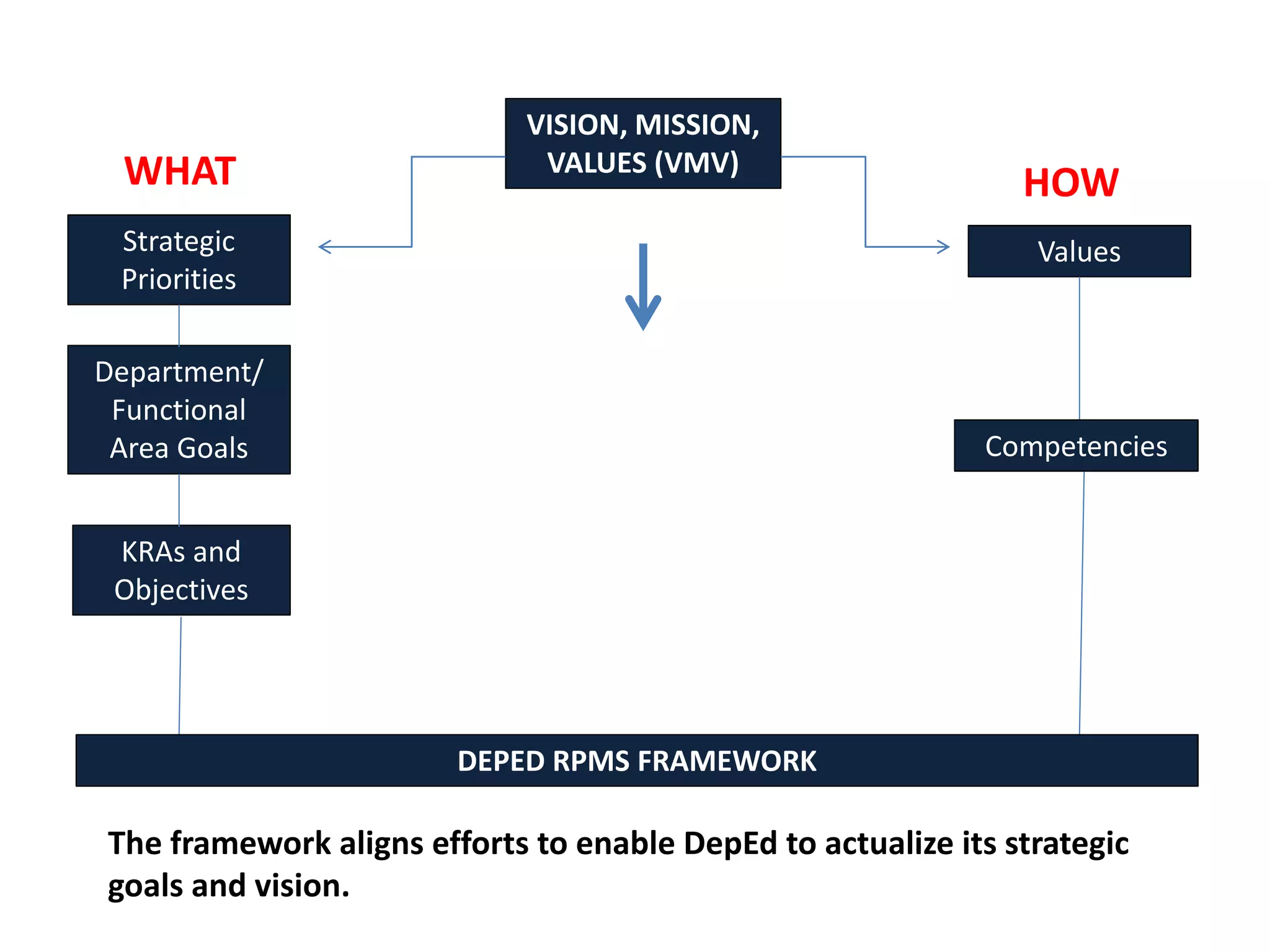
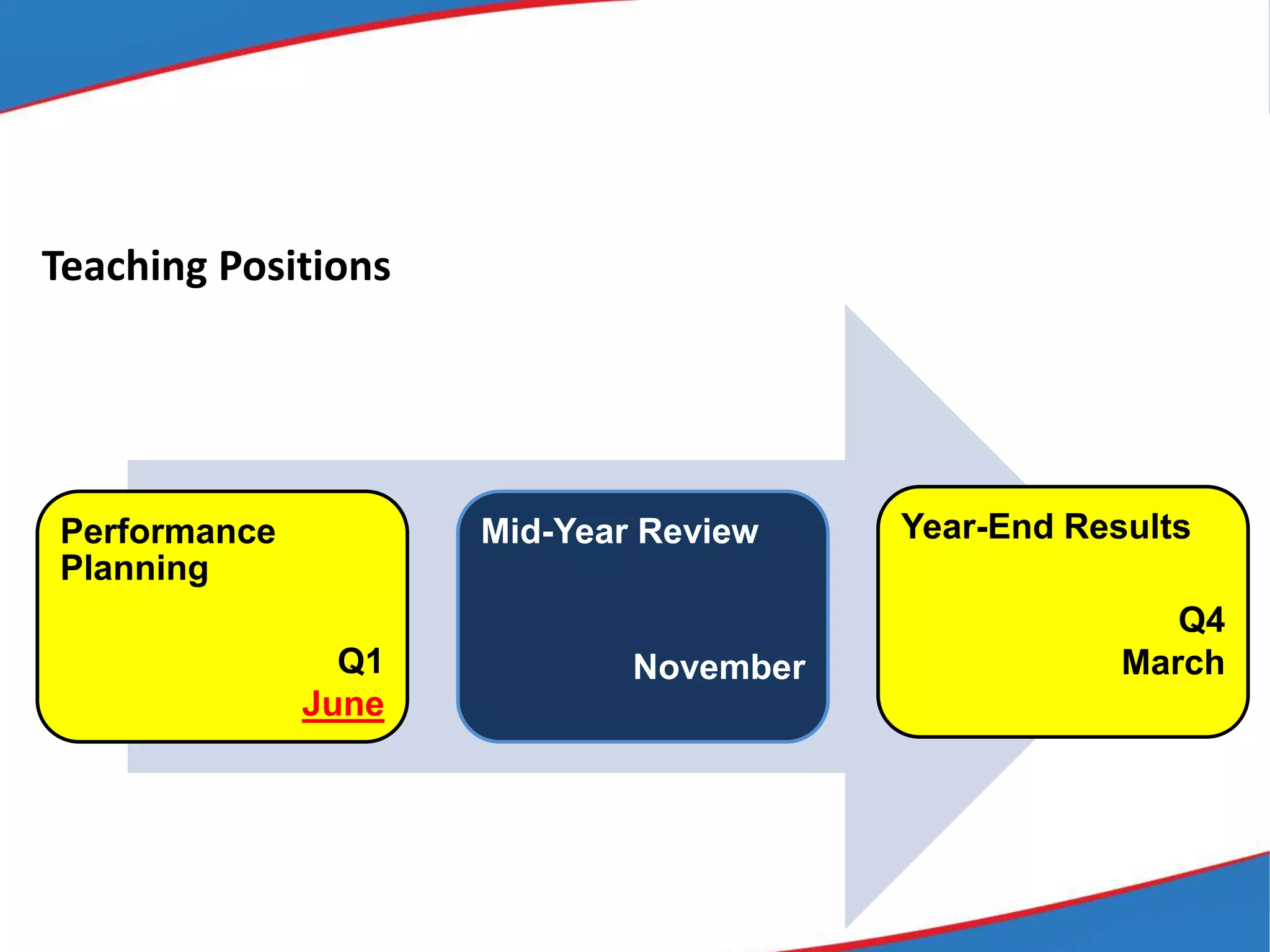
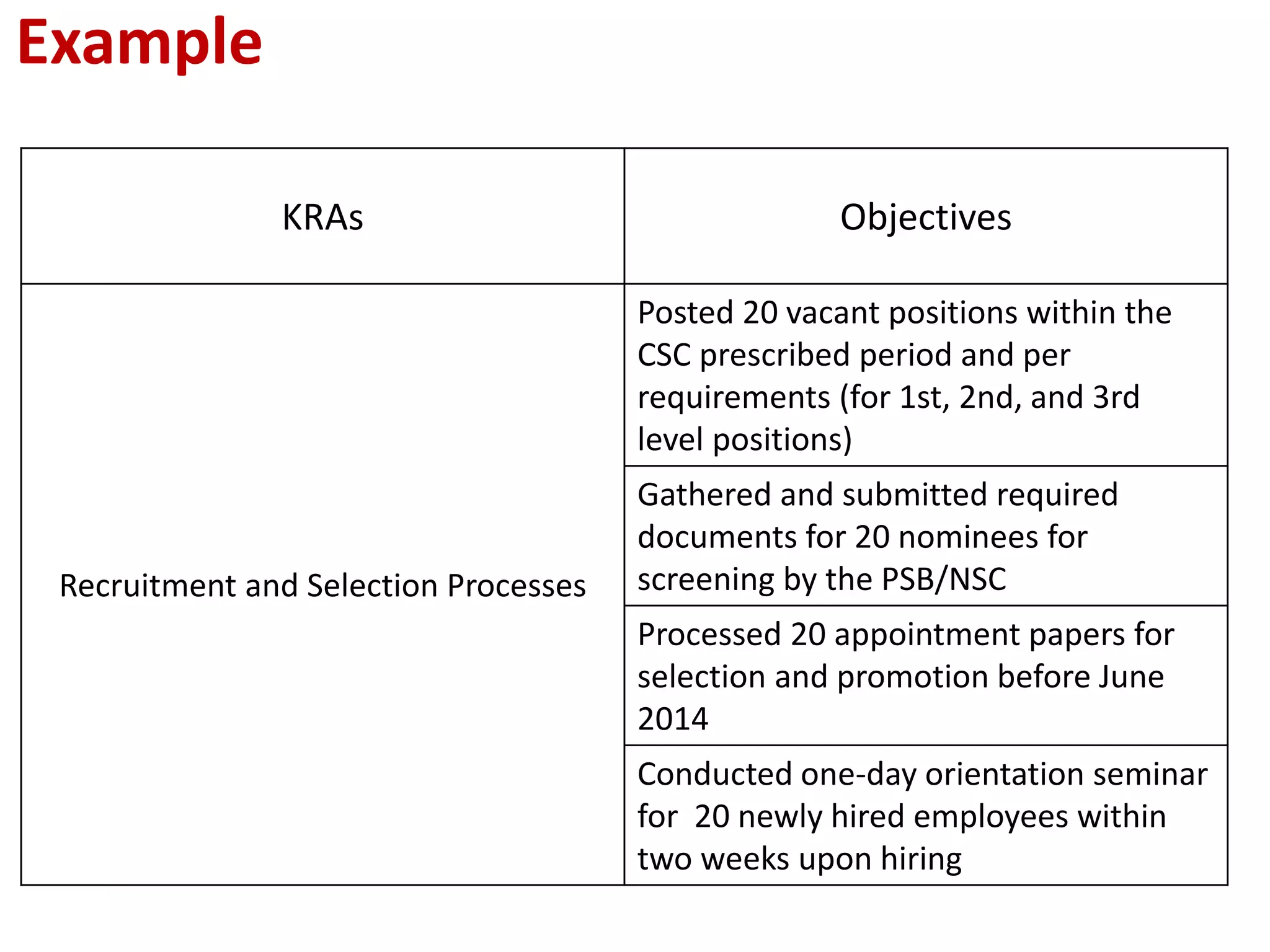
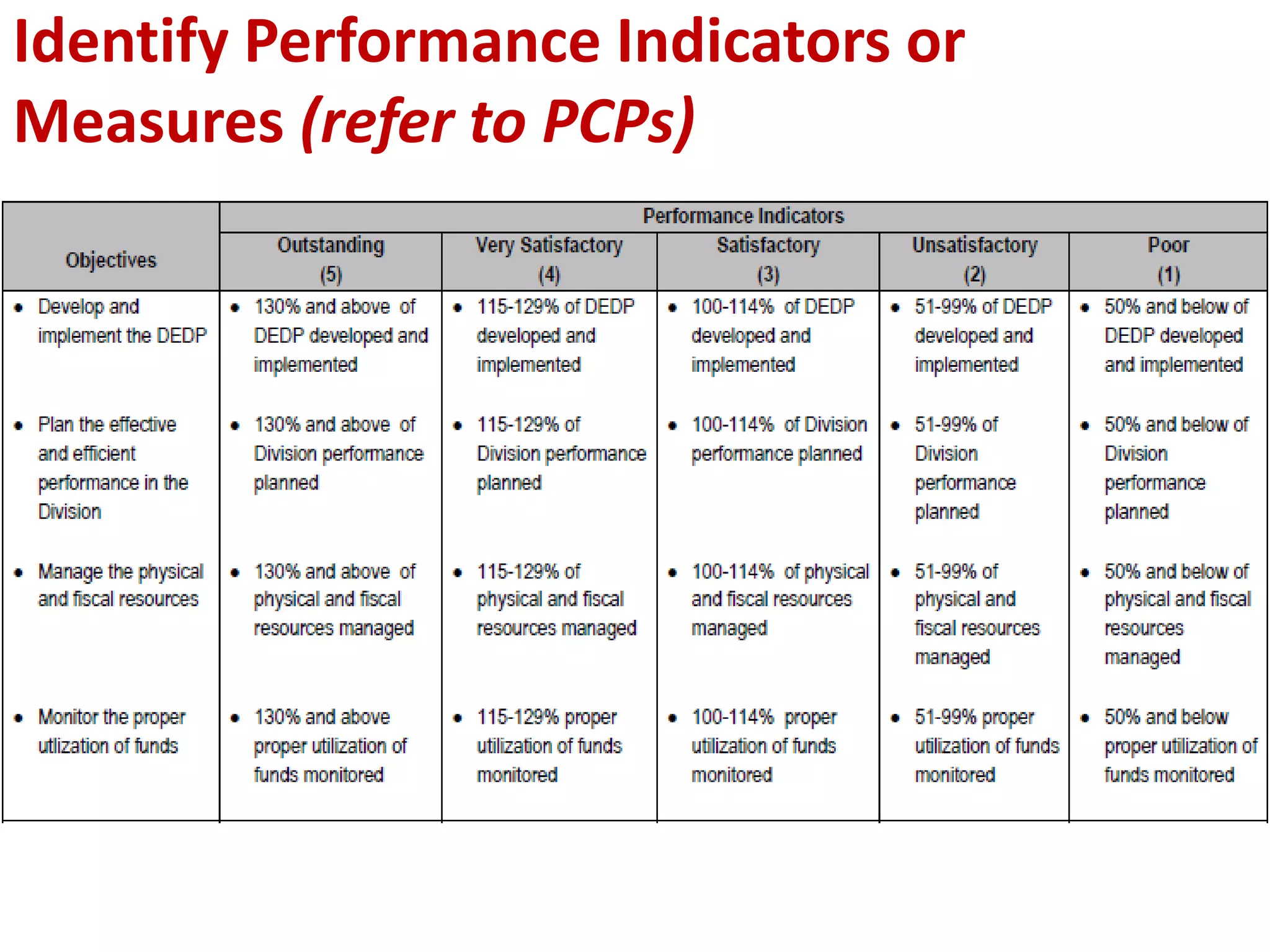
