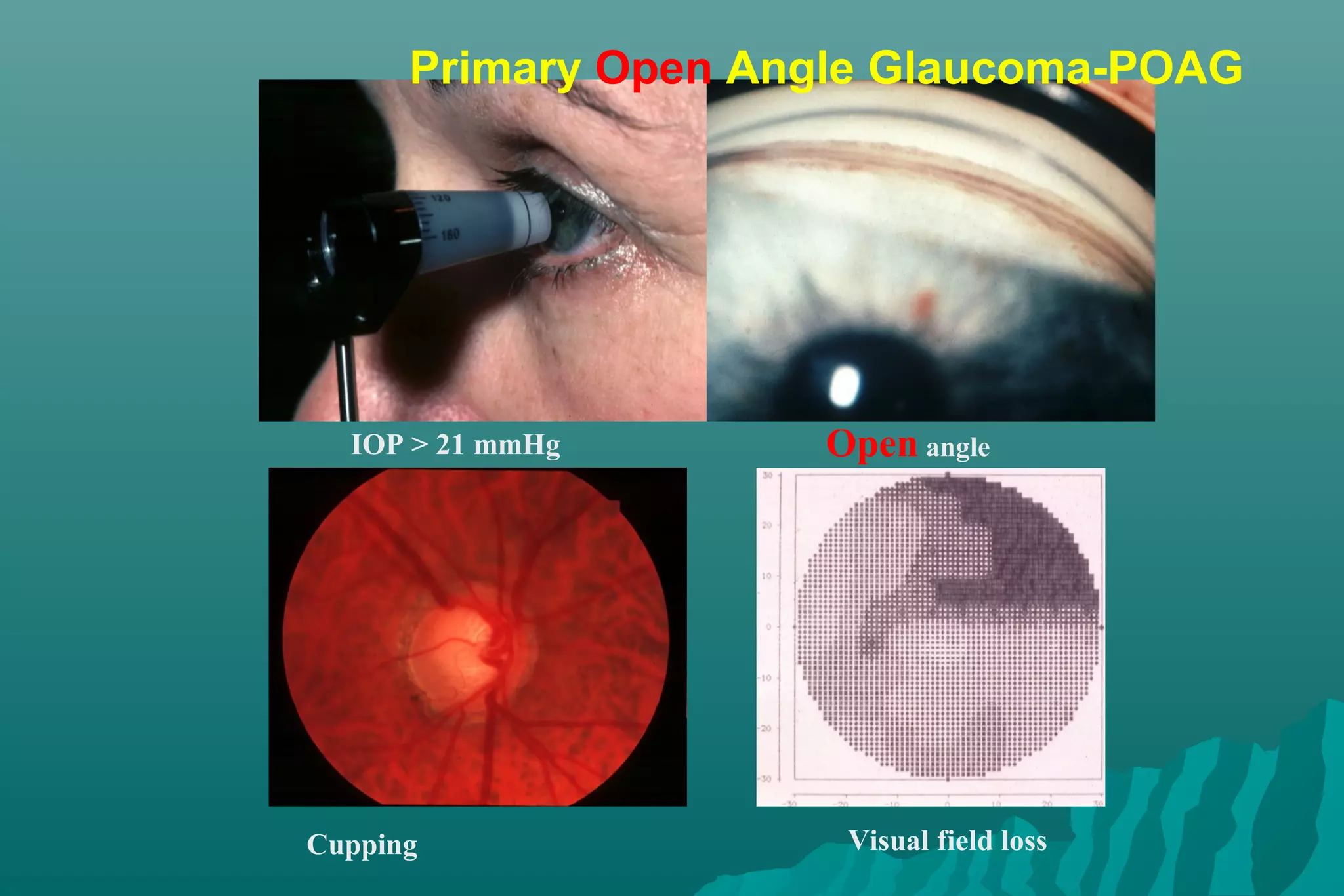
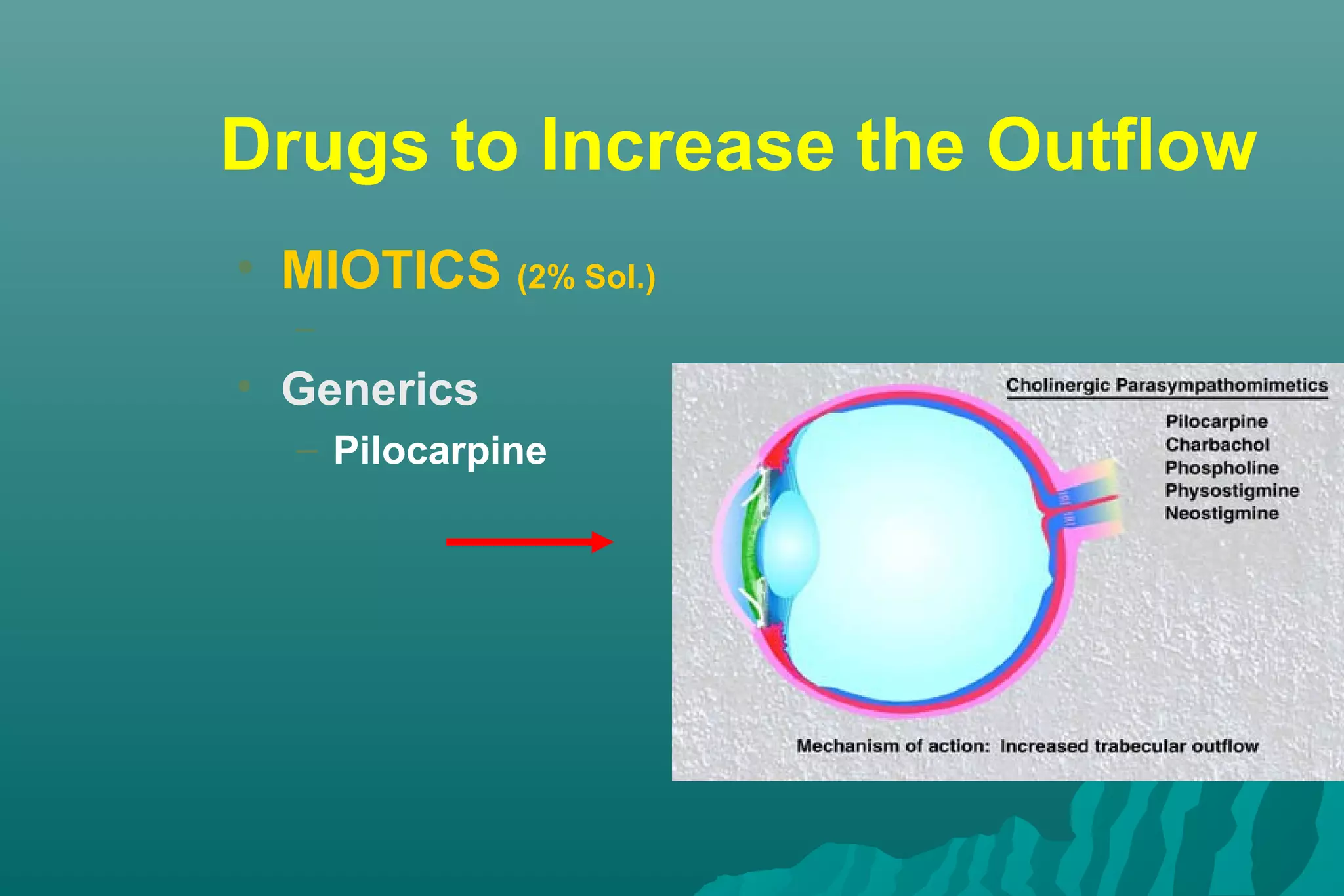
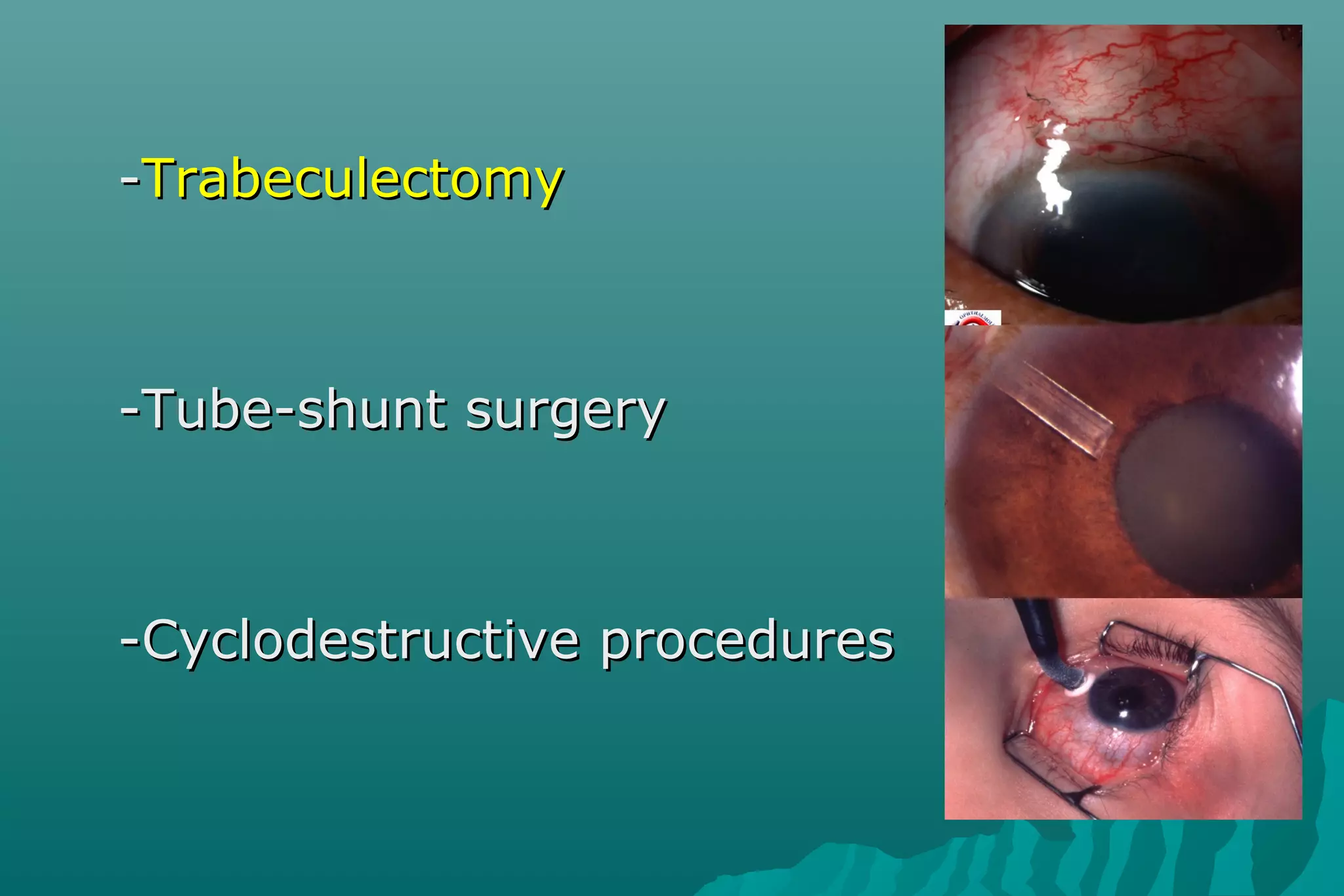
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve and cause vision loss. It is often associated with an abnormally high pressure inside the eye. There are several types of glaucoma including primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), angle-closure glaucoma (ACG), and secondary glaucoma due to other health conditions. Glaucoma is managed through medication, laser treatment, or surgery depending on the type and severity. The goal is to prevent further optic nerve damage and vision loss.