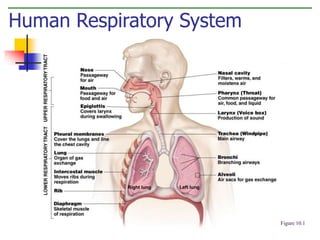
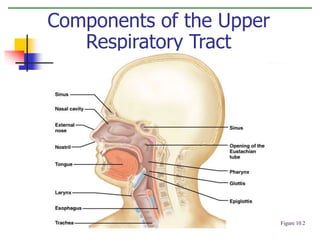
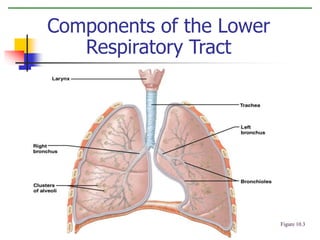
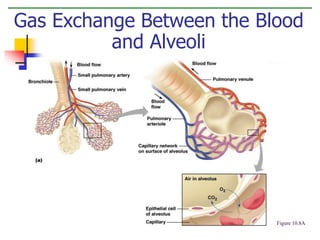
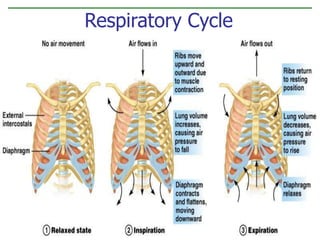
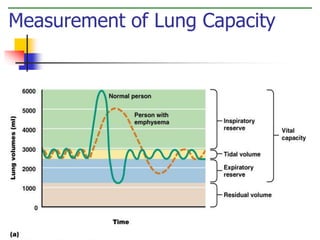
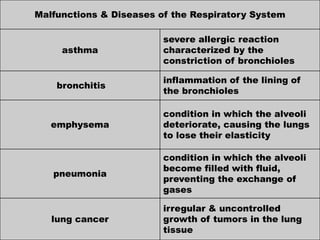
The document discusses the human respiratory system and the process of respiration. It describes the major organs involved, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. It explains that the respiratory system allows for the intake of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide through the processes of inspiration and expiration. The document also outlines some common respiratory diseases and disorders like asthma, bronchitis, emphysema and pneumonia.