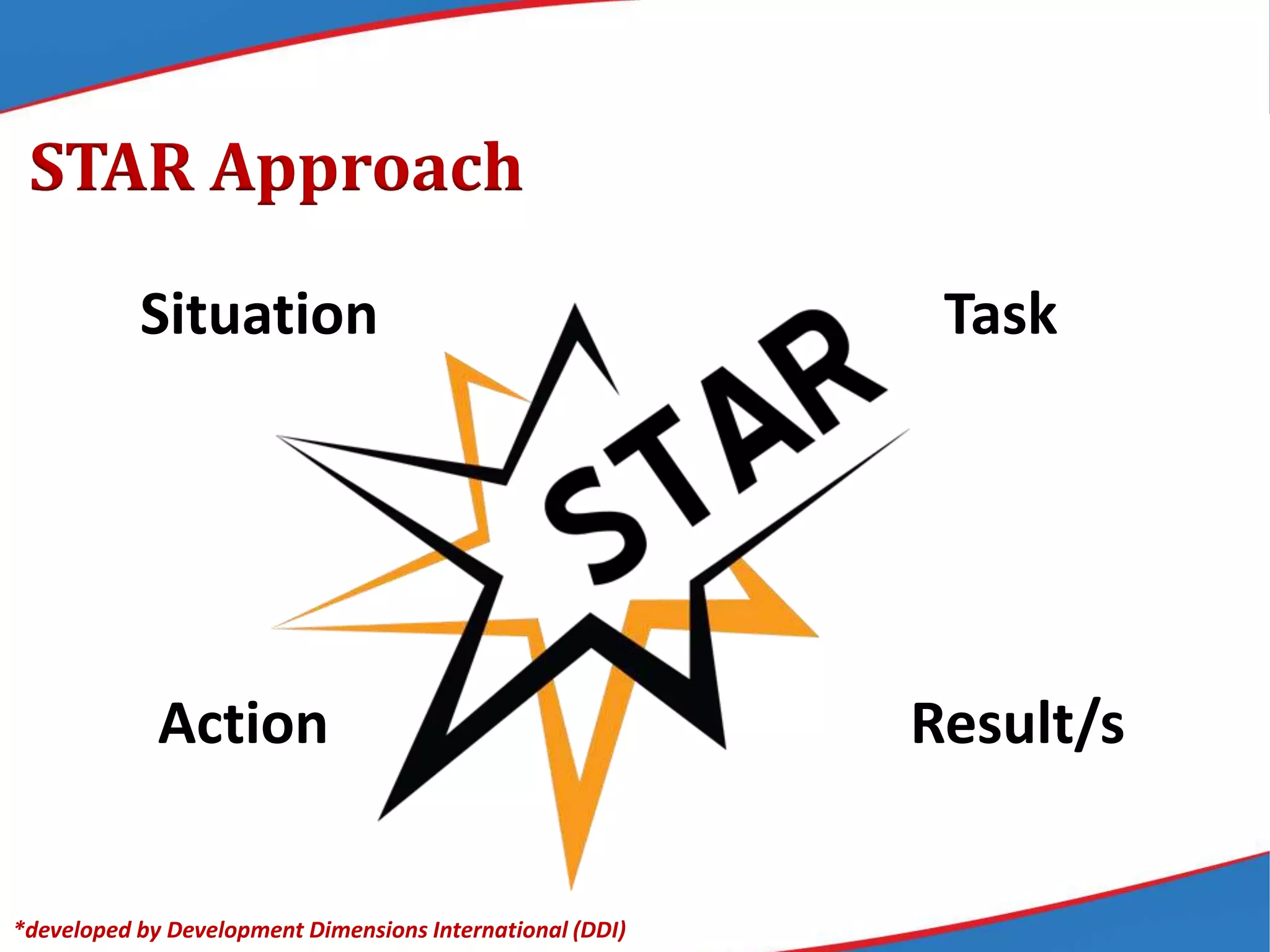
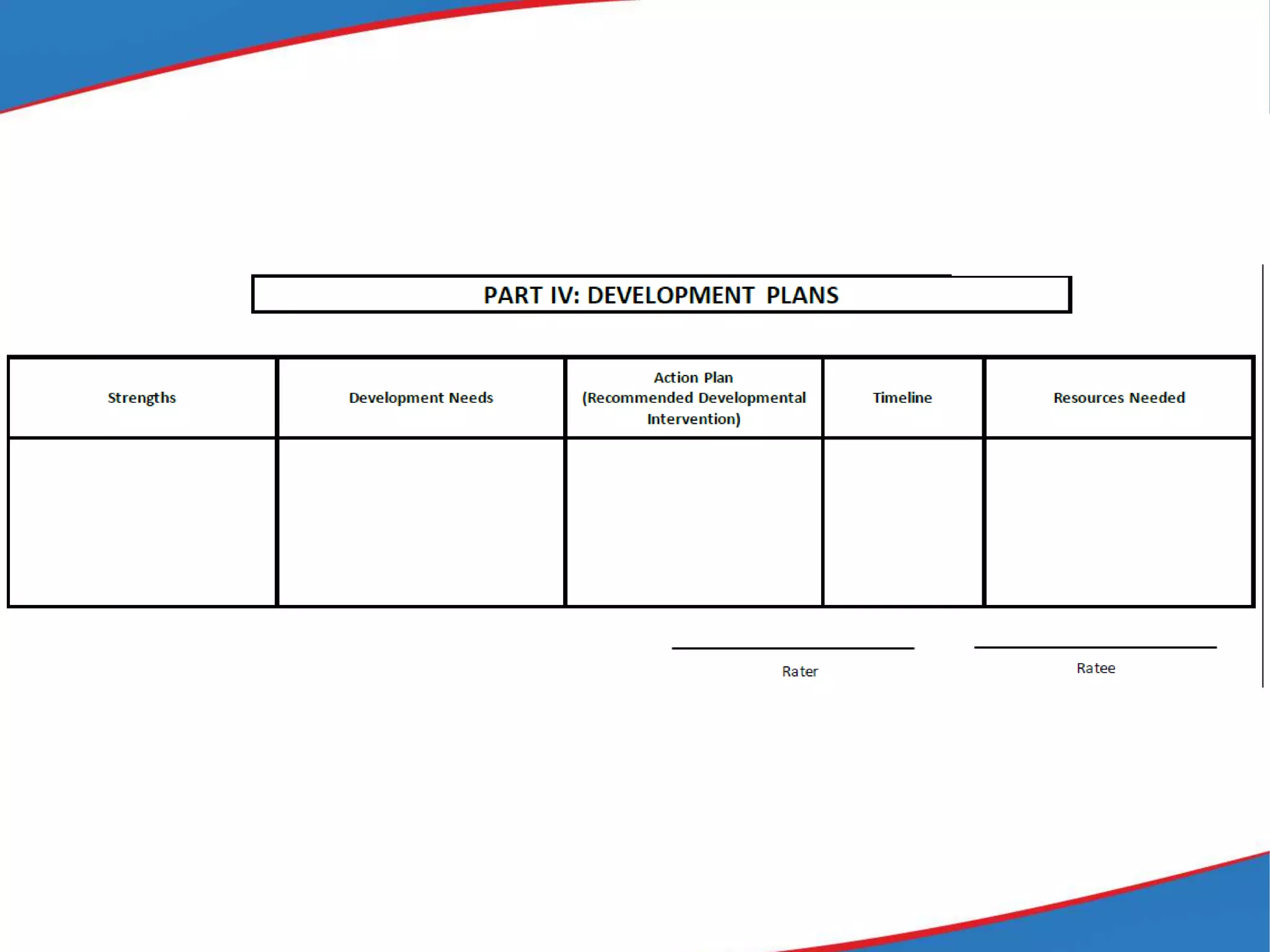
The document provides an overview of the Results-based Performance Management System (RPMS) used by the Department of Education (DepEd) in the Philippines. The RPMS framework aligns employee efforts to achieve DepEd's strategic goals and vision. It is a 4-phase system that includes: 1) performance planning and commitment; 2) performance monitoring and coaching; 3) performance review and evaluation; and 4) performance rewarding and development planning. The RPMS focuses not just on results but how they are achieved through competencies. It provides a systematic approach for continuous work improvement and individual growth.