This document discusses saving, investment, and resource mobilization for economic planning in India. It covers:
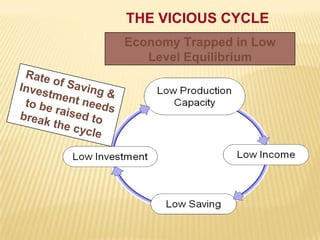
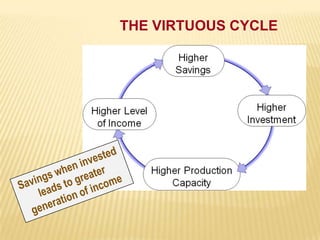
1) The definitions and importance of saving and investment for economic growth. High saving and investment rates can help break out of the "vicious cycle" of poverty, while low rates trap economies.
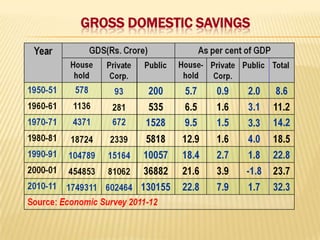
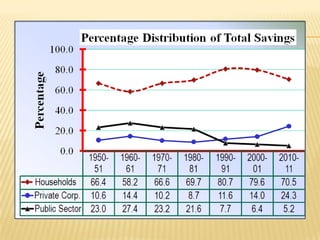
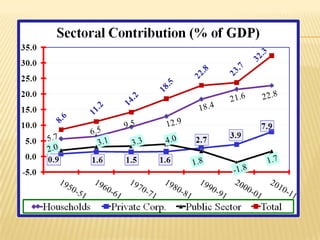
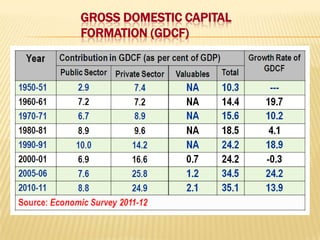
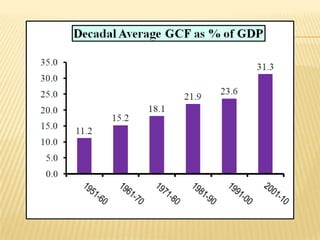
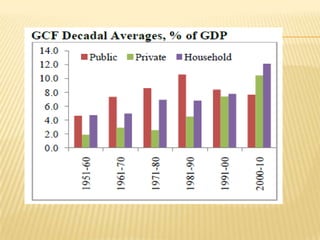
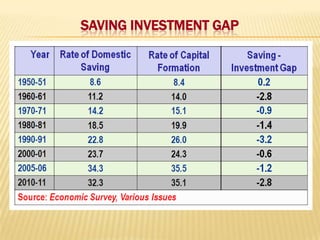
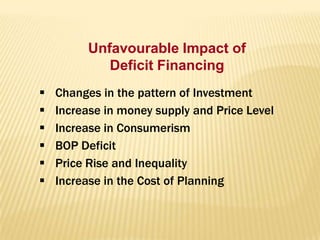
2) Trends showing India's saving and investment rates have been relatively low, along with factors contributing to this like population growth and consumerism. Suggestions to increase rates include expanding banking and reducing non-development spending.
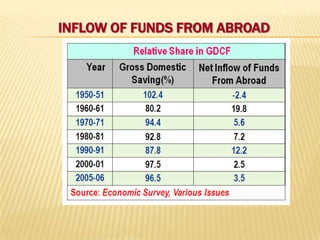
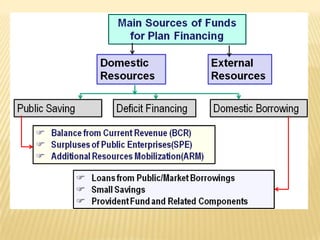
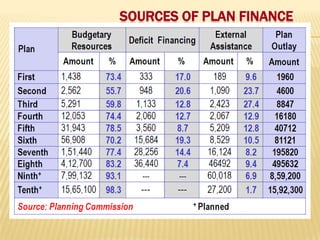
3) The various sources and components of financing India's Five-Year Plans, including budgetary resources, deficit financing, and external financing from abroad. Maintaining a balance between development