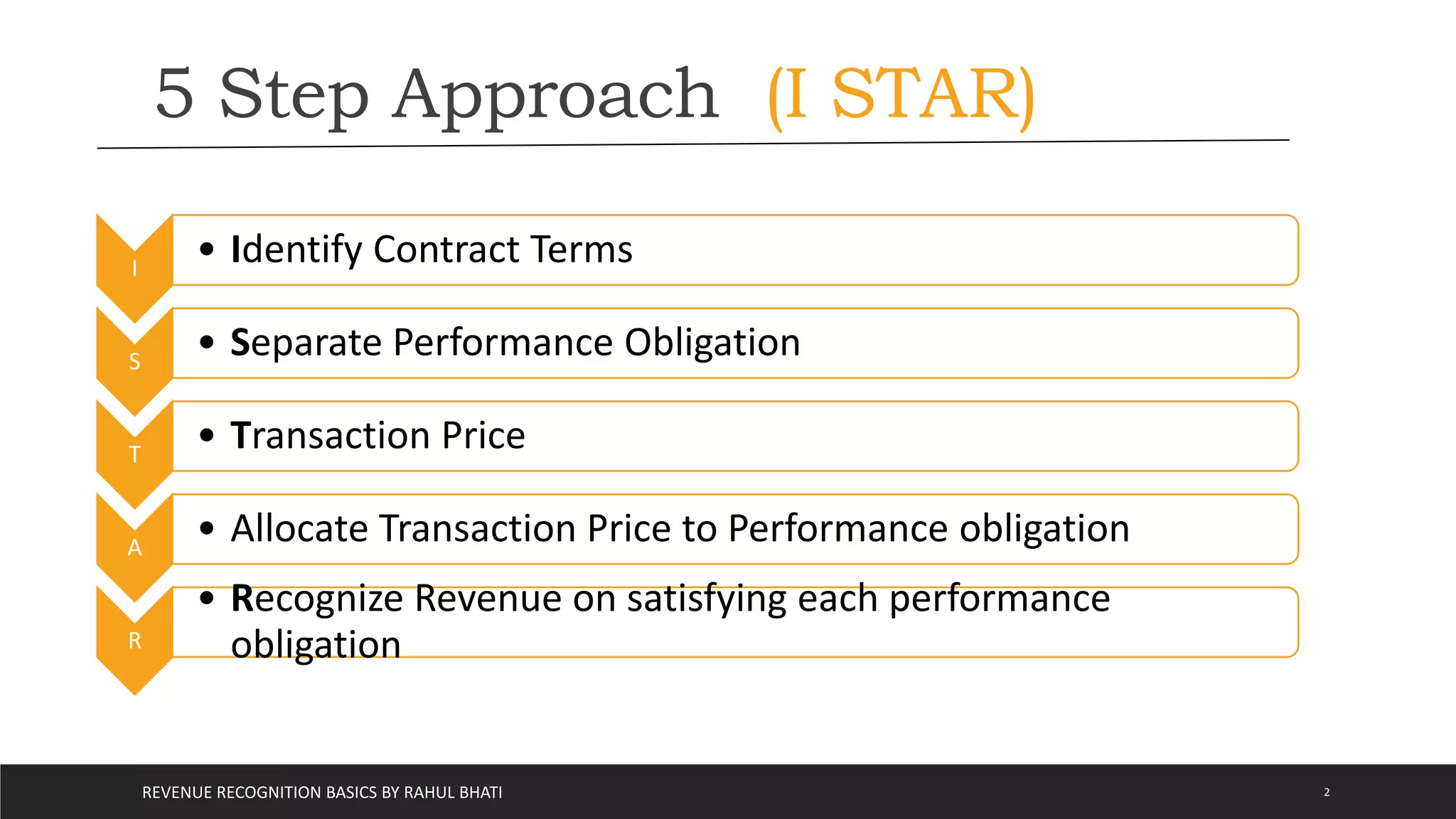
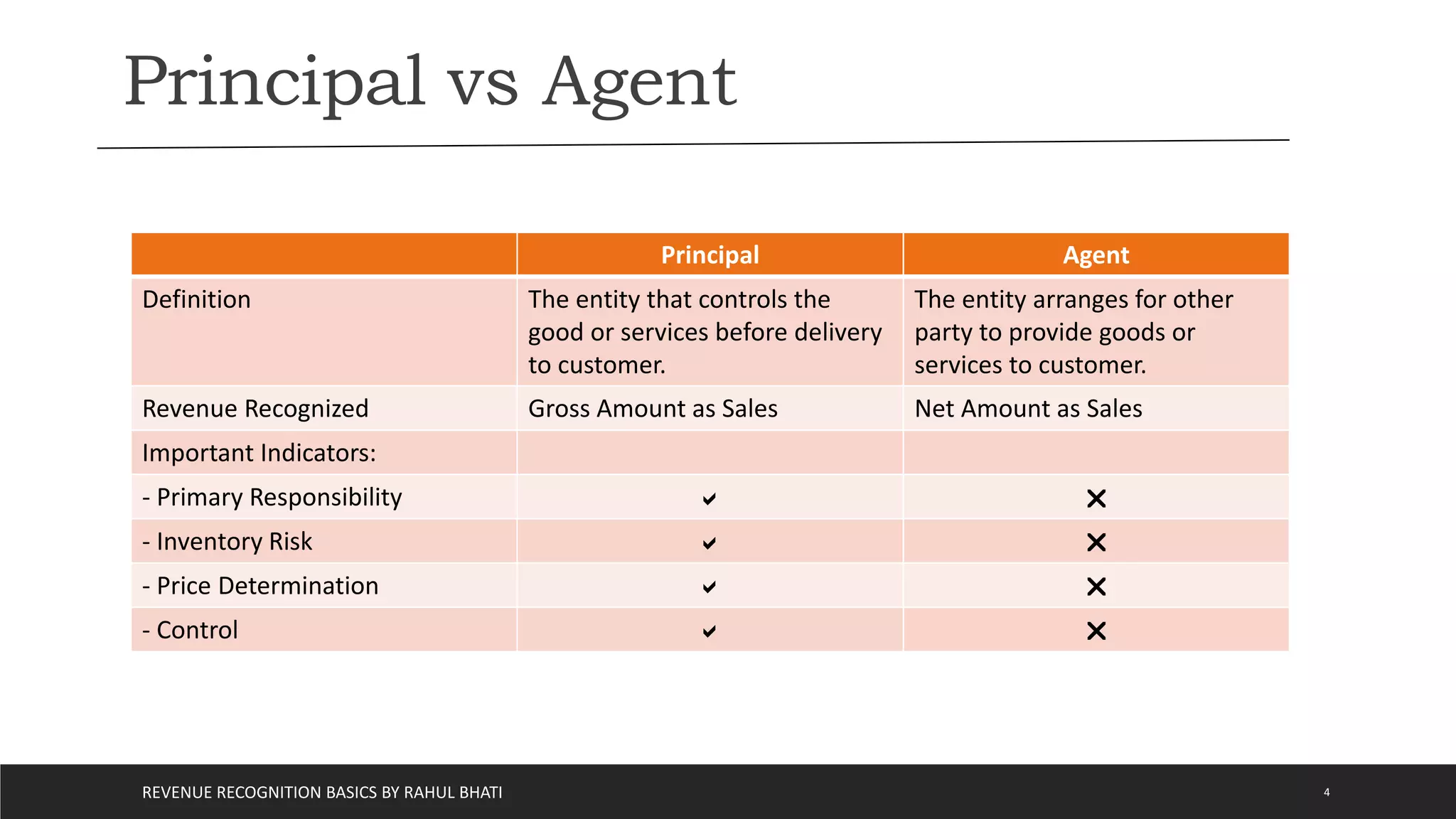
The document outlines the basics of revenue recognition under ASC 606, detailing a 5-step approach including identifying contracts, performance obligations, and transaction prices. It distinguishes between recognizing revenue at a point in time versus over a period and explains the roles of principal and agent in revenue recognition. The document also addresses long-term construction contracts, highlighting methods for revenue recognition such as percentage of completion and completed contracts.