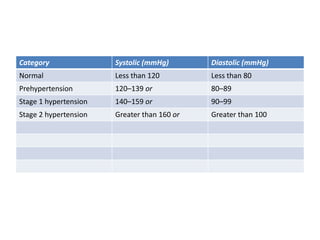
Diuretics are drugs that increase urine output by interfering with sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. They are commonly used to treat hypertension by lowering blood volume and pressure. The main classes of diuretics act on different parts of the kidney tubule: loop diuretics act on the ascending loop of Henle; thiazide diuretics act on the distal tubule; and potassium-sparing diuretics act on the late distal tubule or collecting duct. While all diuretics lower blood pressure, their specific sites of action determine their degree of natriuresis and potassium retention or loss.