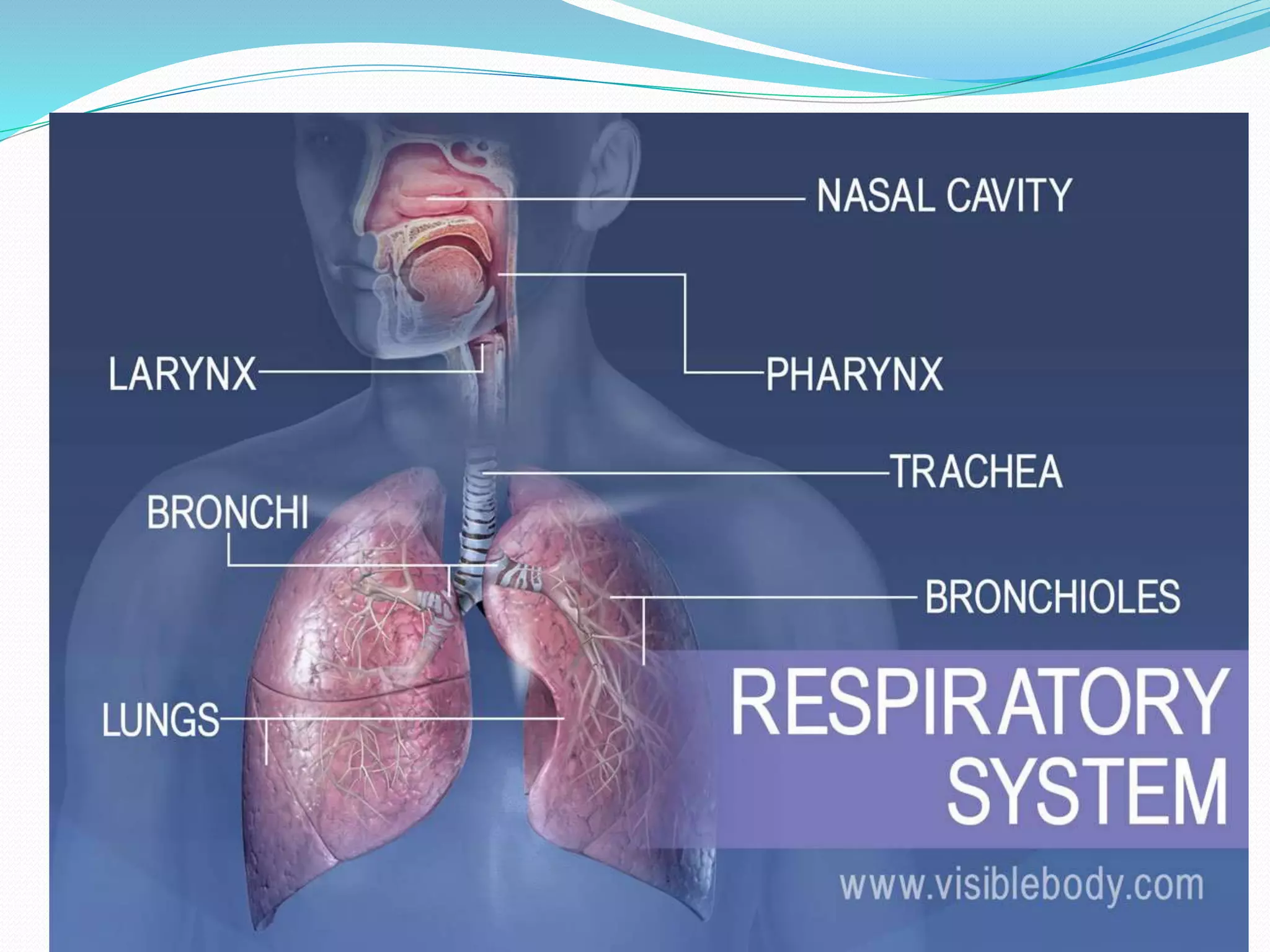
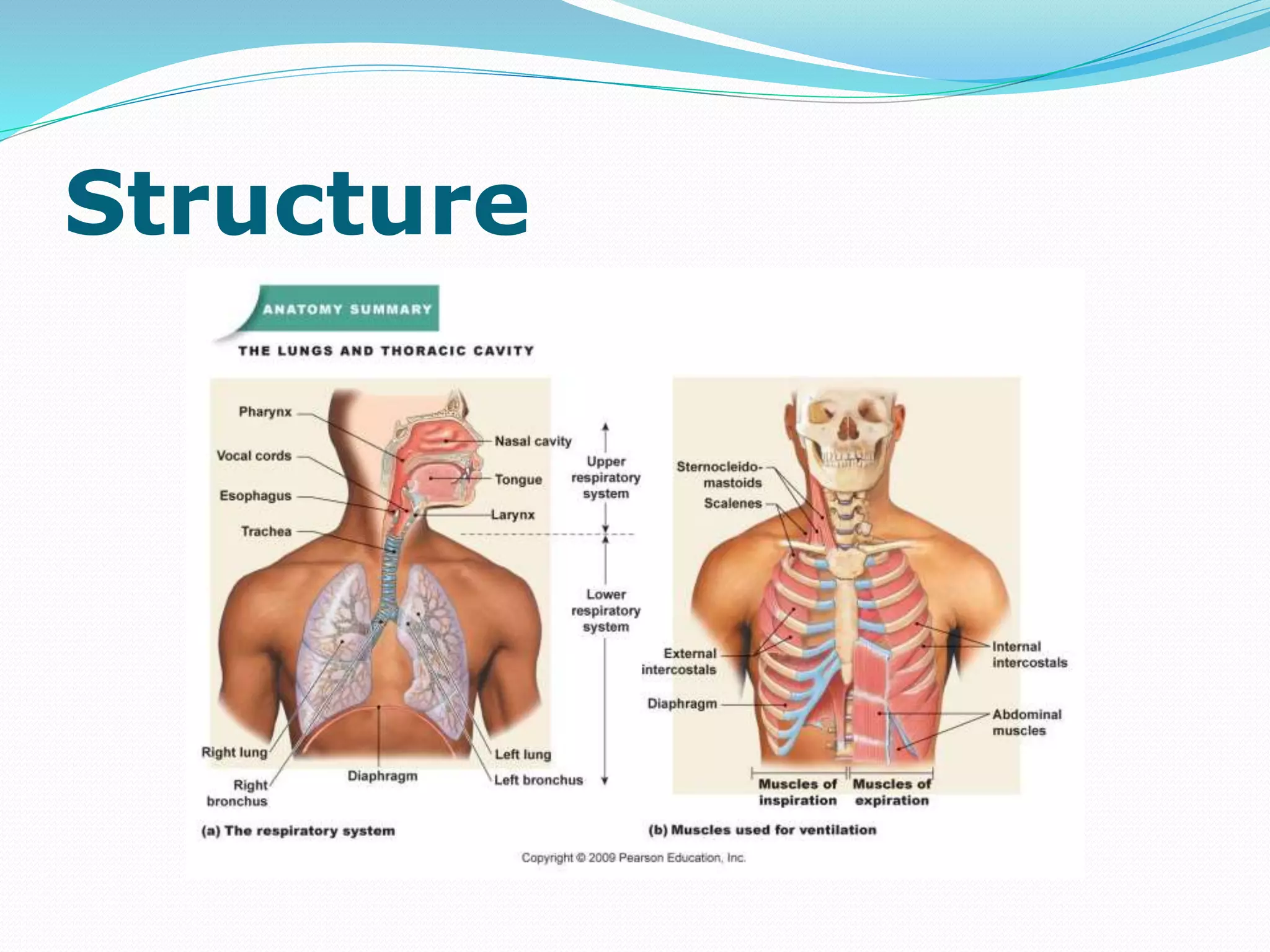
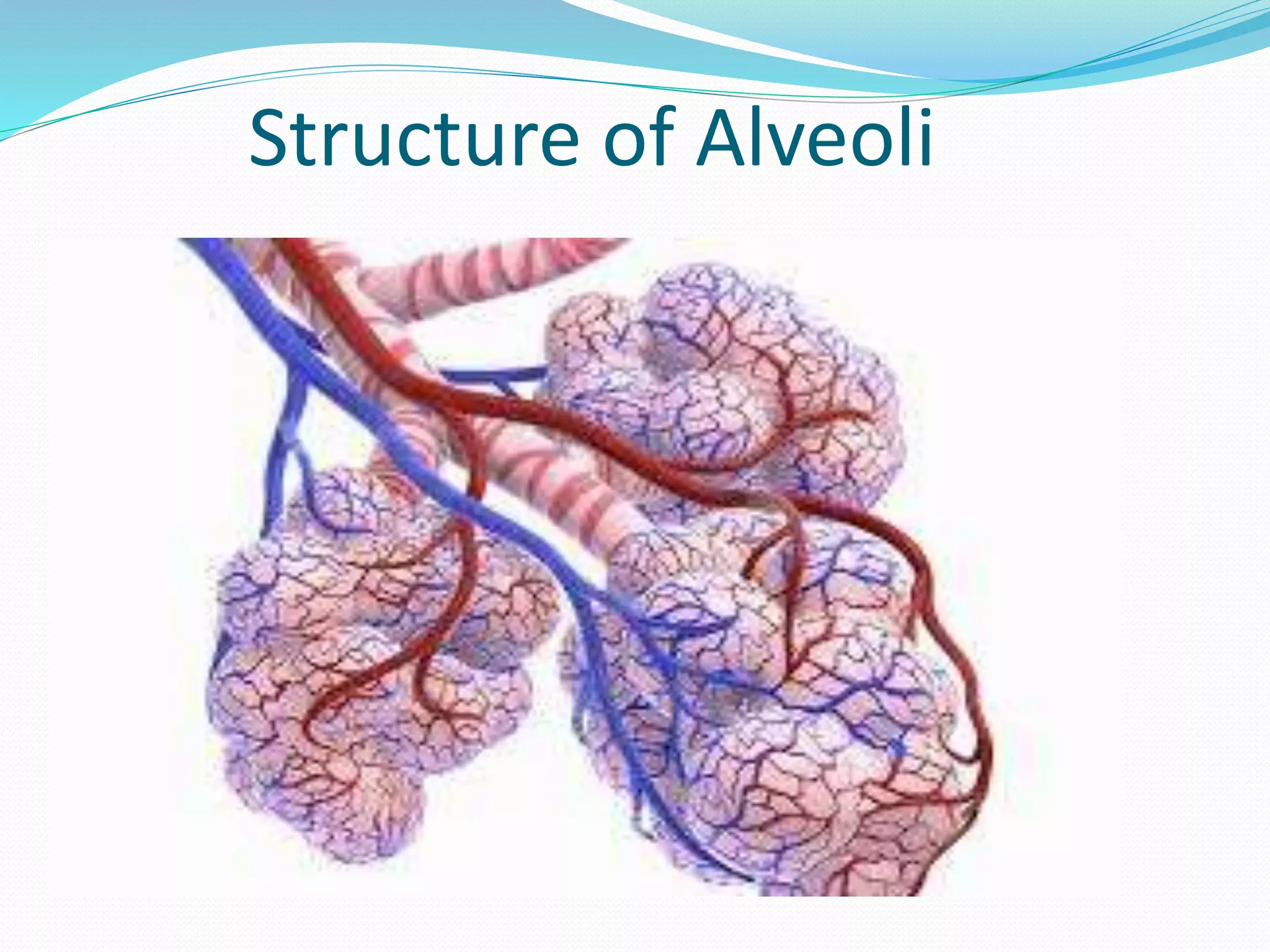
