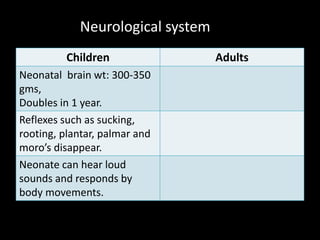
Children's bodies differ from adults' in many key systems:
1. The gastrointestinal system of children has a large tongue, small nasal passages, a relaxed cardiac sphincter, and faster emptying and passage of food compared to adults.
2. In the respiratory system, children have more delicate airways that do not produce mucus, a shorter and straighter eustachian tube, and larger tonsils involved in antibody production.
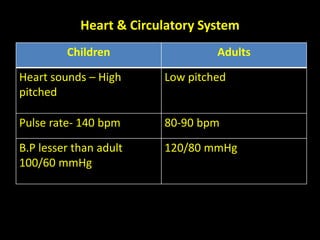
3. The heart of children beats faster, their blood pressure is lower, and pulse rate is higher compared to adults.
This summarizes some of the key differences between children's and adults' bodies outlined in the document.

![Gastro-Intestinal System
Children Adults
Tongue: Large
Nasal and oral passages are small
Small tongue
Large nasal and oral passages
Stomach: Cardiac sphincter is
relaxed
Tight
Emptying time of stomach is about
2-3 hrs in toddlers
Very slow
Food passes very rapidly in infants
and in neonates. [Loose stool]
Slowly and absorption takes
place
[Hard stool]
Liver is 4% of the total body weight
and occupies more space in
abdominal cavity.
Only little space is occupied
by liver.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomicalandphysiologicaldifferences-160513062829/85/Anatomical-and-physiological-differences-2-320.jpg)
![Respiratory system
Children Adults
In neonates and in infants respiratory
tract is very delicate and do not produce
mucus. [Older children produce mucus]
well developed
tissues
Eustachian tube is short and straight and
short distance b/w trachea and bronchi
Long
Tonsils and adenoids are large during
childhood, involved in the production of
antibodies.
Smaller tonsils
Respiratory tract obstruction occurs
commonly in children because of short
airway.
Less chances of
obstruction.
Respiratory rate is more Less](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomicalandphysiologicaldifferences-160513062829/85/Anatomical-and-physiological-differences-3-320.jpg)