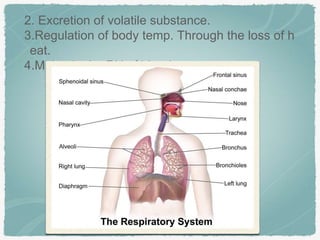
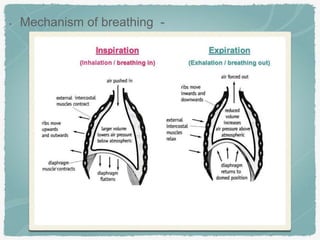
The document discusses the respiratory system as part of a B.Pharm course, highlighting the definitions of breathing and respiration, their functions, and the anatomical structures involved. It details the mechanism of breathing, including respiratory volumes and capacities such as tidal volume and vital capacity. Additionally, it outlines disorders like asthma and emphysema, emphasizing the impact of smoking on respiratory health.