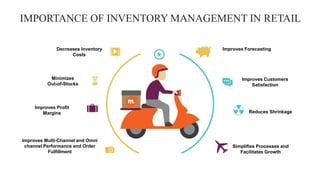
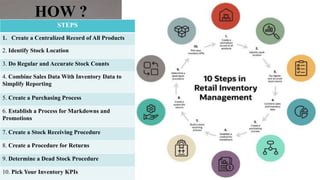
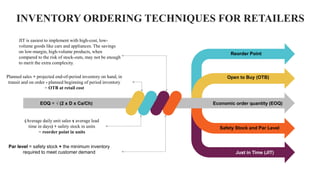
Retail inventory management involves maintaining appropriate stock levels to meet demand without over-purchasing. An inventory management plan guides purchasing, pricing, receiving, counting, and tracking inventory. Key aspects of retail inventory management include classifying items into A, B, and C categories based on value and cost; using techniques like economic order quantity, reorder points, and safety stock; accounting for inventory using FIFO or LIFO; analyzing inventory turnover and forecasting demand. Effective retail inventory management relies on people, processes, technology, understanding sales patterns, leveraging automation, and focusing on customers.