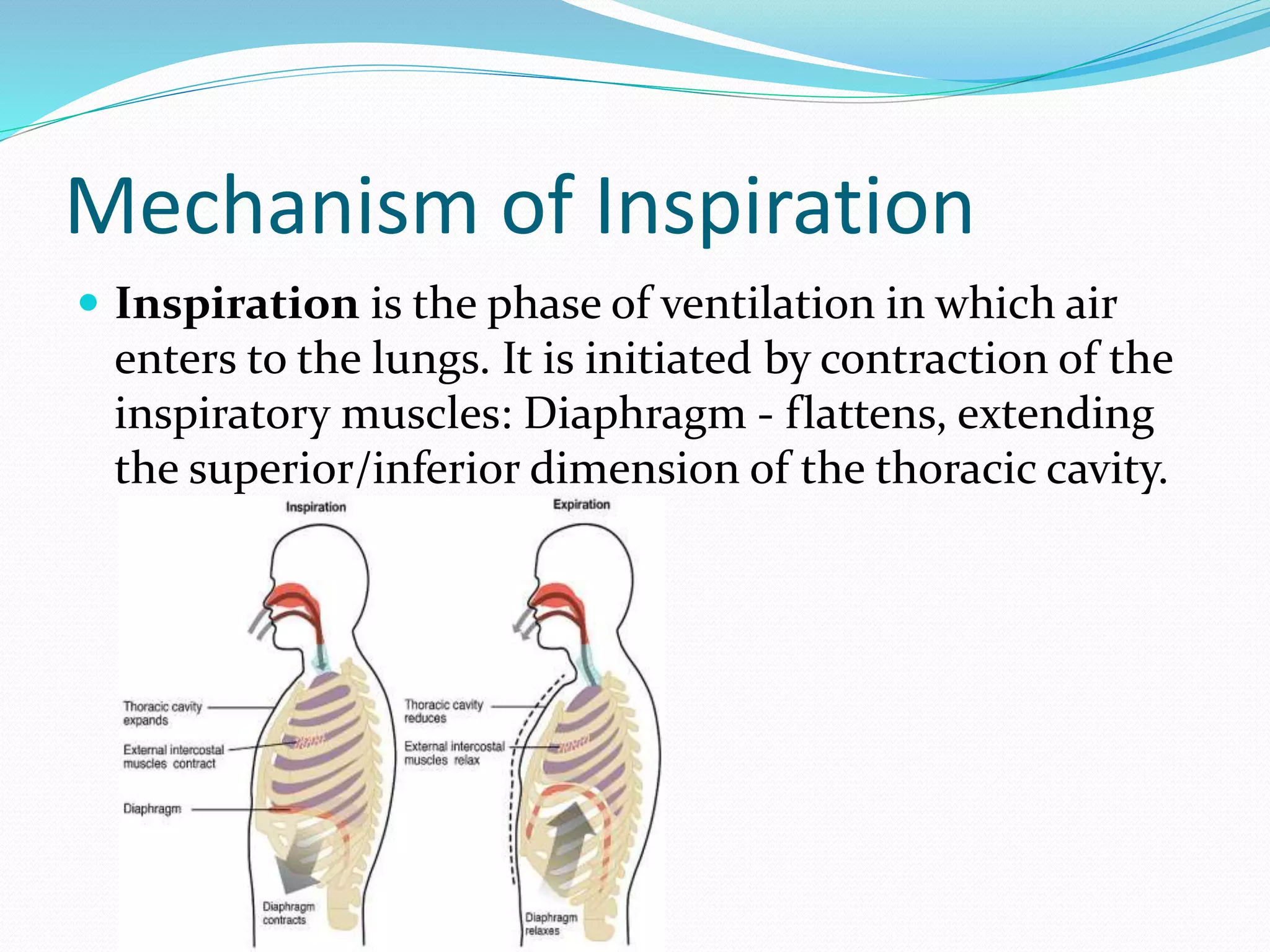
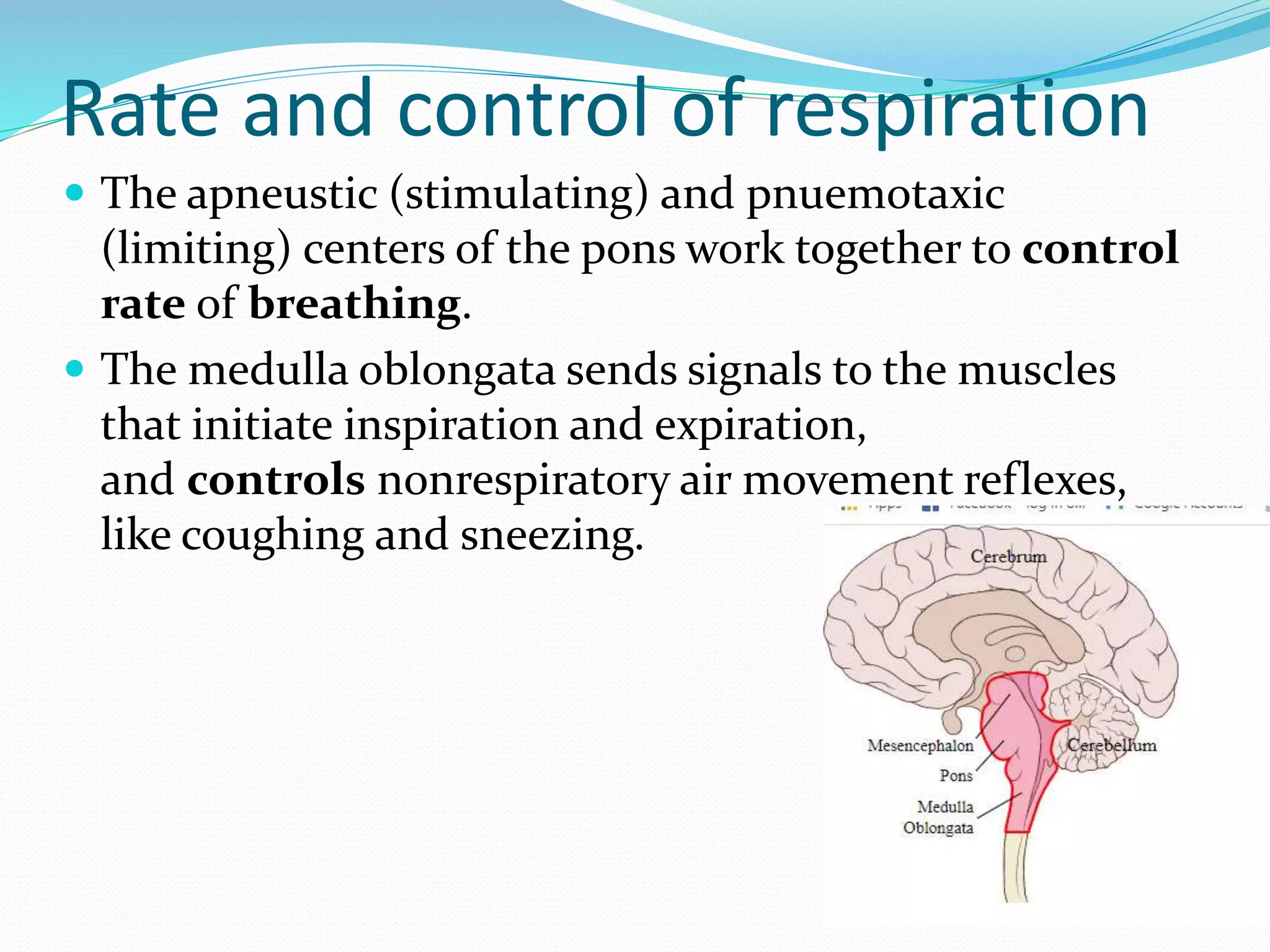
The document outlines the respiratory system, detailing the structure and function of components involved in respiration, including the airways, lungs, and muscles. It explains the processes of pulmonary ventilation, gas diffusion, and the transport of gases, and describes the biochemical and nervous control of respiration. Additionally, it discusses normal respiratory rates and tidal volumes as key clinical parameters.