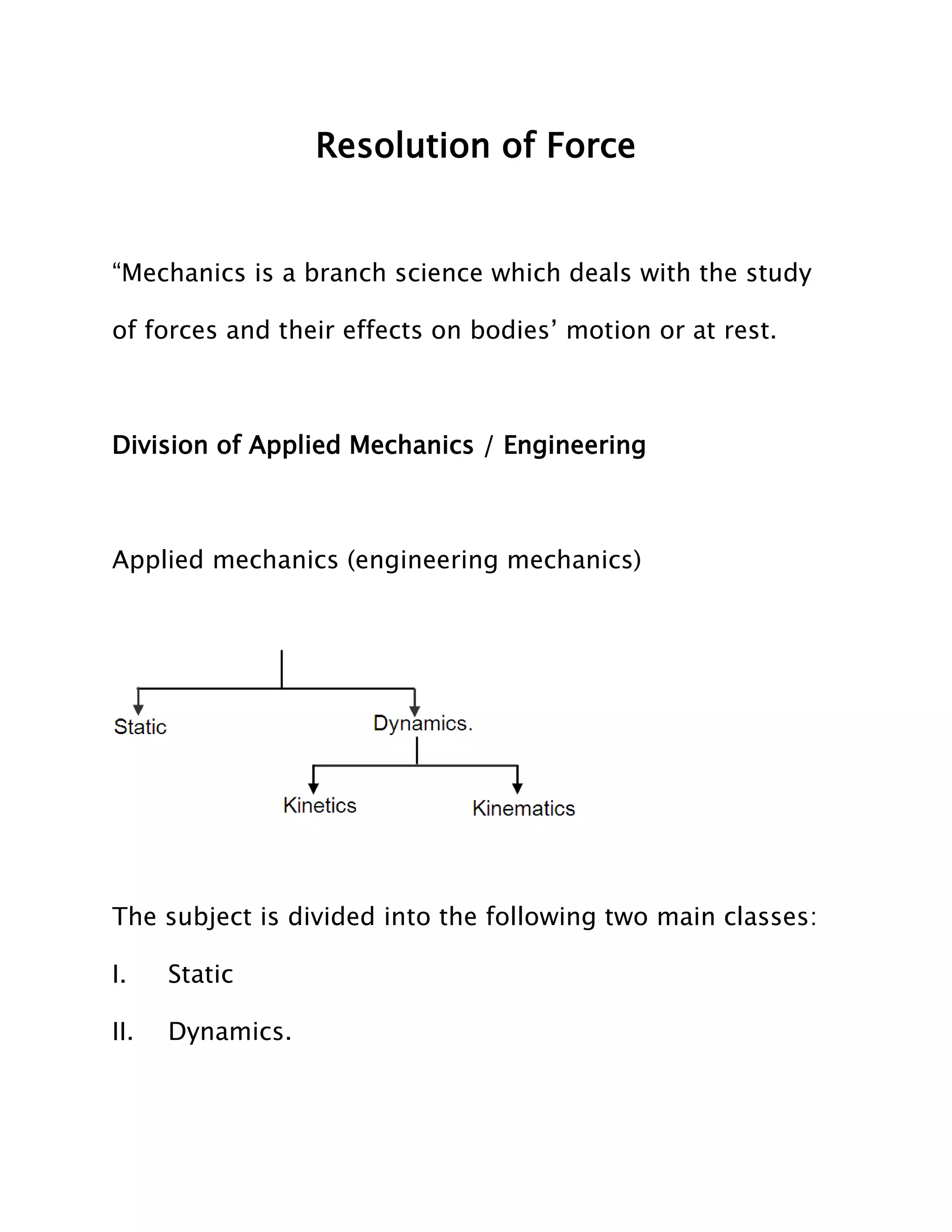
This document discusses mechanics and applied mechanics. It defines mechanics as dealing with forces and their effects on bodies at rest or in motion. Applied mechanics is divided into statics and dynamics. Statics deals with forces on bodies at rest, while dynamics deals with forces on bodies in motion. Dynamics is further divided into kinetics, which considers mass and forces, and kinematics, which does not consider mass or forces. The document also defines important concepts in mechanics like rigid bodies. It discusses the basic principles of applied mechanics, including laws of motion and forces. Finally, it defines characteristics of a force like magnitude, direction, and sense (pull vs. push).