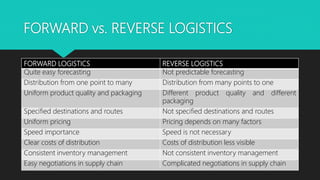
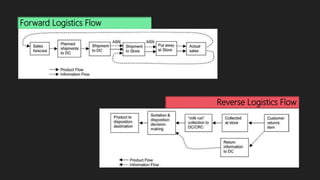
The document discusses reverse logistics, emphasizing its role in managing product flow from consumers back to manufacturers for recovery or disposal. It covers challenges, methods, and examples from industries like electronics and mobile phones, highlighting the significance of effective reverse logistics in enhancing customer satisfaction and financial performance. Overall, it presents a comprehensive view of the importance of reverse logistics in modern supply chain management.